cloc
$ cloc --help
Usage: cloc [options] <file(s)/dir(s)/git hash(es)> | <set 1> <set 2> | <report files>
Count, or compute differences of, physical lines of source code in the
given files (may be archives such as compressed tarballs or zip files,
or git commit hashes or branch names) and/or recursively below the
given directories.
Input Options
--extract-with=<cmd> This option is only needed if cloc is unable
to figure out how to extract the contents of
the input file(s) by itself.
Use <cmd> to extract binary archive files (e.g.:
.tar.gz, .zip, .Z). Use the literal '>FILE<' as
a stand-in for the actual file(s) to be
extracted. For example, to count lines of code
in the input files
gcc-4.2.tar.gz perl-5.8.8.tar.gz
on Unix use
--extract-with='gzip -dc >FILE< | tar xf -'
or, if you have GNU tar,
--extract-with='tar zxf >FILE<'
and on Windows use, for example:
--extract-with="\"c:\Program Files\WinZip\WinZip32.exe\" -e -o >FILE< ."
(if WinZip is installed there).
--list-file=<file> Take the list of file and/or directory names to
process from <file>, which has one file/directory
name per line. Only exact matches are counted;
relative path names will be resolved starting from
the directory where cloc is invoked.
See also --exclude-list-file.
--vcs=<VCS> Invoke a system call to <VCS> to obtain a list of
files to work on. If <VCS> is 'git', then will
invoke 'git ls-files' to get a file list and
'git submodule status' to get a list of submodules
whose contents will be ignored. See also --git
which accepts git commit hashes and branch names.
If <VCS> is 'svn' then will invoke 'svn list -R'.
The primary benefit is that cloc will then skip
files explicitly excluded by the versioning tool
in question, ie, those in .gitignore or have the
svn:ignore property.
Alternatively <VCS> may be any system command
that generates a list of files.
Note: cloc must be in a directory which can read
the files as they are returned by <VCS>. cloc will
not download files from remote repositories.
'svn list -R' may refer to a remote repository
to obtain file names (and therefore may require
authentication to the remote repository), but
the files themselves must be local.
--unicode Check binary files to see if they contain Unicode
expanded ASCII text. This causes performance to
drop noticeably.
Processing Options
--autoconf Count .in files (as processed by GNU autoconf) of
recognized languages. See also --no-autogen.
--by-file Report results for every source file encountered.
--by-file-by-lang Report results for every source file encountered
in addition to reporting by language.
--config <file> Read command line switches from <file> instead of
the default location of /home/dhyang/.config/cloc/options.txt.
The file should contain one switch, along with
arguments (if any), per line. Blank lines and lines
beginning with '#' are skipped. Options given on
the command line take priority over entries read from
the file.
--count-and-diff <set1> <set2>
First perform direct code counts of source file(s)
of <set1> and <set2> separately, then perform a diff
of these. Inputs may be pairs of files, directories,
or archives. If --out or --report-file is given,
three output files will be created, one for each
of the two counts and one for the diff. See also
--diff, --diff-alignment, --diff-timeout,
--ignore-case, --ignore-whitespace.
--diff <set1> <set2> Compute differences in code and comments between
source file(s) of <set1> and <set2>. The inputs
may be any mix of files, directories, archives,
or git commit hashes. Use --diff-alignment to
generate a list showing which file pairs where
compared. See also --count-and-diff, --diff-alignment,
--diff-timeout, --ignore-case, --ignore-whitespace.
--diff-timeout <N> Ignore files which take more than <N> seconds
to process. Default is 10 seconds. Setting <N>
to 0 allows unlimited time. (Large files with many
repeated lines can cause Algorithm::Diff::sdiff()
to take hours.)
--docstring-as-code cloc considers docstrings to be comments, but this is
not always correct as docstrings represent regular
strings when they appear on the right hand side of an
assignment or as function arguments. This switch
forces docstrings to be counted as code.
--follow-links [Unix only] Follow symbolic links to directories
(sym links to files are always followed).
--force-lang=<lang>[,<ext>]
Process all files that have a <ext> extension
with the counter for language <lang>. For
example, to count all .f files with the
Fortran 90 counter (which expects files to
end with .f90) instead of the default Fortran 77
counter, use
--force-lang="Fortran 90",f
If <ext> is omitted, every file will be counted
with the <lang> counter. This option can be
specified multiple times (but that is only
useful when <ext> is given each time).
See also --script-lang, --lang-no-ext.
--force-lang-def=<file> Load language processing filters from <file>,
then use these filters instead of the built-in
filters. Note: languages which map to the same
file extension (for example:
MATLAB/Mathematica/Objective C/MUMPS/Mercury;
Pascal/PHP; Lisp/OpenCL; Lisp/Julia; Perl/Prolog)
will be ignored as these require additional
processing that is not expressed in language
definition files. Use --read-lang-def to define
new language filters without replacing built-in
filters (see also --write-lang-def,
--write-lang-def-incl-dup).
--git Forces the inputs to be interpreted as git targets
(commit hashes, branch names, et cetera) if these
are not first identified as file or directory
names. This option overrides the --vcs=git logic
if this is given; in other words, --git gets its
list of files to work on directly from git using
the hash or branch name rather than from
'git ls-files'. This option can be used with
--diff to perform line count diffs between git
commits, or between a git commit and a file,
directory, or archive. Use -v/--verbose to see
the git system commands cloc issues.
--ignore-whitespace Ignore horizontal white space when comparing files
with --diff. See also --ignore-case.
--ignore-case Ignore changes in case; consider upper- and lower-
case letters equivalent when comparing files with
--diff. See also --ignore-whitespace.
--lang-no-ext=<lang> Count files without extensions using the <lang>
counter. This option overrides internal logic
for files without extensions (where such files
are checked against known scripting languages
by examining the first line for #!). See also
--force-lang, --script-lang.
--max-file-size=<MB> Skip files larger than <MB> megabytes when
traversing directories. By default, <MB>=100.
cloc's memory requirement is roughly twenty times
larger than the largest file so running with
files larger than 100 MB on a computer with less
than 2 GB of memory will cause problems.
Note: this check does not apply to files
explicitly passed as command line arguments.
--no-autogen[=list] Ignore files generated by code-production systems
such as GNU autoconf. To see a list of these files
(then exit), run with --no-autogen list
See also --autoconf.
--original-dir [Only effective in combination with
--strip-comments] Write the stripped files
to the same directory as the original files.
--read-binary-files Process binary files in addition to text files.
This is usually a bad idea and should only be
attempted with text files that have embedded
binary data.
--read-lang-def=<file> Load new language processing filters from <file>
and merge them with those already known to cloc.
If <file> defines a language cloc already knows
about, cloc's definition will take precedence.
Use --force-lang-def to over-ride cloc's
definitions (see also --write-lang-def,
--write-lang-def-incl-dup).
--script-lang=<lang>,<s> Process all files that invoke <s> as a #!
scripting language with the counter for language
<lang>. For example, files that begin with
#!/usr/local/bin/perl5.8.8
will be counted with the Perl counter by using
--script-lang=Perl,perl5.8.8
The language name is case insensitive but the
name of the script language executable, <s>,
must have the right case. This option can be
specified multiple times. See also --force-lang,
--lang-no-ext.
--sdir=<dir> Use <dir> as the scratch directory instead of
letting File::Temp chose the location. Files
written to this location are not removed at
the end of the run (as they are with File::Temp).
--skip-uniqueness Skip the file uniqueness check. This will give
a performance boost at the expense of counting
files with identical contents multiple times
(if such duplicates exist).
--stdin-name=<file> Give a file name to use to determine the language
for standard input. (Use - as the input name to
receive source code via STDIN.)
--strip-comments=<ext> For each file processed, write to the current
directory a version of the file which has blank
and commented lines removed (in-line comments
persist). The name of each stripped file is the
original file name with .<ext> appended to it.
It is written to the current directory unless
--original-dir is on.
--strip-str-comments Replace comment markers embedded in strings with
'xx'. This attempts to work around a limitation
in Regexp::Common::Comment where comment markers
embedded in strings are seen as actual comment
markers and not strings, often resulting in a
'Complex regular subexpression recursion limit'
warning and incorrect counts. There are two
disadvantages to using this switch: 1/code count
performance drops, and 2/code generated with
--strip-comments will contain different strings
where ever embedded comments are found.
--sum-reports Input arguments are report files previously
created with the --report-file option. Makes
a cumulative set of results containing the
sum of data from the individual report files.
--processes=NUM [Available only on systems with a recent version
of the Parallel::ForkManager module. Not
available on Windows.] Sets the maximum number of
cores that cloc uses. The default value of 0
disables multiprocessing.
--unix Override the operating system autodetection
logic and run in UNIX mode. See also
--windows, --show-os.
--use-sloccount If SLOCCount is installed, use its compiled
executables c_count, java_count, pascal_count,
php_count, and xml_count instead of cloc's
counters. SLOCCount's compiled counters are
substantially faster than cloc's and may give
a performance improvement when counting projects
with large files. However, these cloc-specific
features will not be available: --diff,
--count-and-diff, --strip-comments, --unicode.
--windows Override the operating system autodetection
logic and run in Microsoft Windows mode.
See also --unix, --show-os.
Filter Options
--exclude-dir=<D1>[,D2,] Exclude the given comma separated directories
D1, D2, D3, et cetera, from being scanned. For
example --exclude-dir=.cache,test will skip
all files and subdirectories that have /.cache/
or /test/ as their parent directory.
Directories named .bzr, .cvs, .hg, .git, .svn,
and .snapshot are always excluded.
This option only works with individual directory
names so including file path separators is not
allowed. Use --fullpath and --not-match-d=<regex>
to supply a regex matching multiple subdirectories.
--exclude-ext=<ext1>[,<ext2>[...]]
Do not count files having the given file name
extensions.
--exclude-lang=<L1>[,L2[...]]
Exclude the given comma separated languages
L1, L2, L3, et cetera, from being counted.
--exclude-list-file=<file> Ignore files and/or directories whose names
appear in <file>. <file> should have one file
name per line. Only exact matches are ignored;
relative path names will be resolved starting from
the directory where cloc is invoked.
See also --list-file.
--fullpath Modifies the behavior of --match-f, --not-match-f,
and --not-match-d to include the file's path
in the regex, not just the file's basename.
(This does not expand each file to include its
absolute path, instead it uses as much of
the path as is passed in to cloc.)
Note: --match-d always looks at the full
path and therefore is unaffected by --fullpath.
--include-ext=<ext1>[,ext2[...]]
Count only languages having the given comma
separated file extensions. Use --show-ext to
see the recognized extensions.
--include-lang=<L1>[,L2[...]]
Count only the given comma separated languages
L1, L2, L3, et cetera. Use --show-lang to see
the list of recognized languages.
--match-d=<regex> Only count files in directories matching the Perl
regex. For example
--match-d='/(src|include)/'
only counts files in directories containing
/src/ or /include/. Unlike --not-match-d,
--match-f, and --not-match-f, --match-d always
compares the fully qualified path against the
regex.
--not-match-d=<regex> Count all files except those in directories
matching the Perl regex. Only the trailing
directory name is compared, for example, when
counting in /usr/local/lib, only 'lib' is
compared to the regex.
Add --fullpath to compare parent directories to
the regex.
Do not include file path separators at the
beginning or end of the regex.
--match-f=<regex> Only count files whose basenames match the Perl
regex. For example
--match-f='^[Ww]idget'
only counts files that start with Widget or widget.
Add --fullpath to include parent directories
in the regex instead of just the basename.
--not-match-f=<regex> Count all files except those whose basenames
match the Perl regex. Add --fullpath to include
parent directories in the regex instead of just
the basename.
--skip-archive=<regex> Ignore files that end with the given Perl regular
expression. For example, if given
--skip-archive='(zip|tar(.(gz|Z|bz2|xz|7z))?)'
the code will skip files that end with .zip,
.tar, .tar.gz, .tar.Z, .tar.bz2, .tar.xz, and
.tar.7z.
--skip-win-hidden On Windows, ignore hidden files.
Debug Options
--categorized=<file> Save names of categorized files to <file>.
--counted=<file> Save names of processed source files to <file>.
--diff-alignment=<file> Write to <file> a list of files and file pairs
showing which files were added, removed, and/or
compared during a run with --diff. This switch
forces the --diff mode on.
--explain=<lang> Print the filters used to remove comments for
language <lang> and exit. In some cases the
filters refer to Perl subroutines rather than
regular expressions. An examination of the
source code may be needed for further explanation.
--help Print this usage information and exit.
--found=<file> Save names of every file found to <file>.
--ignored=<file> Save names of ignored files and the reason they
were ignored to <file>.
--print-filter-stages Print processed source code before and after
each filter is applied.
--show-ext[=<ext>] Print information about all known (or just the
given) file extensions and exit.
--show-lang[=<lang>] Print information about all known (or just the
given) languages and exit.
--show-os Print the value of the operating system mode
and exit. See also --unix, --windows.
-v[=<n>] Verbose switch (optional numeric value).
-verbose[=<n>] Long form of -v.
--version Print the version of this program and exit.
--write-lang-def=<file> Writes to <file> the language processing filters
then exits. Useful as a first step to creating
custom language definitions. Note: languages which
map to the same file extension will be excluded.
(See also --force-lang-def, --read-lang-def).
--write-lang-def-incl-dup=<file>
Same as --write-lang-def, but includes duplicated
extensions. This generates a problematic language
definition file because cloc will refuse to use
it until duplicates are removed.
Output Options
--3 Print third-generation language output.
(This option can cause report summation to fail
if some reports were produced with this option
while others were produced without it.)
--by-percent X Instead of comment and blank line counts, show
these values as percentages based on the value
of X in the denominator:
X = 'c' -> # lines of code
X = 'cm' -> # lines of code + comments
X = 'cb' -> # lines of code + blanks
X = 'cmb' -> # lines of code + comments + blanks
For example, if using method 'c' and your code
has twice as many lines of comments as lines
of code, the value in the comment column will
be 200%. The code column remains a line count.
--csv Write the results as comma separated values.
--csv-delimiter=<C> Use the character <C> as the delimiter for comma
separated files instead of ,. This switch forces
--file-encoding=<E> Write output files using the <E> encoding instead of
the default ASCII (<E> = 'UTF-7'). Examples: 'UTF-16',
'euc-kr', 'iso-8859-16'. Known encodings can be
printed with
perl -MEncode -e 'print join("\n", Encode->encodings(":all")), "\n"'
--hide-rate Do not show line and file processing rates in the
output header. This makes output deterministic.
--json Write the results as JavaScript Object Notation
(JSON) formatted output.
--md Write the results as Markdown-formatted text.
--out=<file> Synonym for --report-file=<file>.
--progress-rate=<n> Show progress update after every <n> files are
processed (default <n>=100). Set <n> to 0 to
suppress progress output (useful when redirecting
output to STDOUT).
--quiet Suppress all information messages except for
the final report.
--report-file=<file> Write the results to <file> instead of STDOUT.
--sql=<file> Write results as SQL create and insert statements
which can be read by a database program such as
SQLite. If <file> is -, output is sent to STDOUT.
--sql-append Append SQL insert statements to the file specified
by --sql and do not generate table creation
statements. Only valid with the --sql option.
--sql-project=<name> Use <name> as the project identifier for the
current run. Only valid with the --sql option.
--sql-style=<style> Write SQL statements in the given style instead
of the default SQLite format. Styles include
'Oracle' and 'Named_Columns'.
--sum-one For plain text reports, show the SUM: output line
even if only one input file is processed.
--xml Write the results in XML.
--xsl=<file> Reference <file> as an XSL stylesheet within
the XML output. If <file> is 1 (numeric one),
writes a default stylesheet, cloc.xsl (or
cloc-diff.xsl if --diff is also given).
This switch forces --xml on.
--yaml Write the results in YAML.
사용
$ cloc -csv <path>
- time exceeded error
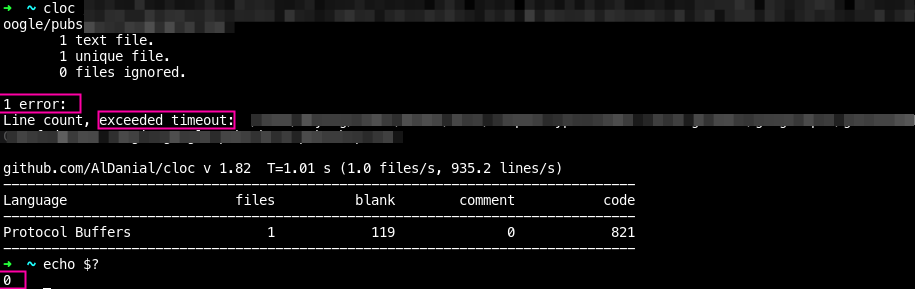
time exceeded timeout error가 발생해도 $?은 0이다.


