AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)
- 관점지향 프로그래밍
- 스프링 어플리케이션은 특별한 경우를 제외하고는 MVC 웹 어플리케이션에서는 Web Layer, Business Layer, Data Layer로 정의한다.
- Web Layer : REST API를 제공, 클라이언트 중심의 로직 적용 (response를 내려주거나 http status를 변경해준다.)
- Business Layer : 내부 정책에 따른 로직을 개발
- Data Layer : 데이터 베이스 및 외부와의 연동을 처리
- 주요 어노테이션 :
- @Aspect : AOP를 정의하는 클래스에 할당
- @Pointcut : AOP를 적용 시킬 지점 설정
- @Before : 메소드 실행하기 이전
- @After : 메소드가 성공적으로 실행 후 예외가 발생되더라도 실행
- @AfterReturing : 메소드 호출 성공 실행 시
- @AfterThrowing : 메소드 호출 실패 예외 발생
- @Around : Before/After 모두 제어
- @Aspect를 사용하면 당연히 @Component를 같이 사용한다.
- Component와 bean의 차이점 : @bean은 클래스에 사용할 수 없고, 메소드에 사용한다.
- aop사용시 build.gradle의 dependencies에 아래 코드 추가.
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop'
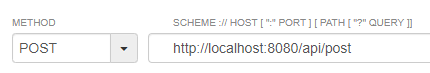
예제1
- dto/User에 id, pw, email을 갖는 객체 생성
- controller/RestApiController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class RestApiController {
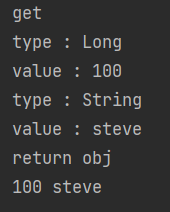
@GetMapping("/get/{id}")
public String get(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestParam String name) {
return id+" "+name;
}
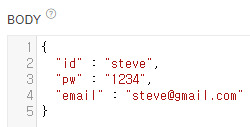
@PostMapping("/post")
public User post(@RequestBody User user) {
return user;
}
}
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut() {}
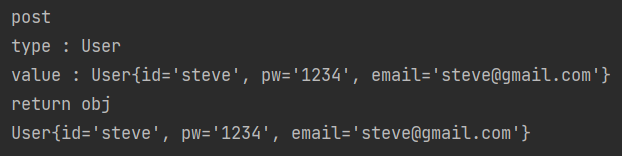
@Before("cut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
System.out.println(method.getName());
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object obj : args) {
System.out.println("type : "+obj.getClass().getSimpleName());
System.out.println("value : "+obj);
}
}
@AfterReturning(value = "cut()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj) {
System.out.println("return obj");
System.out.println(returnObj);
}
}
GET
- Talend Api Tester
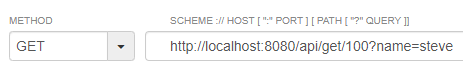
- Server
POST
예제2-custom annotation(Timer)
- controller/RestApiController
@Timer
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public void delete() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 2);
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Timer {}
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimerAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut() {}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop.annotation.Timer)")
private void enableTimer() {}
@Around("cut() && enableTimer()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
stopWatch.stop();
System.out.println("total time : "+stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
}
}
예제3-custom annotation(Decode)
- controller/RestApiController
@Decode
@PutMapping("/put")
public User put(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("put");
System.out.println(user);
return user;
}
- annotation/Decode(파일 생성시 파일 타입을 annotation으로 선택)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Decode {}
@Aspect
@Component
public class DecodeAop {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.aop.controller..*.*(..))")
private void cut() {}
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.example.aop.annotation.Decode)")
private void enableDecode() {}
@Before("cut() && enableDecode()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object arg : args) {
if(arg instanceof User) {
User user = User.class.cast(arg);
String base64Email = user.getEmail();
String email = new String(Base64.getDecoder().decode(base64Email),"UTF-8");
user.setEmail(email);
}
}
}
@AfterReturning(value = "cut() && enableDecode()", returning = "returnObj")
public void afterReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object returnObj) {
if(returnObj instanceof User) {
User user = User.class.cast(returnObj);
String email = user.getEmail();
String base64Email = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(email.getBytes());
user.setEmail(base64Email);
}
}
}
Object Mapper
- 자바에서 json 관련 라이브러리 중 하나
- 구글에 maven repository 검색 -> object mapper(사용할 라이브러리) 검색 -> Jackson Databind 선택 -> Gradle 선택 후 코드 복사 -> 프로젝트의 build.gradle 파일 선택 -> dependencies에 붙여넣기
- 추가되었는지 확인할 때는 오른쪽 바 -> Gradle -> Dependencies -> compileClasspath 확인
- json의 기본 인코딩 타입은 UTF-8이므로 spring을 사용할 땐 자동으로 인코딩 되지만, 자바는 Settings -> Fil Encodings에서 Project Encoding과 Default encoding for properties files를 UTF-8로 설정해야 한다. => 윈도우일 경우만..!
- 위의 설정 후에도 한글이 깨진다면 build.gradle에 아래의 코드를 추가한다.
compileJava.options.encoding = 'UTF-8'
tasks.withType(JavaCompile) {
options.encoding = 'UTF-8'
}
예제
public class Car {
private String name;
@JsonProperty("car_number")
private String carNumber;
@JsonProperty("TYPE")
private String type;
...
}
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<Car> cars;
...
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws JsonProcessingException {
System.out.println("main");
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
User user = new User();
user.setName("홍길동");
user.setAge(10);
Car car1 = new Car();
car1.setName("K5");
car1.setCarNumber("11가 1111");
car1.setType("sedan");
Car car2 = new Car();
car2.setName("Q5");
car2.setCarNumber("22가 2222");
car2.setType("SUV");
List<Car> carList = Arrays.asList(car1, car2);
user.setCars(carList);
String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);
System.out.println(json);
JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readTree(json);
String _name = jsonNode.get("name").asText();
int _age = jsonNode.get("age").asInt();
System.out.println("name : "+_name);
System.out.println("age : "+_age);
JsonNode cars = jsonNode.get("cars");
ArrayNode arrayNode = (ArrayNode)cars;
List<Car> _cars = objectMapper.convertValue(arrayNode, new TypeReference<List<Car>>() {});
System.out.println(_cars);
ObjectNode objectNode = (ObjectNode) jsonNode;
objectNode.put("name", "steve");
objectNode.put("age",20);
System.out.println(objectNode.toPrettyString());
}
}
어노테이션 정리
- SpringBootApplication : Spring boot application으로 설정
- Controller : view를 제공하는 controller로 설정
- RestController : REST API를 제공하는 controller로 설정 (response는 objectmapper를 통해서 json의 형태로 변경되어 응답한다.)
- RequestMapping : URL 주소를 맵핑 (사용할 Http Method를 지정해야 하며, 지정하지 않을경우 모든 메서드가 동작하게 된다.)
- GetMapping : Http GetMethod URL 주소 맵핑
- PostMapping :
- PutMapping :
- DeleteMapping :
- RequestParam : URL Query Parameter 맵핑
- RequestBody : Http Body를 Parsing 맵핑
- Valid : POJO Java Class 검증
- Configration : 1개 이상의 bean을 등록할 때 설정
- Component : 1개의 class 단위로 bean으로 등록할 때 설정
- Bean : 1개의 외부 라이브러리로 부터 생성한 객체를 등록 시 사용(new로 객체를 생성 후 직접 bean으로 등록할 때 사용)
- Autowired : DI를 위한 곳에 사용
- Qualifier : @Autowired 사용시 bean이 2개 이상 일 때, 사용할 bean을 명시
- Resource : @Autowired + @Qualifier의 개념