References
아래 링크의 강의 중 Section 21. Linked Lists의 내용을 추려 이번 글을 작성하였습니다.
The Coding Interview Bootcamp: Algorithms + Data Structures on Udemy
Solution
class Node {
// node에다 새로운 instance 생설할 때마다 constructor가 자동으로 실행됨.
// argument next의 기본값은 null로 설정. tail node에는 next가 없기 때문.
constructor(data, next = null) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
insertFirst(data) {
// 새로이 node를 insert하게 되면 head에 할당되어 있던 기존 값은 next에 할당되고 새 값이 head로 치환됨.
// this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
this.insertAt(data, 0);
}
insertLast(data) {
// const last = this.getLast();
// if (last) {
// // There are some existing nodes in our chain
// last.next = new Node(data);
// } else {
// // The chain is empty
// this.head = new Node(data);
// }
this.insertAt(data, this.size());
}
size() {
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return counter;
}
getFirst() {
// return this.head;
return this.getAt(0);
}
getLast() {
// if (!this.head) {
// return null;
// }
// let node = this.head;
// // this.head를 while문으로써 한 칸씩 옮겨가며 node.next가 없을 때까지 탐색
// while (node) {
// // next가 없다면 현재 탐색값인 node 반환.
// if (!node.next) {
// return node;
// }
// // next가 있다면 node를 node.next로 치환.
// node = node.next;
// }
return this.getAt(this.size() - 1);
}
clear() {
this.head = null;
}
removeFirst() {
// if (!this.head) {
// return;
// }
// this.head = this.head.next;
this.removeAt(0);
}
removeLast() {
// // 아무 node도 없다면?
// if (!this.head) {
// return;
// }
// // node가 하나밖에 없다면?(next가 false라면?)
// if (!this.head.next) {
// this.head = null;
// return;
// }
// let previous = this.head;
// let node = this.head.next;
// // next가 존재하는 동안 while 돌리기
// while (node.next) {
// previous = node;
// node = node.next;
// }
// // while 다 돌고 나면 마지막 값 null로 만들어 삭제
// previous.next = null;
this.removeAt(this.size() - 1);
}
getAt(index) {
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
if (counter === index) {
return node;
}
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1);
if (!previous || !previous.next) {
return;
}
previous.next = previous.next.next;
}
insertAt(data, index) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data);
return;
}
// index 0에 insert할 경우 현재 head(this.head)를 next에 할당하고 this.head의 값으로 insert 값을 치환.
if (index === 0) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
return;
}
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1) || this.getLast();
const node = new Node(data, previous.next);
previous.next = node;
}
forEach(fn) {
let node = this.head;
let counter = 0;
while (node) {
fn(node, counter);
node = node.next;
counter++;
}
}
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
yield node;
node = node.next;
}
}
}
module.exports = { Node, LinkedList };Node
Head & Tail
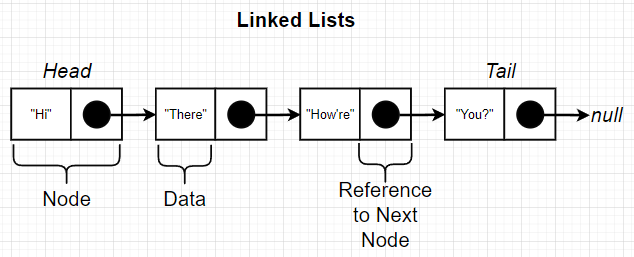
linked list에 속한 node는 기본적으로 reference를 갖는다. 이 node들 중 마지막 값에 해당하여 reference를 갖지 않는 것이 바로 tail이다.
node 안의 data에는 유효한 값이라면 type을 구분하지 않고 저장할 수 있다.
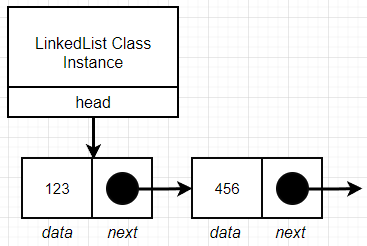
linked list class 내에 insert, remove, get 등 다양한 method를 작성하여 linked list 내의 node를 자유롭게 편집할 수 있다.
linked list는 단 한 개의 head property만 받는다. 즉, 첫 번째 node만을 인식하고, linked list 안에 현재 node가 몇 개인지, 어떤 data를 담고 있는지 전혀 신경 쓰지 않는다. 따라서 특정한 data를 얻기 위해서는 linked list 전체를 탐색해야 한다.
