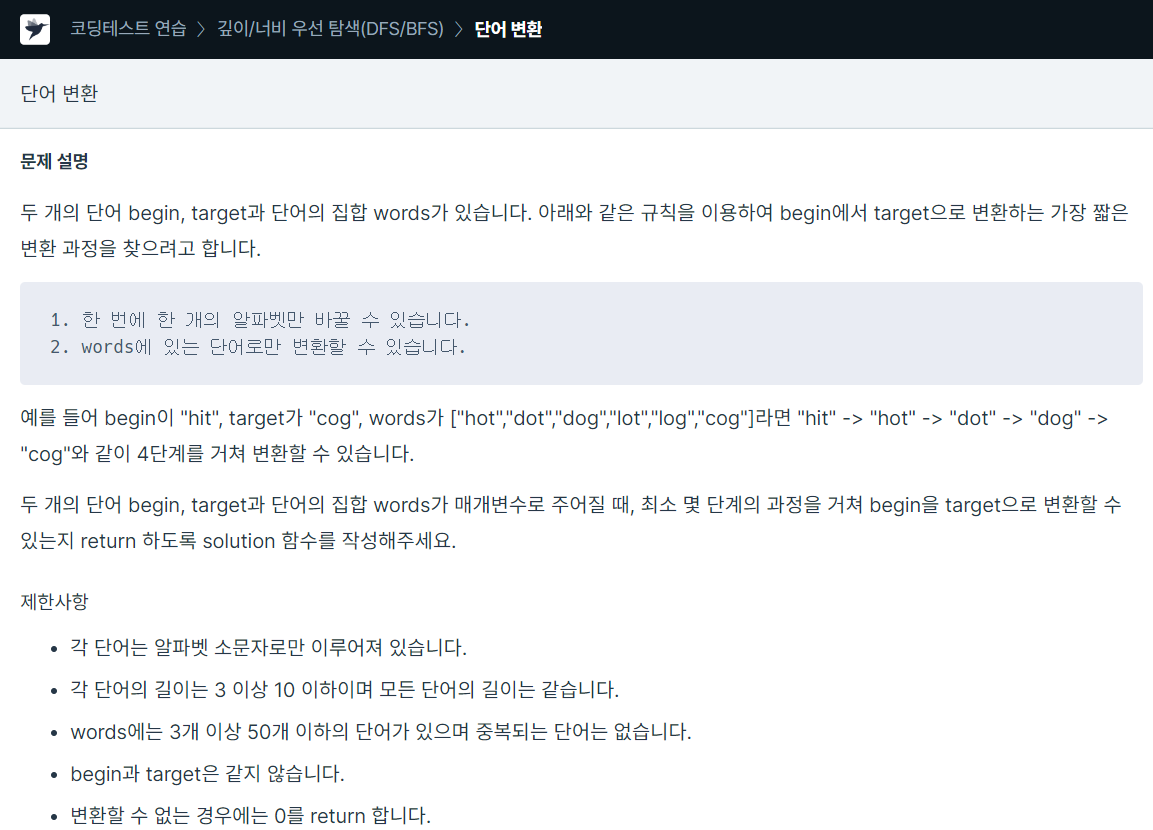

import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public boolean check(String a, String b){
int cnt = 0;
int l = a.length();
for(int i=0; i<l;i++){
if(a.charAt(i) == b.charAt(i))
cnt++;
}
if(cnt +1 == l)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public int solution(String begin, String target, String[] words) {
int answer = 0;
boolean[] visited = new boolean[words.length];
Deque<String[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new String[] {begin,"0"});
while(!q.isEmpty()){
String tmp = q.peek()[0], deph = q.peek()[1];
int d = Integer.valueOf(deph);
q.poll();
if(tmp.equals(target))
return d;
for(int i=0; i< words.length; i++){
if(!visited[i] && check(tmp, words[i])){
// System.out.println(deph + words[i]);
visited[i] = true;
q.add(new String[] {words[i], String.valueOf(d+1)});
}
}
}
return answer;
}
}최소 단계를 구해야하므로 bfs로 해결한 문제
q에 deph와 현재 단어를 저장해 나가면서 target 단어를 찾았을때 return
단어가 같은 경우는 없고 단어중 알파벳 하나만 다를 때 bfs 진행 가능하다. 배열이므로 deph를 String 형식으로 진행했다.
이 문제를 통해 charAt, Integer.valueOf, String.valueOf를 다시한번 상기할 수 있었다.

뛰어난 글이네요, 감사합니다.