CPP-Module-02
Ad-hoc polymorphism, operator overloading and Orthodox Canonical class form
c++ and the flags -Wall -Wextra -Werror
class names in UpperCamelCase
No Leaks
Your classes must be designed in the Orthodox Canonical Form, except when explicitely stated otherwise.
functions below:
• Default constructor
• Copy constructor
• Copy assignment operator
• Destructor
ex00: My First Class in Orthodox Canonical Form
Orthodox Canonical Form 구현
class Fixed {
private:
int _fixed_point_number;
static const int _fractionalBits = 8;
public:
Fixed(); // 기본 생성자
Fixed(const Fixed &fixed); // 복사 생성자
Fixed &operator=(const Fixed &other); // 대입 연산자
~Fixed(); // 소멸자
int getRawBits(void) const;
void setRawBits(int const raw);
};1. 기본 생성자
Fixed::Fixed() : _fixed_point_number(0) {
std::cout << "Default constructor called" << std::endl;
}2. 복사 생성자
Fixed::Fixed(const Fixed &fixed) {
std::cout << "Copy constructor called" << std::endl;
*this = fixed;
}3. 복사 대입 연산자
Fixed &Fixed::operator=(const Fixed &other) {
std::cout << "Copy assignment operator called" << std::endl;
if (this != &other) {
this->_fixed_point_number = other.getRawBits();
}
return (*this);
}4. 소멸자
Fixed::~Fixed() {
std::cout << "Destructor called" << std::endl;
}Test
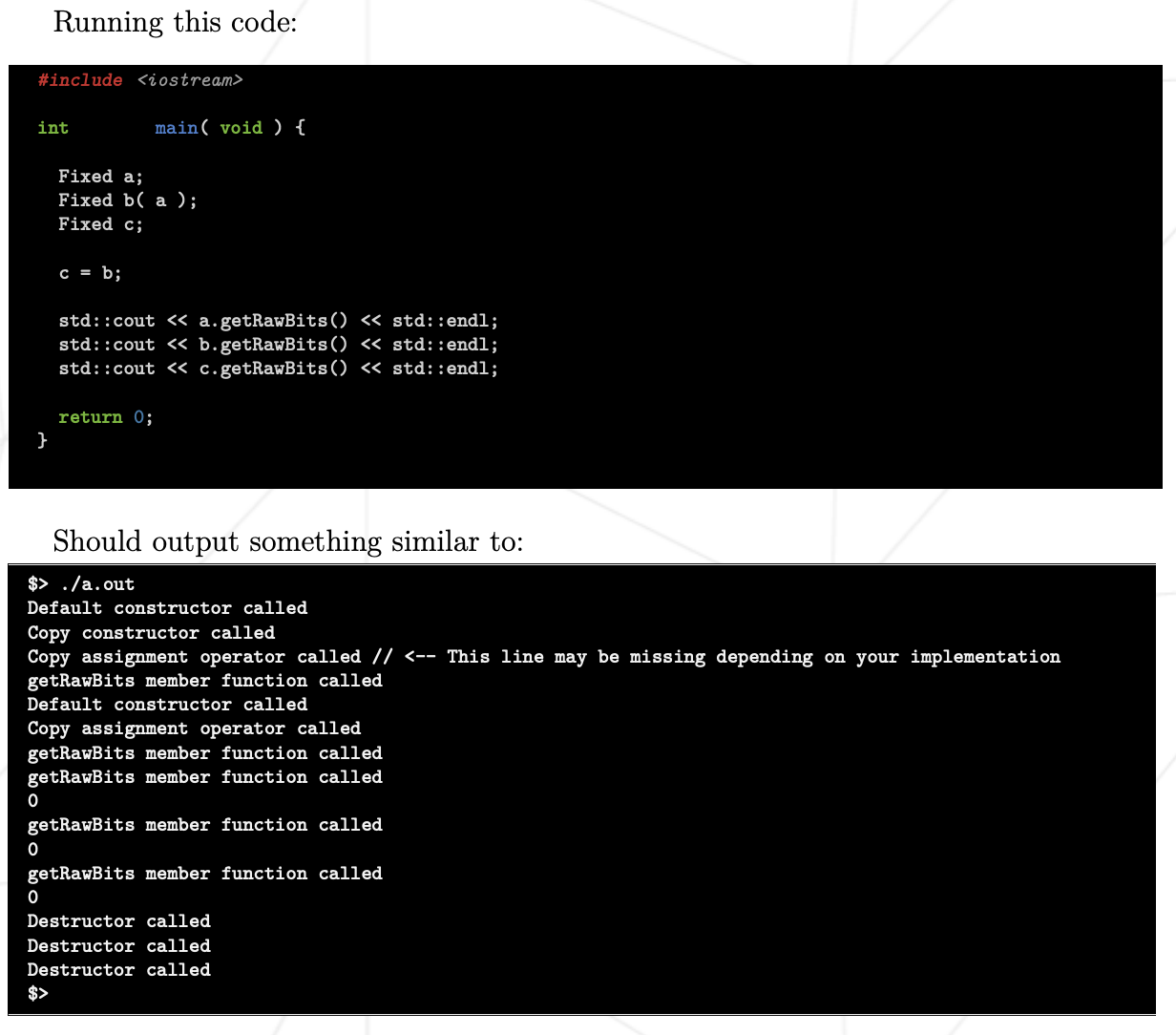
int main(void) {
Fixed a;
Fixed b(a);
Fixed c;
c = b;
std::cout << a.getRawBits() << std::endl;
std::cout << b.getRawBits() << std::endl;
std::cout << c.getRawBits() << std::endl;
return 0;
}Default constructor called // a 생성
Copy constructor called // b(a) 생성
Default constructor called // c 생성
Copy assignment operator called // c = b
getRawBits member function called // a.getRawBits()
0
getRawBits member function called // b.getRawBits()
0
getRawBits member function called // c.getRawBits()
0
Destructor called // c 소멸
Destructor called // b 소멸
Destructor called // a 소멸ex02: Now we’re talking
Add public member functions to your class to overload the following operators:
• The 6 comparison operators: >, <, >=, <=, == and !=.
• The 4 arithmetic operators: +, -, *, and /.
• The 4 increment/decrement (pre-increment and post-increment, pre-decrement and post-decrement) operators, that will increase or decrease the fixed-point value from the smallest representable ϵ such as 1 + ϵ > 1.
Fixed 클래스
class Fixed {
private:
int _fixed_point_value;
static const int _fractionalBits = 8;
public:
// 생성자 및 소멸자
Fixed();
Fixed(const int num);
Fixed(const float num);
Fixed(const Fixed &other);
Fixed &operator=(const Fixed &fixed);
~Fixed();
// 비교 연산자
bool operator<(const Fixed &fixed) const;
bool operator>(const Fixed &fixed) const;
bool operator<=(const Fixed &fixed) const;
bool operator>=(const Fixed &fixed) const;
bool operator==(const Fixed &fixed) const;
bool operator!=(const Fixed &fixed) const;
// 산술 연산자
Fixed operator+(const Fixed &fixed);
Fixed operator-(const Fixed &fixed);
Fixed operator*(const Fixed &fixed);
Fixed operator/(const Fixed &fixed);
// 증감 연산자
Fixed &operator++(); // 전위 증가
Fixed operator++(int); // 후위 증가
Fixed &operator--(); // 전위 감소
Fixed operator--(int); // 후위 감소
// 변환 및 유틸리티 함수
int getRawBits(void) const;
void setRawBits(int const raw);
int toInt(void) const;
float toFloat(void) const;
// 정적 유틸리티 함수
static const Fixed &min(const Fixed &a, const Fixed &b);
static const Fixed &max(const Fixed &a, const Fixed &b);
static Fixed &min(Fixed &a, Fixed &b);
static Fixed &max(Fixed &a, Fixed &b);
};
// 출력 연산자
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Fixed &fixed);고정 소수점 변환
// 정수 → 고정 소수점
Fixed::Fixed(const int num) : _fixed_point_value(num << _fractionalBits) {}
// 실수 → 고정 소수점
Fixed::Fixed(const float num) : _fixed_point_value(roundf(num * (1 << _fractionalBits))) {}
// 고정 소수점 → 정수
int Fixed::toInt(void) const {
return (_fixed_point_value >> _fractionalBits);
}
// 고정 소수점 → 실수
float Fixed::toFloat(void) const {
return (_fixed_point_value / static_cast<float>(1 << _fractionalBits));
}연산자 오버로딩
// 비교 연산자
bool Fixed::operator<(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value < fixed._fixed_point_value);
}
// 산술 연산자
Fixed Fixed::operator*(const Fixed &fixed) {
Fixed newFixed(this->toFloat() * fixed.toFloat());
return (newFixed);
}// 증감 연산자
// 전위 증가 (++a)
Fixed &Fixed::operator++() {
this->_fixed_point_value++;
return (*this);
}
// 후위 증가 (a++)
Fixed Fixed::operator++(int) {
Fixed old(*this);
this->_fixed_point_value++;
return old;
}전위 연산자 : 값 증가 후 참조 반환
후위 연산자 : 복사본 저장, 값 증가 후 복사본 반환
비교 연산자
// 작음 (<)
bool Fixed::operator<(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value < fixed._fixed_point_value);
}
// 큼 (>)
bool Fixed::operator>(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value > fixed._fixed_point_value);
}
// 작거나 같음 (<=)
bool Fixed::operator<=(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value <= fixed._fixed_point_value);
}
// 크거나 같음 (>=)
bool Fixed::operator>=(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value >= fixed._fixed_point_value);
}
// 같음 (==)
bool Fixed::operator==(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value == fixed._fixed_point_value);
}
// 다름 (!=)
bool Fixed::operator!=(const Fixed &fixed) const {
return (this->_fixed_point_value != fixed._fixed_point_value);
}산술연산자
// 덧셈 (+)
Fixed Fixed::operator+(const Fixed &fixed) {
Fixed newFixed(this->toFloat() + fixed.toFloat());
return (newFixed);
}
// 뺄셈 (-)
Fixed Fixed::operator-(const Fixed &fixed) {
Fixed newFixed(this->toFloat() - fixed.toFloat());
return (newFixed);
}
// 곱셈 (*)
Fixed Fixed::operator*(const Fixed &fixed) {
Fixed newFixed(this->toFloat() * fixed.toFloat());
return (newFixed);
}
// 나눗셈 (/)
Fixed Fixed::operator/(const Fixed &fixed) {
Fixed newFixed(this->toFloat() / fixed.toFloat());
return (newFixed);
}출력 스트림 연산자
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, const Fixed &fixed) {
os << fixed.toFloat();
return (os);
}정적 멤버 함수
static const Fixed &min(const Fixed &a, const Fixed &b);
static Fixed &min(Fixed &a, Fixed &b);
//return (a > b) ? a : b;정적 함수의 경우 클래스의 객체를 생성하지 않고도 호출할 수 있음
Fixed max_value = Fixed::min(a, b);- 특정 객체에 바인딩 되지 않기 때문에 this 포인터가 없음
- const 객체용, 일반 객체용
오버로딩(const의 유무에 맞게)
- 참조 반환 (복사 방지)
// const 참조자 매개변수와 const 참조자 반환
static const Fixed &max(const Fixed &a, const Fixed &b);
// 일반 참조자 매개변수와 일반 참조자 반환
static Fixed &max(Fixed &a, Fixed &b);아래와 같이 유연하게 사용가능!
int main() {
// 비-const 객체 케이스
Fixed a(5);
Fixed b(10);
Fixed &larger = Fixed::max(a, b); // 버전 2 호출
larger = Fixed(20); // 가능! 반환된 참조를 통해 원본 수정
// const 객체 케이스
const Fixed c(15);
const Fixed d(20);
const Fixed &largerConst = Fixed::max(c, d); // 버전 1 호출
// largerConst = Fixed(25); // 컴파일 에러! const 참조는 수정 불가
// 혼합 케이스 - const와 비-const
const Fixed &mixed = Fixed::max(a, c); // 버전 1 호출
// mixed = Fixed(30); // 컴파일 에러! const 참조는 수정 불가
}이 경우 Fixed 클래스는 단순한 구조이지만, 일반적인 설계 원칙으로서 min/max 같은 유틸리티 함수는 참조 반환이 일반적
???
// 참조 반환 방식
const Fixed &max = Fixed::max(a, b); // 복사 없음, a나 b 중 하나를 직접 참조
// 값 반환 방식이었다면
Fixed max = Fixed::max(a, b); // 복사 발생, 독립된 새 객체 생성참조 반환은 객체의 복사본을 생성하지 않고 기존 객체에 대한 참조만 반환한다.
특히 큰 객체의 경우, 불필요한 복사는 성능 저하를 일으킬 수 있다.
참조는 원본 객체의 별칭이므로 원본의 변경이 참조를 통해서도 보이고,
값 반환은 원본과 독립된 복사본을 생성하므로 이후 원본 변경이 반영되지 않는다.
