백준 24481 java : 그래프, DFS
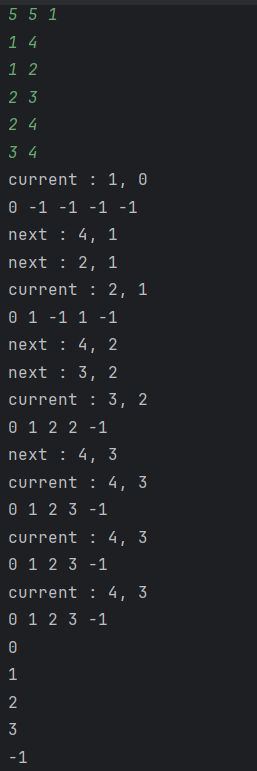
재귀 말고 스택을 사용하니까 꺼내는 순서 때문에 풀이가 잘 안된다. 게다가 지금 풀이도 메모리와 시간 소모가 너무 크다.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.*;
public class bj24481 {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N, M, R;
static ArrayList<Integer>[] graph;
public static void main(String[] args) {
inputData();
findAnswer();
sc.close();
}
public static void inputData() {
int i, u, v;
N = sc.nextInt();
M = sc.nextInt();
R = sc.nextInt();
graph = new ArrayList[N + 1];
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
//무방향 그래프
for(i = 0; i < M; i++){
u = sc.nextInt();
v = sc.nextInt();
graph[u].add(v);
graph[v].add(u);
}
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
Collections.sort(graph[i], Comparator.reverseOrder());
}
}
public static void findAnswer() {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
boolean []visited = new boolean[N + 1];
int [] depth = new int[N + 1];
Arrays.fill(depth, -1);
int current, i;
depth[R] = 0;
visited[R] = true;
stack.push(R);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
current = stack.pop();
System.out.println("current : " + current + ", " + depth[current]);
visited[current] = true;
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++){
System.out.print(depth[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (int next : graph[current]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
depth[next] = depth[current] + 1;
System.out.println("next : " + next + ", " + depth[next]);
stack.push(next);
}
}
}
for(i = 1; i <= N; i++){
System.out.println(depth[i]);
}
}
}