redirection
> >& >> <
명령 > 파일
- 명령 > 파일
- > : STDOUT
명령의 출력으로 나오는 STDOUT 을 파일로 '밀어'넣는다. (파일 입장에서는 입력)
- > : STDOUT
명령>& 파일
- 명령 >& 파일
- > : STDOUT
- & : STDERR
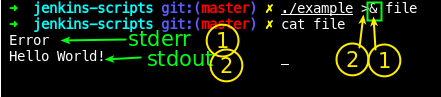
명령의 stdout, stderr 을 파일로 '밀어'넣는다. (파일 입장에서는 입력) - 주의!!!: 순서가 '&>' 로 하면 명령이 백그라운드로 동작하라가 인식이됨
$ ps -aux &>ps -aux프로세스가 백그라운드로 동작함
- E.g.,
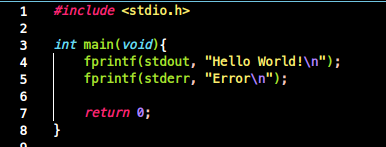
명령 fd> 파일
- 명령 'fd'> 파일
- 지정한 파일 스크립터를!! '밀어' 넣는다. (파일 입장에서는 입력)
- STDOUT: 1
date1> ./output.txt: date 명령의 표준출력을 output.txt에 밀어 넣음
- STDERR: 2
date2> ./output.txt: date 명령의 표준에러를 output.txt에 밀어 넣음
- STDOUT: 1
- 지정한 파일 스크립터를!! '밀어' 넣는다. (파일 입장에서는 입력)
$ 명령 2> /dev/null: 명령의 error를 보기 싫은 경우
- 명령 중간 중간 Error를 보기 싫은 경우 stderr(2)를 /dev/null로 밀어버림
- 예제
/에서 du를 사용하는데, 중간 중간/proc쪽 접근 불가 에러 보기 싫음
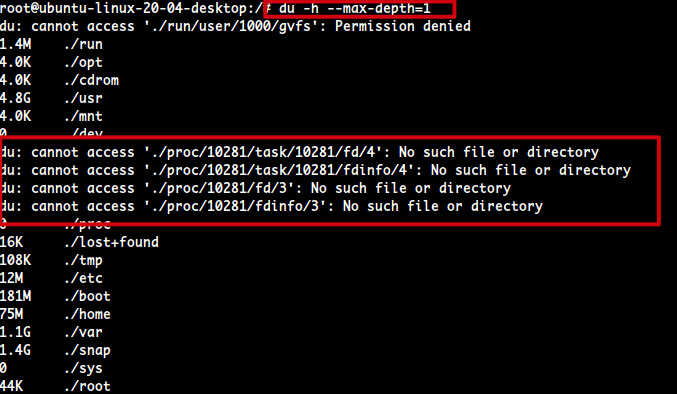
- stderr(2)를 /dev/null로 밀어버림
$ du -h --max-depth=1 2> /dev/null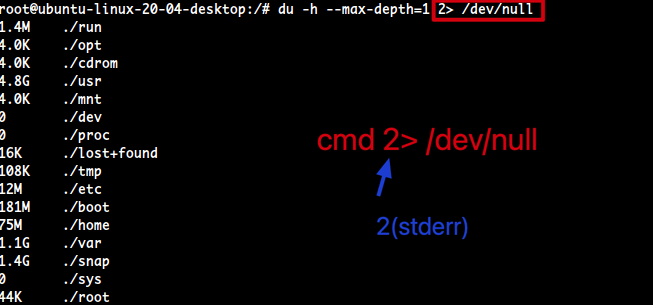
명령 fd>&fd 파일
$ 명령 fd>&fd 파일- >&가 나와서 또, stdout 과 stderr 을 내보내는 것 아님? 이라 할 수 있지만!
fd_src>&fd_dst로 변경하는 것이다!
- 예제
$ 명령 2>&1 ./output.txt- stderr(2)을 stdout(1)으로 내보낸다.
$ 명령 1>&2 ./output.txt- stdout(1)을 stderr(2)로 내보낸다.
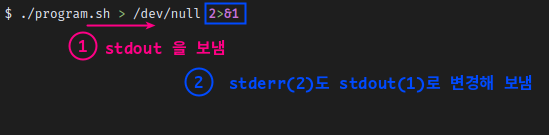
stdout, stderr을 모두 /dev/null로 가게하기
$ ./program.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
>>
>>- 지정한 파일에 stdout을 이어 붙임
echo -n "hello" >> sample.txt # 없으면 새로 생성
echo -e "\tworld!" >> sample.txt
echo "nice to meet you" >> sample.txt
==== sample.txt ====
hello world!
nice to meet youcmd >> file 2>&1
$ cat files.txt >> file 2>&1- 파일을
>>로 append 로 연다. cmd의 stderr(2)를 stdout(1)로 redirect한다.- 결론:
cmd의 stderr(2)를 stdout(1)로 redirect하여 file에 append한다.
cmd >>file1 2>>file2
$ cat files.txt >>file1 2>>file2- file1과 file2을
>>로 append 로 연다. cmd의 stdout(1)은 file1, stderr(2)은 file2로 redirect한다.
| :pipe
명령 | 명령
- 위의 redirection
>,>>,>&과의 차이 점은 뒤에오는 dst가파일이 아닌또 명령이라는 것!!

- pipe는 src 명령의 STDOUT을 dst 명령의 STDIN으로 보낸다.
$ ls | grep "find"
$ tmux show-buffer | xclip -sel clipboardEOF
cat > ./hello.txt << EOF
> Name: Hello
> Age: 28
> EOF
