
[Queue] Queue using Two Stacks
난이도: ★☆☆☆☆ • solved on: 2025-11-21
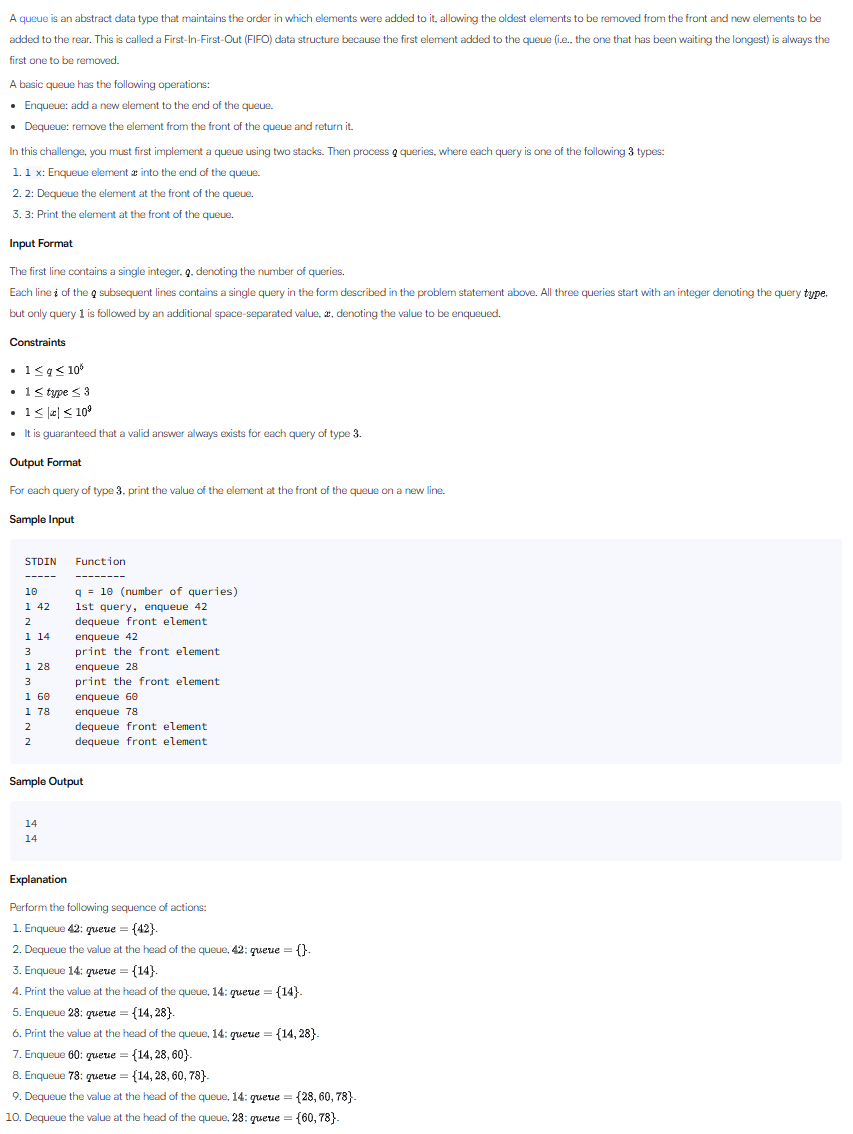
문제 요약
- 문제 유형: 스택(Stack), 큐(Queue), 시뮬레이션
- 요구사항: 두 개의 스택만 이용해 큐의 기능(삽입, 삭제, 조회)을 구현해야 한다.
사용 개념
-
자료구조
- Queue (자바 기본 자료구조)
- Stack (문제 의도)
-
알고리즘/기법
- 두 개의 스택을 이용한 큐 구현
- 지연 이동(lazy transfer) 방식
-
핵심 키워드
- enqueue / dequeue
- inStack, outStack
- amortized O(1)
풀이 아이디어
- 문제 분해
- 원래 문제 의도는 스택 2개로 큐를 직접 구현하는 것이다.
- 하지만 자바의
ArrayDeque를 큐처럼 사용하는 방식이다.
핵심 로직 흐름
push(x): inStack에 push pop(): outStack이 비어 있으면 inStack 모두 outStack으로 이동, 그 후 pop peek(): outStack이 비어 있으면 이동, 그 후 peek
- 이렇게 하면 각 원소는 이동을 딱 한 번만 하므로 평균 O(1) 로 동작한다.
예외 처리
- 비어 있는 큐에서 pop 혹은 peek이 호출되지 않도록 주의한다.
코드
방법 1. Queue 자료구조 그대로 사용
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
Queue<String> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
String line;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
line = br.readLine();
String[] arr = line.split(" ");
if (arr[0].equals("1")) {
queue.add(arr[1]);
} else if (arr[0].equals("2")) {
queue.poll();
} else if (arr[0].equals("3")) {
System.out.println(queue.peek());
} else {
System.err.println("undefined command " + arr[0]);
}
}
}방법 2. 스택 2개로 큐 구현 (문제 의도 충족)
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
Deque<Integer> inStack = new ArrayDeque<>();
Deque<Integer> outStack = new ArrayDeque<>();
int q = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
while (q-- > 0) {
String[] cmd = br.readLine().split(" ");
if (cmd[0].equals("1")) { // enqueue
inStack.push(Integer.parseInt(cmd[1]));
}
else if (cmd[0].equals("2")) { // dequeue
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
while (!inStack.isEmpty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
}
outStack.pop();
}
else if (cmd[0].equals("3")) { // peek
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
while (!inStack.isEmpty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
}
System.out.println(outStack.peek());
}
}
}
}시간·공간 복잡도
방법 1.
- 시간 복잡도: O(1) per operation
- 공간 복잡도: O(N)
방법 2.
- 시간 복잡도: Amortized O(1)
(이동은 최대 한 번만 일어나므로 전체적으로 효율적) - 공간 복잡도: O(N)
어려웠던 점
- BufferedReader 사용법이 정확히 기억나지 않아 블로그를 참고했다.
- 문제 의도가 “스택으로 큐 구현”임을 나중에 깨달았고, 처음엔 단순 큐로 해결했다.
배운 점 및 팁
- 두 개의 스택을 이용해 큐를 구현하는 핵심 개념은 inStack ↔ outStack 지연 이동이다.
- 헤비한 연산(pop 모두 이동)은 가끔 일어나지만, 전체적으로는 amortized O(1) 성능이 된다.
- 입력이 많은 문제에서는 Scanner보다 BufferedReader가 훨씬 빠르다.
참고 및 링크
- 문제 링크: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/one-week-preparation-kit-queue-using-two-stacks/problem
- 참고 블로그/깃허브: https://m.blog.naver.com/ka28/221850826909
추가 연습 문제
-
비슷한 유형:
-
확장 문제:
