
[Java Arraylist]
난이도: ★★☆☆☆ • solved on: 2025-11-03
문제 요약
- 문제 유형: 자료구조, 구현
- 요구사항:
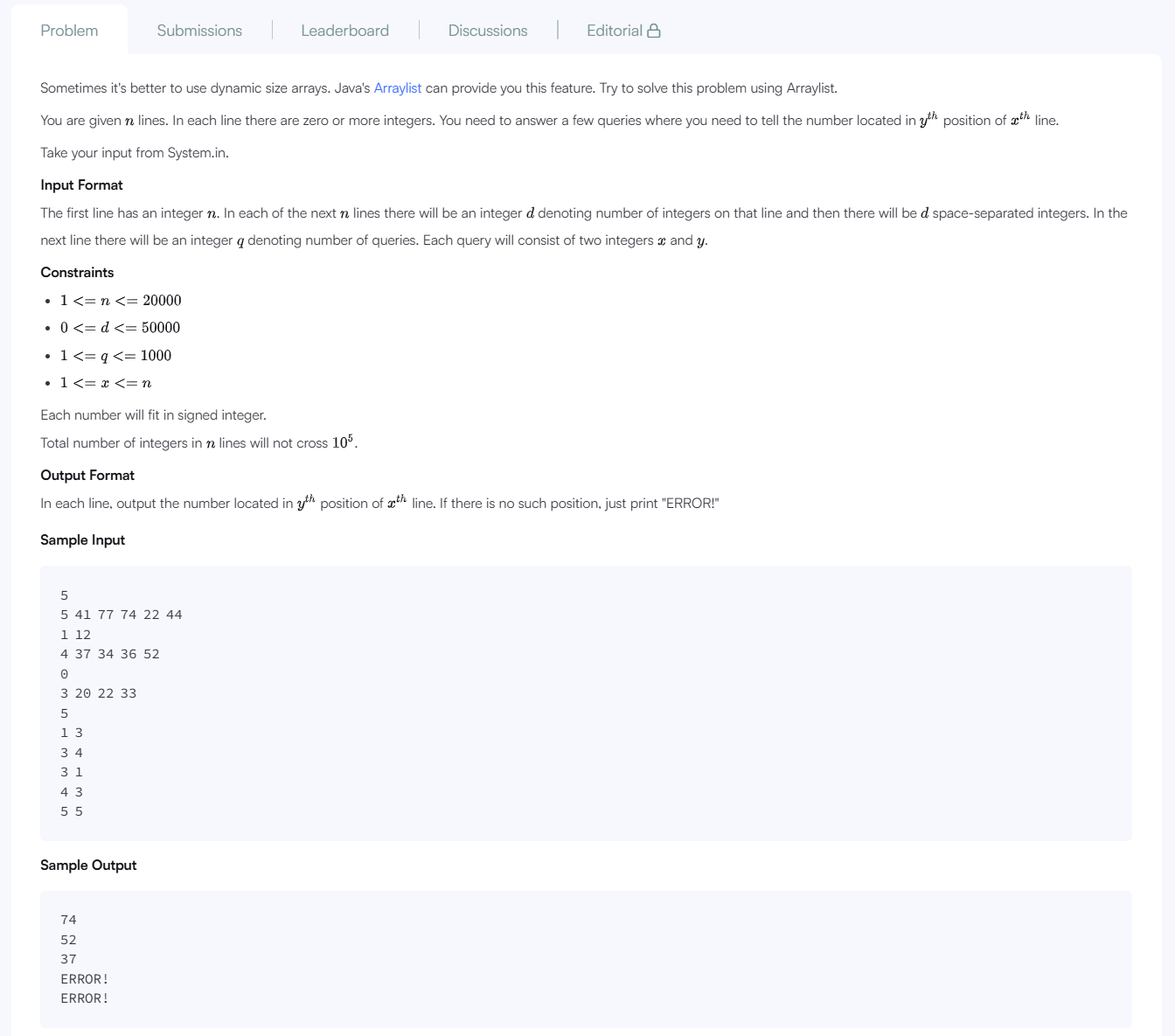
여러 개의 리스트(ArrayList)를 입력받고, 이후 주어진 쿼리(x, y)에 따라 x번째 리스트의 y번째 요소를 출력해야 한다.
단, 해당 인덱스가 존재하지 않으면"ERROR!"를 출력해야 한다.
사용 개념
- 자료구조
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>: 중첩 리스트 구조로 각 줄마다 리스트를 저장BufferedReader: 빠른 입력 처리를 위해 사용
-
알고리즘/기법
- 입력 파싱 및 예외 처리
- 리스트 인덱스 검증 (Out of Range 방지)
-
핵심 키워드
- Dynamic Array
- List of Lists
- Index Bound Check
풀이 아이디어
문제 분해
- 첫 줄에서 리스트의 개수
n을 입력받는다.- 각 줄마다 첫 번째 숫자는 리스트의 원소 개수
k, 이후k개의 정수를 리스트에 추가한다.- 이후
q개의 쿼리(x, y)를 받아,result[x-1][y-1]값을 출력한다.- 존재하지 않는 인덱스면
"ERROR!"출력.핵심 로직 흐름
for i in 0..n: read line → split by space k = first number if k == 0 → 빈 리스트 추가 else → k개 숫자를 리스트에 추가 for i in 0..q: read x, y if x 또는 y가 범위 초과 → "ERROR!" else → result[x-1][y-1] 출력
예외 처리
- 리스트 개수가 0일 때 (
k == 0): 반드시 빈ArrayList를 추가해야 함.x또는y인덱스가 범위를 벗어나는 경우"ERROR!"출력.
코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.valueOf(br.readLine());
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
int k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> itemBox = new ArrayList<>();
String line = br.readLine();
String[] tmpInts = line.split(" ");
k = Integer.valueOf(tmpInts[0]);
if (k == 0) {
result.add(itemBox);
continue;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
itemBox.add(Integer.valueOf(tmpInts[j]));
}
result.add(itemBox);
}
int q = Integer.valueOf(br.readLine());
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
x = Integer.valueOf(line.split(" ")[0]);
y = Integer.valueOf(line.split(" ")[1]);
if (result.size() < x) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
continue;
}
if (result.get(x - 1).size() < y) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
continue;
}
System.out.println(result.get(x - 1).get(y - 1));
}
}
}시간·공간 복잡도
- 시간 복잡도: O(N + Q)
(입력 리스트 생성 + 쿼리 처리) - 공간 복잡도: O(Σk)
(입력된 모든 리스트 원소 총합)
어려웠던 점
-
BufferedReader사용법을 까먹음readLine()후split(" ")처리로 문자열 배열로 변환하는 부분을 다시 복습함.
-
빈 리스트 처리 누락
k == 0일 때result에 빈ArrayList를 추가하지 않아IndexOutOfBoundsException발생.
→ 빈ArrayList추가 이후continue처리로 수정.
배운 점 및 팁
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>는 중첩된 데이터 구조를 다룰 때 매우 유용하다.- 입력 데이터가 많은 경우
BufferedReader+String.split()조합이Scanner보다 훨씬 빠르다. - 인덱스 접근 전 반드시
size()비교로 범위 검증을 해야 한다.
(특히 HackerRank 같은 플랫폼에서는IndexOutOfBoundsException이 곧 “Runtime Error”로 간주됨.)
참고 및 링크
- 문제 링크: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/java-arraylist/problem
- 참고 블로그/깃허브: 없음
추가 연습 문제
-
비슷한 유형 (GPT 추천):
- HackerRank: Java List — 리스트의 삽입/삭제 연습 문제
-
확장 문제 (GPT 추천):
- HackerRank: Java 1D Array (Part 2) — 배열과 인덱스 이동 로직의 확장 응용
