백준 4358 java : 자료구조
trees.put(line, trees.getOrDefault(line, 0) + 1);
trees.getOrDefault(line, 0) + 1
trees 맵에 line을 키로 갖는 값이 있다면 가져와서 + 1, 없다면 0으로 저장
trees.put(line, trees.getOrDefault(line, 0) + 1); Collections.sort(names);java에서의 맵 자료구조는 c++과 다르게 키값 기준 정렬을 지원하지 않는다. 그래서 키값 또는 키값+원소값을 ArrayList로 옮겨 저장해서 정렬을 수행한다.
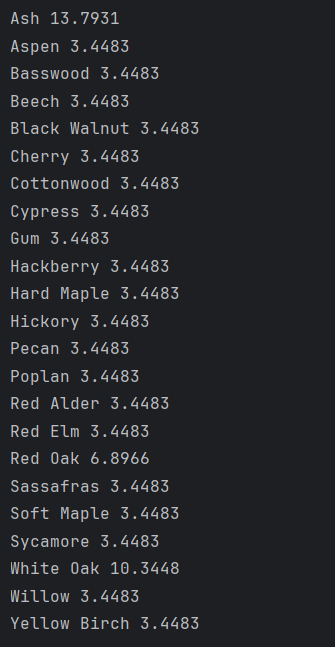
System.out.printf("%s %.4f%n", key, rate);소숫점 아래 몇째자리까지 출력할 것인지 지정할 때 printf를 사용한다.
import java.util.*;
public class BJ4358 {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static Map<String, Integer> trees = new HashMap<>();
static int total = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
inputData();
findAnswer();
sc.close();
}
public static void inputData(){
while (sc.hasNextLine()) {
String line = sc.nextLine();
if (line.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
trees.put(line, trees.getOrDefault(line, 0) + 1);
total++;
}
}
public static void findAnswer(){
//자바는 c++과 달리 자료구조를 유지한채로 키값 기준 정렬이 불가능함
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>(trees.keySet());
Collections.sort(names);
for (String key : names) {
Integer value = trees.get(key);
double rate = (double) value / total * 100;
System.out.printf("%s %.4f%n", key, rate);
}
}
}