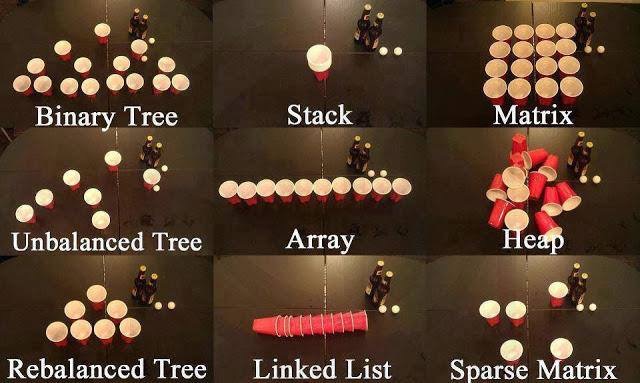
: 동적 할당으로 데이터를 저장하는 방법. 배열의 중간에 데이터를 삽입하는데에 있어서 배열이 가진 데이터 이동 문제점을 해결할 수 있는 방법.
[장점]
- 데이터가 메모리 내의 어느 공간에서나 위치할 수 있음.
- 저장과 수정이 간단 - 데이터 수를 정확히 예측할 수 없을때 좋음.
- 중간 지점에서 자료 추가/삭제가 O(1)의 시간에 가능.
[단점]
- Random access가 불가능 - nextNode를 따라서 다음 저장된 값을 찾기 때문에 원하는 값의 위치를 찾으려면 처음부터 순차적으로 탐색해야하므로 O(n)의 시간이 필요함.
- 배열과 다르게 포인터 변수를 저장하므로 그만큼 메모리를 더 차지함.
'->'와 '.'의 차이:
1. '.' 은 클래스의 멤버를 직접 접근합니다.
2. '->'은 포인터를 통해 멤버를 접근합니다.
3. x->y == (*x).y
A. Singly Linked List (SLL)
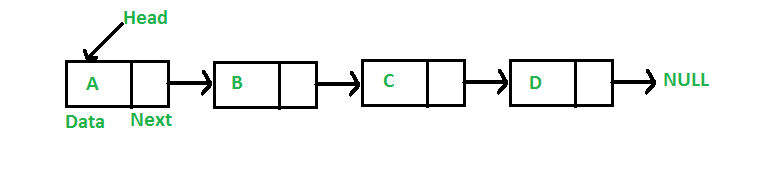
a. Singly Linked List 구현
// a linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
// 링크드 리스트 출력 함수
void printList(Node* head)
{
// cursor 변수 초기화
Node* cursor = new Node();
if(head == NULL) {// 헤드가 NULL일 경우
cout<<"The head is NULL";
}
else { // 헤드가 NULL이 아닐 경우
cursor = head->next;
while(cursor != NULL) {
cout << cursor->data << " "; // 현재 노드의 데이터 출력
cursor = cursor->next; // 다음 노드로 이동
}
}
}
// 새로운 노드를 링크드 리스트에 삽입하는 함수
Node* insert(Node* head, int new_data)
{
// 헤드가 NULL일 경우
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "The head is NULL";
return head;
}
// 새로운 노드 생성
Node* new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = head->next;
// 새로운 노드를 헤드 다음에 삽입
head->next = new_node;
return head;
}
// 링크드 리스트에서 노드를 삭제하는 함수
Node* deleteNode(Node* head, int key)
{
// 헤드가 NULL일 경우
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "The head is NULL";
return head;
}
// 삭제할 노드의 이전 노드 찾기
Node* cursor = new Node();
cursor = head;
while(cursor->next->data != key) {
cursor = cursor->next;
}
// 삭제할 노드를 temp 변수에 저장하고
// 삭제할 노드를 건너뛰어 연결
Node* temp = new Node();
temp = cursor->next;
cursor->next = cursor->next->next;
delete temp;
return head;
}
int main()
{
// 헤드 노드 생성 > 포인터 아님! 노드임!
Node* head = new Node();
//맨 앞 노드의 삽입이나 삭제 연산을 단순화할 수 있기 때문!
// 노드 삽입
head = insert(head, 1);
head = insert(head, 2);
head = insert(head, 3);
// 링크드 리스트 출력
printList(head);
cout<<endl;
// 노드 삭제
head = deleteNode(head, 1);
// 링크드 리스트 출력
printList(head);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
# Result
3 2 1
3 2b. Singly Linked List에서의 새로운 노드 삽입
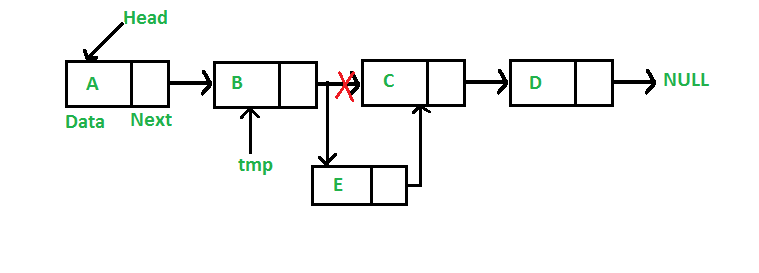
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
// 1. Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "The given previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
// 2. Allocate new node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 3. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 4. Make next of new node as
// next of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 5. move the next of prev_node
// as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
}c. Singly Linked List에서의 기존 노드 삭제
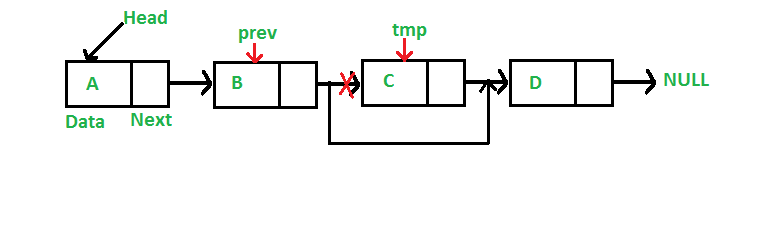
Node* deleteNode(Node* head, int key)
{
if (head == NULL) {
cout << "The head is NULL";
return head;
}
Node* cursor = new Node();
cursor = head;
while(cursor->next->data != key) {
cursor = cursor->next;
}
Node* temp = new Node();
temp = cursor->next;
cursor->next = cursor->next->next;
delete temp;
return head;
}B. Doubly Linked List (DLL)
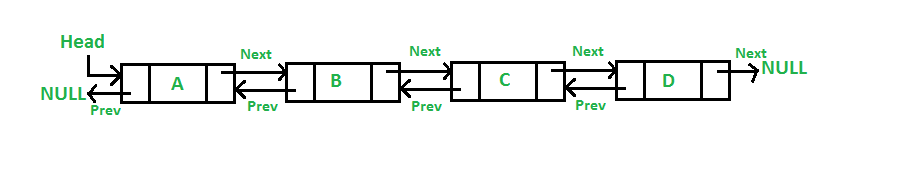
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
friend class DLL;
private:
int data;
Node* pNext;
Node* pPrev;
public:
Node();
Node(int data);
~Node();
};
class DLL {
private:
Node* pHead;
Node* pTail;
Node* pCursor;
public:
DLL();
~DLL();
void insertion(int);
void deletion(int);
void traversal();
void reverseTraversal();
int size();
};
Node::Node() {
this->pPrev = NULL;
this->pNext = NULL;
}
Node::Node(int data) {
this->data = data;
this->pPrev = NULL;
this->pNext = NULL;
}
Node::~Node() {}
DLL::DLL() {
pHead = new Node();
pTail = new Node();
pCursor = new Node();
pHead->pNext = pTail;
pTail->pPrev = pHead;
}
DLL::~DLL() {}
void DLL::insertion(int data) {
Node* temp = new Node(data);
pCursor = pHead->pNext;
pHead->pNext = temp;
temp->pNext = pCursor;
pCursor->pPrev = temp;
temp->pPrev = pHead;
}
void DLL::deletion(int data) {
if(pHead->pNext == pTail) cout<<"No node exists"<<endl;
else {
pCursor = pHead->pNext;
while(pCursor != pTail) {
if(pCursor->data == data) {
pCursor->pPrev->pNext = pCursor->pNext;
pCursor->pNext->pPrev = pCursor->pPrev;
delete pCursor;
return ;
} else {
pCursor = pCursor->pNext;
}
}
}
}
void DLL::traversal() {
if(pHead->pNext == pTail) cout<<"No node exists"<<endl;
else {
pCursor = pHead->pNext;
while(pCursor != pTail) {
cout<<pCursor->data<<" ";
pCursor = pCursor->pNext;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
void DLL::reverseTraversal() {
if(pTail->pPrev == pHead) cout<<"No node exists"<<endl;
else {
pCursor = pTail->pPrev;
while(pCursor != pHead) {
cout<<pCursor->data<<" ";
pCursor = pCursor->pPrev;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
int DLL::size() {
int size = 0;
if(pHead->pNext == pTail) return size;
else {
pCursor = pHead->pNext;
while(pCursor != pTail) {
size++;
pCursor = pCursor->pNext;
}
return size;
}
}
int main() {
DLL dll;
dll.insertion(1);
dll.insertion(2);
dll.insertion(3);
dll.traversal();
dll.reverseTraversal();
cout<<"After deletion"<<endl;
dll.deletion(3);
dll.traversal();
dll.reverseTraversal();
cout<<"size: "<<dll.size()<<endl;
return 0;
}a.새로운 노드 삽입
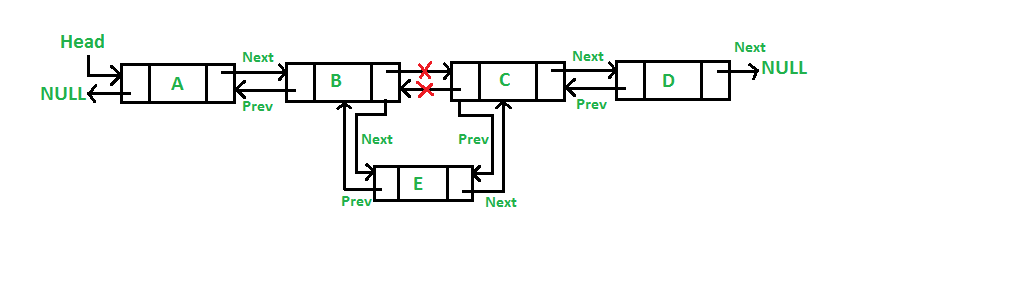
/* Given a node as prev_node, insert
a new node after the given node */
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
/*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */
if (prev_node == NULL)
{
cout<<"the given previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
/* 2. allocate new node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* 3. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
/* 5. Make the next of prev_node as new_node */
prev_node->next = new_node;
/* 6. Make prev_node as previous of new_node */
new_node->prev = prev_node;
/* 7. Change previous of new_node's next node */
if (new_node->next != NULL) new_node->next->prev = new_node;
}b. 기존 노드 삭제
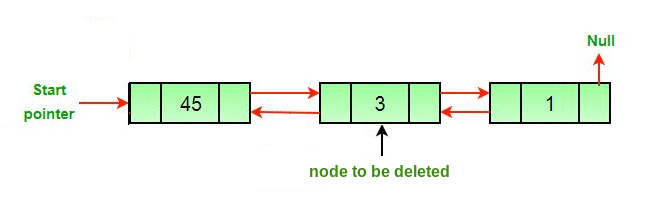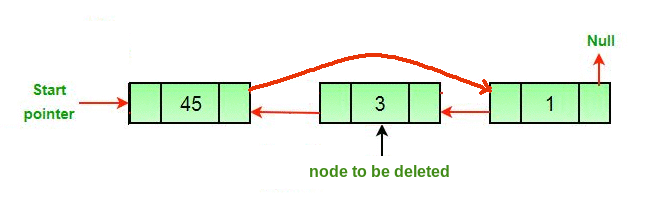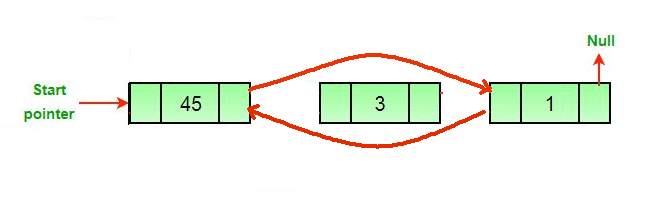
// C++ program to delete a node from
// Doubly Linked List
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* a node of the doubly linked list */
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node* prev;
};
/* Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List.
head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer.
del --> pointer to node to be deleted. */
void deleteNode(Node** head_ref, Node* del)
{
/* base case */
if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL)
return;
/* If node to be deleted is head node */
if (*head_ref == del)
*head_ref = del->next;
/* Change next only if node to be
deleted is NOT the last node */
if (del->next != NULL)
del->next->prev = del->prev;
/* Change prev only if node to be
deleted is NOT the first node */
if (del->prev != NULL)
del->prev->next = del->next;
/* Finally, free the memory occupied by del*/
free(del);
return;
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to insert a node at the
beginning of the Doubly Linked List */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* since we are adding at the beginning,
prev is always NULL */
new_node->prev = NULL;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* change prev of head node to new node */
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list
This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
Node* head = NULL;
/* Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 10);
cout << "Original Linked list ";
printList(head);
/* delete nodes from the doubly linked list */
deleteNode(&head, head); /*delete first node*/
deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete middle node*/
deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete last node*/
/* Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL */
cout << "\nModified Linked list ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}C. Circular Linked List (CLL)
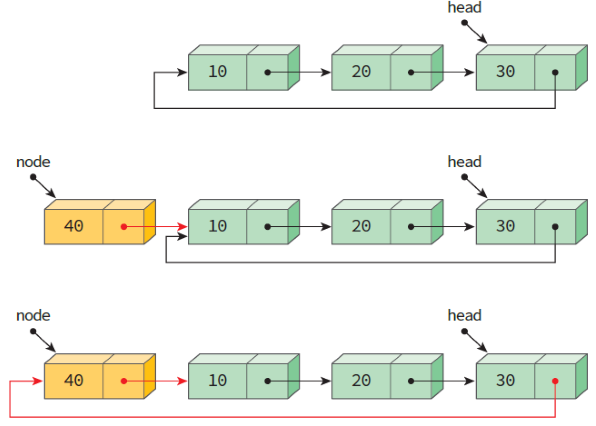
a. 앞부분 삽입
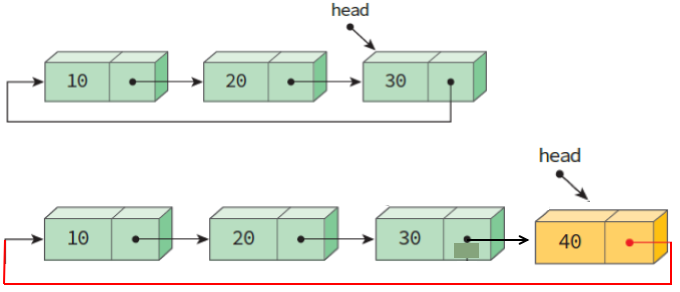
b. 뒷부분 삭제
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int element;
typedef struct { // 노드 타입
element data;
struct ListNode *link;
} ListNode;
// 리스트의 항목 출력
void print_list(ListNode* head)
{
ListNode* p;
if (head == NULL) return;
p = head->link;
do {
printf("%d->", p->data);
p = p->link;
} while ( p! = head );
printf("%d->", p->data); // 마지막 노드
}
// 앞부분 삽입
ListNode* insert_first(ListNode* head, element data)
{
ListNode *node = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
node->data = data;
if (head == NULL) {
head = node;
node->link = head;
}
else {
node->link = head->link;
head->link = node;
}
return head;
}
// 뒷부분 삽입
istNode* insert_last(ListNode* head, element data)
{
ListNode *node = (ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
node->data = data;
if (head == NULL) {
head = node ;
node->link = head;
}
else {
node->link = head->link;
head->link = node;
head = node;
}
return head; // 변경된 헤드 포인터 반환
}
// 메인
int main(void)
{
ListNode *head = NULL;
// list = 10->20->30->40
head = insert_last(head, 20);
head = insert_last(head, 30);
head = insert_last(head, 40);
head = insert_first(head, 10);
print_list(head);
return 0;
}
/* 실행결과
10->20->30->40->
*/