백준 2564 java : 구현, 기하학, oop
왜 직사각형이 아니라 직선으로 풀었는가?
직사각형 내부에는 접근할 필요가 없다. 또한 직사각형으로 풀이한 결과 각 점을 x, y로 변환한 이후 동근이와 상점 간 거리를 구하기 위한 추가 연산이 필요하다. 그래서 직사각형 지도를 북동남서 형태로 직선으로 폈다.
왜 class를 사용했는가?
java 언어는 class를 구현하기 쉽다. 방향과 거리를 함께 운용해야 하는데, c++과 달리 pair클래스가 없어서 Location이라는 클래스를 생성해서 사용했다.
class의 값을 입력, 접근할 때 직접 접근과 간접 접근의 차이?
만약 Lacation 클래스에서 direction, distance같은 필드, 인스턴스 변수들이 public 접근제어를 갖고 있다면, 두 가지 방법으로 입력 및 접근이 가능하다.
direction = sc.nextInt();
distance = sc.nextInt();
dongguen = new Location(0, 0);
dongguen.setDirection(direction);
dongguen.setDistance(distance);또는
dongguen = new Location(0, 0);
dongguen.direction = sc.nextInt();
dongguen.distance = sc.nextInt();그러나 아래의 경우, 인스턴스 변수에 직접 접근하기 때문에 oop의 캡슐화(정보은닉)를 깰 수 있다. 그러므로 인스턴스 변수는 private 접근제어와 setter, getter 메서드와 같은 간접 접근을 사용하는 것이 권장된다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class bj2564 {
static class Location{
private int direction;
private int distance;
public Location(int direction, int distance) {
this.direction = direction;
this.distance = distance;
}
public int getDirection() {
return direction;
}
public void setDirection(int direction) {
this.direction = direction;
}
public int getDistance() {
return distance;
}
public void setDistance(int distance) {
this.distance = distance;
}
}
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static Location dongguen;
static Location[] stores;
static int width, height;
public static void main(String[] args) {
inputData();
System.out.println(findAnswer());
sc.close();
}
public static void inputData() {
int N, i;
int direction, distance;
width = sc.nextInt();
height = sc.nextInt();
N = sc.nextInt();
stores = new Location[N];
for(i = 0; i < N; i++) {
direction = sc.nextInt();
distance = sc.nextInt();
Location store = new Location(0, 0);
store.setDirection(direction);
store.setDistance(distance);
stores[i] = store;
}
direction = sc.nextInt();
distance = sc.nextInt();
dongguen = new Location(0, 0);
dongguen.setDirection(direction);
dongguen.setDistance(distance);
}
public static int findAnswer() {
int answer = 0;
int i;
int total_length = (width + height) * 2;
int dongguen_location = findLocation(dongguen.getDirection(), dongguen.getDistance());
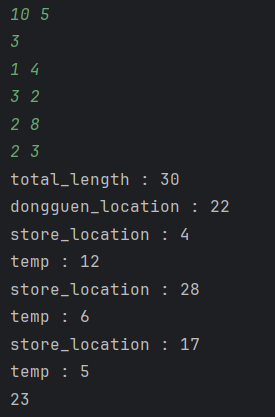
System.out.println("total_length : " + total_length);
System.out.println("dongguen_location : " + dongguen_location);
for(i = 0; i < stores.length; i++) {
int store_location = findLocation(stores[i].getDirection(), stores[i].getDistance());
System.out.println("store_location : " + store_location);
int clockwise = Math.abs(dongguen_location - store_location);
int counterClockwise = total_length - clockwise;
int temp = Math.min(clockwise, counterClockwise);
System.out.println("temp : " + temp);
answer += temp;
}
return answer;
}
public static int findLocation(int direction, int distance) {
int location;
//북 - 동 - 남 - 서 순으로 사각형을 직선으로 편다고 생각
if(direction == 1) {//북
location = distance;
}
else if(direction == 2) {//남
location = (width - distance) + width + height;
}
else if(direction == 3) {//서
location = (height - distance) + width + height + width;
}
else {//동
location = distance + width;
}
return location;
}
}