안녕하세요. 본질을 추구하는 백엔드 개발자 3년차 우주호입니다.
주 개발환경인 Spring Framework가 어떤 순서로 실행되는지 도식화로 간단히 정리해보고자 합니다.
아래의 도식화는 'https://yoo-hyeok.tistory.com/139' 게시글을 참고하여 작성하였습니다.
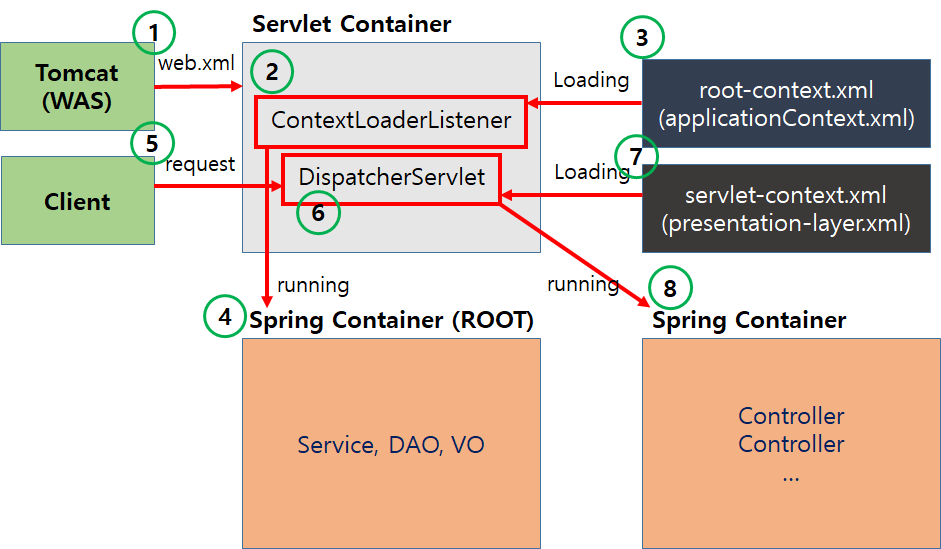
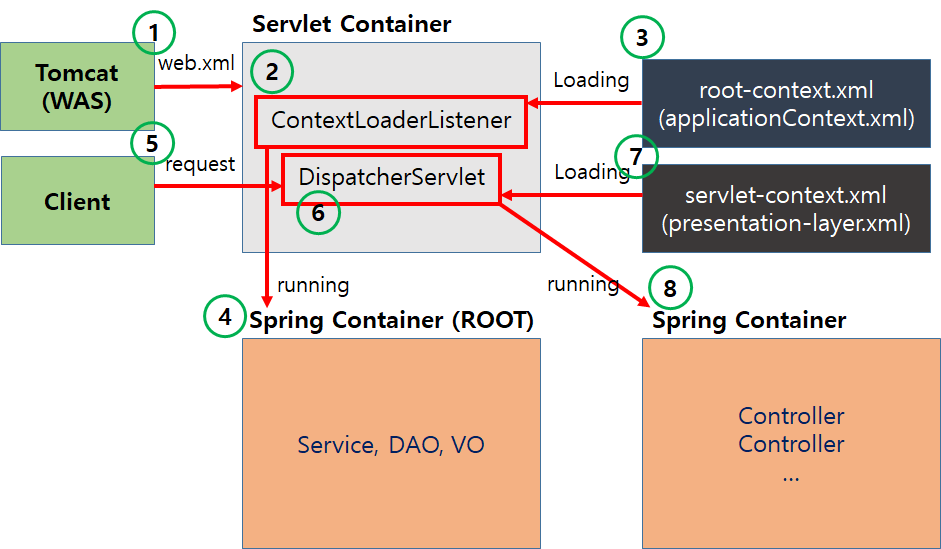
1. 웹 어플리케이션이 실행되면 Tomcat(WAS)에 의해 web.xml 로딩하게 됩니다.
web.xml은 Deployment Descriptor(배포 서술자)로 불립니다. 프로젝트 설정에 대한 기본정보를 가지고 있으며 Spring 프로젝트 실행 전 1차적으로 거쳐갑니다.
web.xml
<!-- The definition of the Root Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Creates the Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- Processes application requests -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>2. web.xml에 등록되어있는 ContextLoaderListener 생성.
ContextLoaderListener는 ServletContextListener 인터페이스를 구현하며, ApplicationContext 생성합니다.
3. ContextLoaderListener가 root-context.xml 로딩
ContextLoaderListener는 Servlet을 초기화하는 용도로 사용.
타 Servlet에서 생성된 Bean은 서로 접근 못하지만, ContextLoaderListener를 통해 공통 Bean으로 접근가능합니다.
4. root-context.xml등록되어있는 설정에 따라 Spring Container(ROOT) 구동
root-context.xml에서는 view와 관련되지 않은 객체를 정의합나다. Service, Repository(DAO), DB 등 비즈니스 로직과 관련된 설정을 담당합니다.
5. Client로부터 Web Application 요청
6. DispatcherServlet 생성
7. DispatcherServlet이 servlet-context.xml 로딩
8. Spring Container구동되며 응답에 맞는 Controller들 동작