// 7.순환
int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 1)return 1;
else retrun n* factorial(n - 1);
}
int factorialIter(int n) {
int result = 1;
for (int k = n; k > 0; k--)
result = result * k;
return result;
}
//순환:함수 호출 오버헤드
//반복: 수행속도 빠르지만 순환 구현 어려움
//순환 >> 반복 가능
//거듭제곱: 순환 O(logn) | 반복 O(n)
int fibo(int n) {
if (n == 0)return 0;
if (n == 1)return 1;
else return fibo(n - 1) + fibo(n - 2);
} //O(n)
//8.트리
//포화 이진 트리: 각 레벨에 노드가 꽉 차있음(2^h-1)
//완전 이진 트리: 상위 레벨 꽉 차있고 마지막 레벨 왼쪽부터 순서대로
bool isLeaf() { return left == NULL && right == NULL; }
bool isEmpty() { return root == NULL; }
int getCount() { return isEmpty() ? 0 : getCount(root); }
int getCount(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL)return 0;
return 1 + getCount(node->getLeft()) + getCount(node->getRight());
}
int getLeafCount() { return isEmpty() ? 0 : getLeafCount(root); }
int getLeafCount(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL)return 0;
if (node->isLeaf() == true) return 1;
else getLeafCount(node->getLeft()) + getLeafCount(node->getRight());
}
int getHeight() { return isEmpty() ? 0 : getHeight(root); }
int getHeight(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int hLeft = getHeight(node->getLeft());
int hRight = getHeight(node->getRight());
return hLeft > hRight ? hLeft + 1 : hRight + 1;
} //트리 높이 = 서브 트리 높이 + 1
/*
- 전위: VLR 룻왼오
- 중위: LVR 왼룻오
- 후위: LRV 왼오룻
*/
class BinaryTree {
//...
void preorder() { preorder(root); }
void preorder(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
printf("%c", node->getData);
if (node->getLeft() != NULL)preorder(node->getLeft);
if (node->getRight() != NULL)preorder(node->getRight);
}
}
void inorder() { inorder(root); }
void inorder(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
if (node->getLeft() != NULL)inorder(node->getLeft());
printf("%c", node->getData());
if (node->getRight() != NULL)inorder(node->getRight());
}
}
void postorder() { postorder(root); }
void postorder(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node->getLeft() != NULL)postorder(node->getLeft());
if (node->getRight() != NULL)postorder(node->getRight());
printf("%c", node->getData());
}
void levelorder() {
if (!isEmpty()) {
CircularQueue q;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
BinaryNode* n = q.dequeue();
if (n != NULL) {
printf("%c", n->getData());
q.enqueue(n->getLeft());
q.enqueue(n->getRight());
}
}
} //위에서부터 한줄한줄 읽기
printf("\n");
}
};
//수식 트리 계산
int evaluate() { return evaluate(root); }
int evaluate(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL)return 0;
else {
int op1 = evaluate(node->getLeft());
int op2 = evaluate(node->getRight());
switch (node->getData()) {
//...
}
}
return 0;
}
//파일 용량 계산: 후위 순회
int calcSize(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL)return 0;
return node->getData()
+ calcSize(node->getLeft())
+ calcSize(node->getRight());
}
//9. 이진 탐색 트리
//: 중위순회(inorder) = 오름차순 정렬
BinaryNode* searchRecur(BinaryNode* n, int key) {
if (n == NULL)reutrn NULL;
if (key == n->getData())return n;
else if (key < n->getData())
searchRecur(n->getLeft(), key);
else searchRecur(n->getRight(), key);
}
BinaryNode* searchIter(BinaryNode* n, int key) {
while (n != NULL) {
if (key == n->getData()) return n;
else if (key < n->getData())
n = n->getLeft();
else n = n->getRight();
}
return NULL;
}
//삭제 함수 중 삭제 하려는 노드가 자식을 하나만 가진 경우
else if (node->getLeft() == NULL || node->getRight() == NULL) {
BinaryNode* child = (node->getLeft() != NULL) ?
node->getLeft() : node->getRight();
if (node == root)root = child;
else {
if (parent->getLeft() == node)
parent->setLeft(child);
else parent->setRight(child);
}
}
/*
>> 이진 탐색 트리의
- 최선 : 균형, h = logn, O(logn)
- 최악: 경사, h = n, O(n)
*/
//사전
int compare(Record* n) { return compare(n->word); }
int compare(char* w) { return strcmp(w, word); }
//10. 우선 순위 큐: 힙으로 구현 - 완전 이진 트리, 반 정렬 상태 유지
void heapify(int current) { //최소 힙으로 변환
int leftChild = 2 * current + 1;
int rightChild = 2 * current + 2;
int smallest = current;
if (leftChild < heap.size()
&& heap[leftChild] < heap[smallest])
smallest = leftChild;
if (rightChild < heap.size()
&& heap[rightChild] < heap[smallest])
smallest = rightChild;
if (smallest != current) {
swap(heap[current], heap[smallest]);
heapify(smallest);
}
}
void insert(int key) {//삽입: Upheap
if (isFull())retrun;
int i = ++size;
/*
트리 거슬러 올라가면서 부모 노드와 비교
루트가 아니고 부모보다 키값이 크면 부모를 끌어내리고
한 레벨 위로 상승
*/
while (i != 1 && key > getParent(i).getKey()) {
node[i] = getParent(i);
i /= 2;
}
node[i].setKey(key); //최종 위치에 데이터 복사
}
HeapNode remove() { //삭제: Downheap - ;루트'가 삭제됨
if (isEmpty())error();
HeapNode item = node[1]; //루트 노드 (꺼낼 요소)
HeapNode last = node[size--]; //힙의 마지막 노드
int parent = 1; //마지막 노드의 위치를 루트로 생각함
int child = 2; //루트의 왼쪽 자식 위치
while (child <= size) { //힙 트리를 벗어나지 않는 동안
if (child < size //큰 값을 오른쪽 자식이 갖고 있음
&& getLeft(parent).getKey() < getRight(parent).getKey())
child++;
if (last.getKey() >= node[child].getKey())
break;
//한 단계 아래로 이동
node[parent] = node[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
node[parent] = last; //마지막 노드를 최종 위치에 저장
return item; //루트 노드 반환
}
/*
<힙의 시간 복잡도>
: 삽입 최악 = 삭제 최악 = O(logn)
-> 힙 정렬: O(nlogn)
*/
//11.그래프
//완전그래프: 모든 정점이 연결돼있는 그래프
//간선 수: (n*(n-1))/2
//인접 행렬 이용
void insertVertex(char name) { //정점 삽입
if (!isFull()) vertices[size++] = name;
else printf("그래프 정점 개수 초과!");
}
void insertEdge(int u, int v) { //간선 삽입
setEdge(u, v, 1);
setEdge(v, u, 1);
}
class SrchAMGraph :public AdjMatGraph { //인접 행렬로 DFS
protected:
bool visited[MAX_VTXS];
public:
void resetVisited() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
visited[i] = false;
}
bool isLinked(int u, int v) { return getEdge(u, v) != 0; }
void DFS(int v) {
visited[v] = true;
printf("%c", getVertex(v));
for (int w = 0; w < size; w++) {
if (isLinked(v, w) && visited[w] == false) DFS(w);
}
}
};
void BFS(int v){ //인접 ㅎ행렬로 BFS 구현
visited[v] = true;
printf("%c", getVertex(v));
CircularQueue q;
q.enqueue(v);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int v = q.dequeue();
for (int w = 0; w < size; w++) {
if (isLinked(v, w) && visited[w] == false) {
visited[w] = true;
printf("%c", getVertex(w));
q.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
class ConnectedComponentGraph :public SrchAMGramp {
private:
int label[MAX_VTXS];
public:
void labelDFS(int v, int color) {
visited[v] = true;
label[v] = color;
for (int w = 0; w < size; w++) {
if (isLinked(v, w) && visited[w] == false)
labelDFS(w, color);
}
}
void findConnectedComponent() {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false)
labelDFS(i, ++count);
}
printf("그래프 연결 성분 개수: %d\n", count);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf("%c = %d", getVertex(i), label[i]);
printf("\n");
}
};
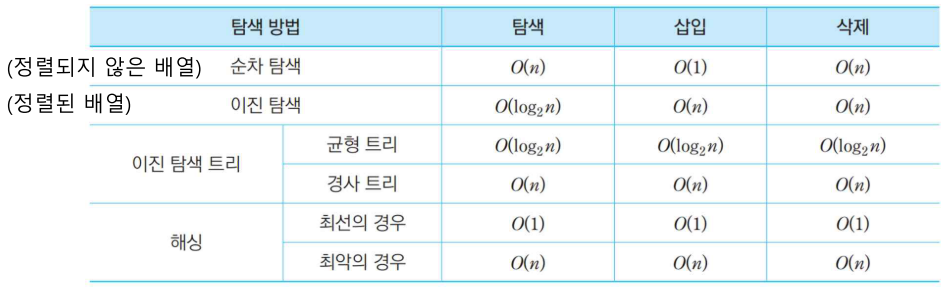
//14. 탐색
/*
<맵 구현>
1. 정렬되지 않은 배열 사용
2. 정렬된 배열 사용
3. 이진탐색트리 이용 (AVL)**
4. 해싱 이용**
- 이진 탐색: 자료들이 배열에 저장 -> 삽입/삭제 비효율
- 이진 탐색 트리: 빠르게 삽입/삭제
<AVL>
- 모든 노드의 왼쪽 오른쪽 서브트리 높이차가 1 이하인 이진 탐색 트리
- 스스로 재배치하여 균형 상태 유지
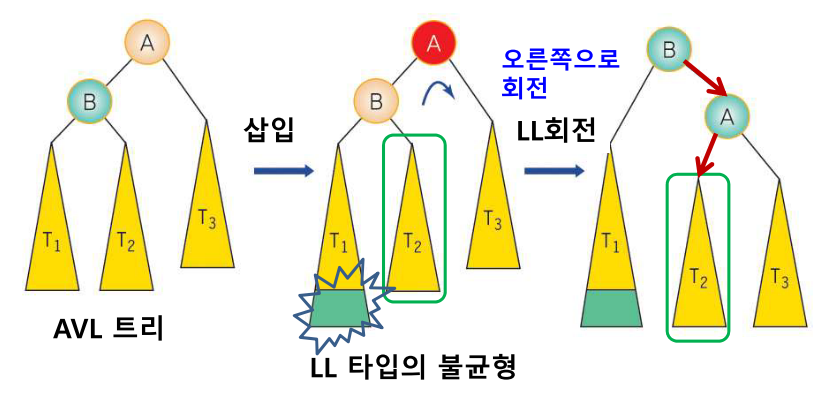
<LL회전>
1. B의 오른쪽 자식을 A의 왼쪽 자식으로 만든다
2. A를 B의 오른쪽 자식으로 만든다
*/
if (hDiff > 1) {
if (getHeightDiff(parent->getLeft()) > 0)
parent = rotateLL(parent);
else parent = rotateLR(parent);
}
BinaryNode* rotateLL(BinaryNode* parent) {
BinaryNode* child = parent->getRight();
child->setRight(parent);
return child;
}
void insert(int data) {
if (isEmpty()) root = new BinaryNode(data);
else root = insertAVL(root, data);
}
BinaryNode* insertAVL(BinaryNode* parent, int data) {
if (data < parent->getData()) {
if (parent->getLeft() != NULL)
parent->setLeft(insertAVL(parent->getLeft(), data));
else parent->setLeft(new BinaryNode(data));
return reBalance(parent);
}
else if (data > parent->getData()) {
if (parent->getLeft() != NULL)
parent->setRight(insertAVL(parent->getRight(), data));
else parent->setRight(new BinaryNode(data));
return reBalance(parent);
}
else {
printf("중복 키 에러!");
return NULL;
}
}
/*
<해싱>
- 좋은 해시 함수의 조건
1. 충돌이 적어야함
2. 함수 값이 테이블 주소 영역 내에 고르게 분포
3. 계산이 빨라야함
- 오버플로우 처리 방법
1. 선형 조사법
: 충돌이 일어난 해시 테이블의 다른 위치를 찾아 저장
-> 간단하지만 군집화 현상으로 효율 저하
-> 이차 조사법, 이중 해싱법(재해싱)
2. 체이닝
: 각 버킷에 삽입/삭제가 용이한 '연결 리스트' 할당
*/A.순환
- 순환: O(logn) | 함수 호출 오버헤드
- 반복: O(n) | for/while을 이용해 수행속도가 빠르지만 순환적인 문제에서 프로그램 작성이 복잡함
- 순환 -> 반복 가능
피보나치 수열
: 순환호출이 비효율적임 <- 같은 항 중복 계산
int fib(int n){
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1) return 1;
return (fib(n-1) + fib(n-2));
}B.트리 - 이진트리
- 차수: 노드의 자식 노드의 개수
- n개의 노드를 가진 트리는 n-1개의 간선을 가짐
- 높이가 h: 최소 h개, 최대 2^h-1개의 노드를 가짐
- n개의 노드를 가진 트리의 최대 높이는 n, 최소 높이는 |log(n+1)|
> bool isLeaf() { return left == NULL
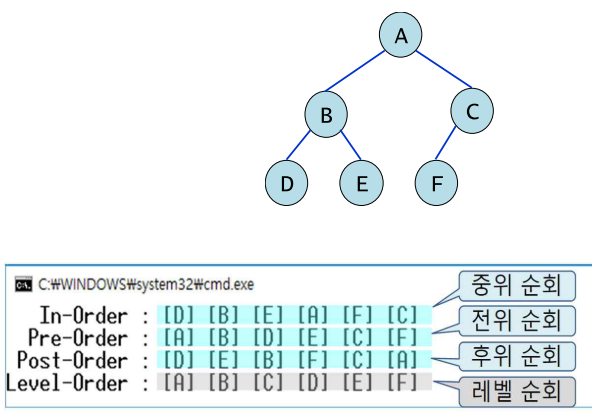
&& right == NULL; }- 이진트리의 기본 순회
a) 전위(preorder): 루트 - 왼쪽 - 오른쪽 (VLR)
b) 중위(inorder): 왼쪽 - 루트 - 오른쪽 (LVR)
c) 후위(postorder): 왼쪽 - 오른쪽 - 루트 (LRV)
[예시]: inorder
void inorder(BinaryNode* node{
if(node != NULL){
if(node->getLeft() != NULL){
inorder(node->getLeft());
}
printf(" [%c] ", node->getData());
if(node->getRight() != NULL){
inorder(node->getRight());
}
}
}
[예시]: levelorder - '큐' 사용
void levelorder(){
if(!isEmpty()){
CircularQueue q;
q.enqueue(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
BinaryNode* n = q.dequeue();
if(n != NULL){
printf(" [%c] ", n->getData());
q.enqueue(n->getLeft());
q.enqueue(n->getRight());
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
- 노드 개수 계산 - getCount()함수
int getCount(){ return isEmpty() ? 0 : getCount(root); }
int getCount(BinaryNode* node){
if(node == NULL) return 0;
return 1 + getCount(node->getLeft())
+ getCount(node->getRight());
}- 단말 노드 개수 계산 - getLeafCount()함수
int getLeafCount(){ return isEmpty() ? 0 : getLeafCount(root); }
int getLeafCount(){
if(node == NULL) return 0;
if(node->isLeaf()) retrun 1;
else return getLeafCount(node->getLeft())
+ getLeafCount(node->getRight());
}- 트리 높이: 서브트리 높이 + 1
int getHeight(){ return isEmpty() ? 0 : getHeight(root); }
int getHeight(BinaryNode* node){
if(node == NULL) return 0;
int hLeft = getHeight(node->getLeft());
int hRight = getHeight(node->getRight());
return (hLeft > hRight) ? hLeft + 1 : hRight + 1;
}
+) hLeft == hRight인 경우: root 노드만 있을 때- 수식트리의 계산
int evaluate() { return evaluate(root); }
int evaluate(BinaryNode* node){
if(node == NULL) return 0;
else{
int op1 = evaluate(node->getLeft());
int op2 = evaluate(node->getRight());
switch(node->getData){
...
}
return 0;
}
}- 폴더 용량 계산: 후위 순회
int calcSize(BinaryNode* node){
if(node == NULL) return 0;
return node->getData()
+ calcSize(node->getLeft())
+ calcSize(node->getRight());
}c. 이진 탐색 트리
- 왼쪽서브트리key <= 루트key <= 오른쪽서브트리key
- 중위 순회 -> 오름차순으로 정렬
- 탐색 연산
a) 키값이 루트와 같으면: 탐색 끝!
b) 키값이 루트보다 작으면: 왼쪽 자식 기준으로 재탐색
c) 키값이 루트보다 크면: 오른쪽 자식 기준으로 재탐색
[반복으로 구현한 탐색 함수]
BinaryNode* searchlter(BinaryNode* n, int key){
while(n != NULL){
if(key == n->getData()) return n;
else if(key < n->getData()) n = n->getLeft();
else n = n->getRight();
}
return NULL;
}
[순환으로 구현한 탐색 함수]
void insertRecur(BinaryNode* r, BinaryNode* n){
if(n->getData() == r->getData()) return;
elseif(n->getData() < r->getData()){
if(r->getLeft() == NULL) r->setLeft(n);
else insertRecur(r->getLeft(), n);
}
else{
if(r->getRight() == NULL) r->setRight(n);
else insertRecur(r->getRight(), n));
]
}
[삭제함수에서...]
삭제하려는 노드가 왼쪽 또는 오른쪽 자식만 가진 경우
-> 부모 노드의 자식으로 자식노드의 자식을 직접 연결
if(node == root) root = child;- 성능 분석
a) 최선: h = logn | O(logn)
b) 최악: h = n | O(n)
[영어사전]
- 오름차순(inorder)으로 출력
int compare(Record* n) { return compare(n->word); }
int compare(char* w) { return strcmp(w, word) }- 탐색/삽입에서
...
if(n->compare(r) == 0) return;
else if(n->compare(r) > 0)
...- 삭제에서
...
while(node != NULL && node->compare(data) != 0){
parent = node;
node = (node->compare(data) < 0) ?
node->getleft() : node->getright();
...D. 우선순위 큐 - 힙
a) 완전이진트리의 일종
b) 우선순위 큐를 위해 만들어진 자료구조
c) 일종의 '반 정렬 상태' 유지
d) 삽입/삭제 모두 최악의 경우에 O(logn)
e) 최대 힙: 부모노드키값 >= 자식노드키값 최소 힙: 부모노드키값 <= 자식노드키값
f) n개의 노드를 가지고 있는 힙의 높이는 O(logn)
g) 전체 정렬 보다는 가장 큰 값 몇게만 필요할 때 유용함
- 삽입 -> Upheap
...
while(i != 1 && key->getParent.getKey()){
node[i] = getParent(i);
i /= 2;
}
...- 삭제: 항상 루트(가장 큰 값을 가진 노드)가 삭제됨! -> Downheap
...
if(child < size &&
getLeft(parent).getKey() < getright(parent).getKey())
child++; //큰 값을 오른쪽 자식이 갖고 있음
if(last.getKey() >= node[child].getKey())
break;
...
- 힙 정렬
void heapSort(int a[], int n){
MaxHeap h;
...
//최대힙에서는 삭제시 가장 큰 값이 반환되므로
//오름차순으로 정렬하기 위해서
//삭제 항목을 배열의 끝부터 앞으로 채워나감
for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--)
a[i] = h.remove()->getKey();
}E. 그래프
- 오일러 정리: 모든 정점에 연결된 간선의 수가 짝수이면 오일러 경로 존재함.
- 완전 그래프의 간선 수: (n x (n-1)) / 2
1. 인접 행렬(adjacency matrix)
void insertVertex(char name){
if(!isFull()) vertices[size++] = name;
else printf("Error: 그래프 정점 개수 초과!\n");
}
void insertEdge(int u, int v){
setEdge(u,v,1);
setEdge(v,u,1);
}
void display(FILE* fp = stdout){
...
}- DFS 구현
class SrchAMGraph : public AdjMatGraph{
protected:
bool visited[MAX_VTXS];
public:
void resetVisited(){
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
visited[i] = false;
}
bool isLinked(int u, int v){ return getEdge(u, v) != 0; }
void DFS(int v){
fisited[v] = true;
printf("%c ", getVertex(v));
for(int w = 0; w < size; w++)
if(isLinked(v, w) && visited[w] == false)
DFS(w);
}
}- BFS 구현
#include "AdjListGraph.h"
#include "CircularQueue.h"
...
void BFS(int v){
visited[v] = true;
printf("%c ", getVertex(v));
CircularQueue que;
que.enqueue(v);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int v = que.dequeue();
for(int w = 0; w < size; w++)
if(isLinked(v, w) && visited[w] == false){
visited[w] = true;
printf("%c ", getVertex(w));
que,enqueue(w);
}
}
}2. 인접 리스트 -> X
F. 탐색
G. AVL 트리
a) 스스로 노드를 재배치하여 균형 상태 유지
b) 평균/최선/최악: O(logn)
c) 탐색 연산: 이진탐색트리와 동일
d) 삽입/삭제 연산: 균형상태가 깨질 수 있음
-> 불균형 상태로 변한 가장 가까운 조상 노드의
서브 트리들에 대해 다시 균형을 맞춤- 균형 인수(bf, balance factor)
: = 왼쪽 서브트리 높이 - 오른쪽 서브트리 높이
: 모든 노드의 균형 인수가 -1 ~ 1 이면 AVL 트리
>> LL타입
: 가장 가까우면서 균형 인수가 ±2인 조상노드의 왼쪽 서브트리(L)의 왼쪽서브트리(L)에 삽입
-> LL회전(= 오른쪽 회전)
: a) B의 오른쪽 자식을 A의 왼쪽 자식으로 만든다
: b) A를 B의 오른쪽 자식의 노드로 만든다
BinaryNode* reBalance(BinaryNode* parent){
int hDiff = getHeightDiff(parent);
if(hDiff > 1){
if(getHeightDiff(parent->getLeft()) > 0)
parent = rotateLL(parent);
else parent = rotateLR(parent);
...
}
BinaryNode* rotateLL(BinaryNode* parent){
BinaryNode* child = parent->getLeft();
parent->setLeft(child->getRight());
child->setRight(parent);
return child;
}
Void insert(int data){
if(isEmpty()) root = new BinaryNode(data);
else root = insertAVL(root, data);
}
BinaryNode* insertAVL(BinaryNode* parent, int data){
if(data < parent->getData()){
if(parent->getLeft() != NULL)
parent->setLeft(insertAVL(parent->getLeft(),data));
else parent->setLeft(new BinaryNode(data));
return reBalance(parent);
}
else if(data > parent->getData()){
if(parent->getRight() != NULL)
parent->setRight(insertAVL(parent->getRight(), data));
else parent->setRight(new BinaryNode(data));
return reBalance(parent);
}
else{ printf("중복 키 에러!\n"); return NULL; }
}H. 해싱
- 이상적인 해싱 함수: O(1)
- 좋은 해시 함수의 조건
a) 충돌이 적어야 함
b) 함수 값이 테이블의 주소 영역 내에 고르게 분포
c) 계산이 빨라야 함 - 구조적 문제 해결법
a) 선형 조사법
b) 이차 조사법
c) 체이닝