
[Stack] Maximum Element
난이도: ★★★☆☆ • solved on: 2025-11-08
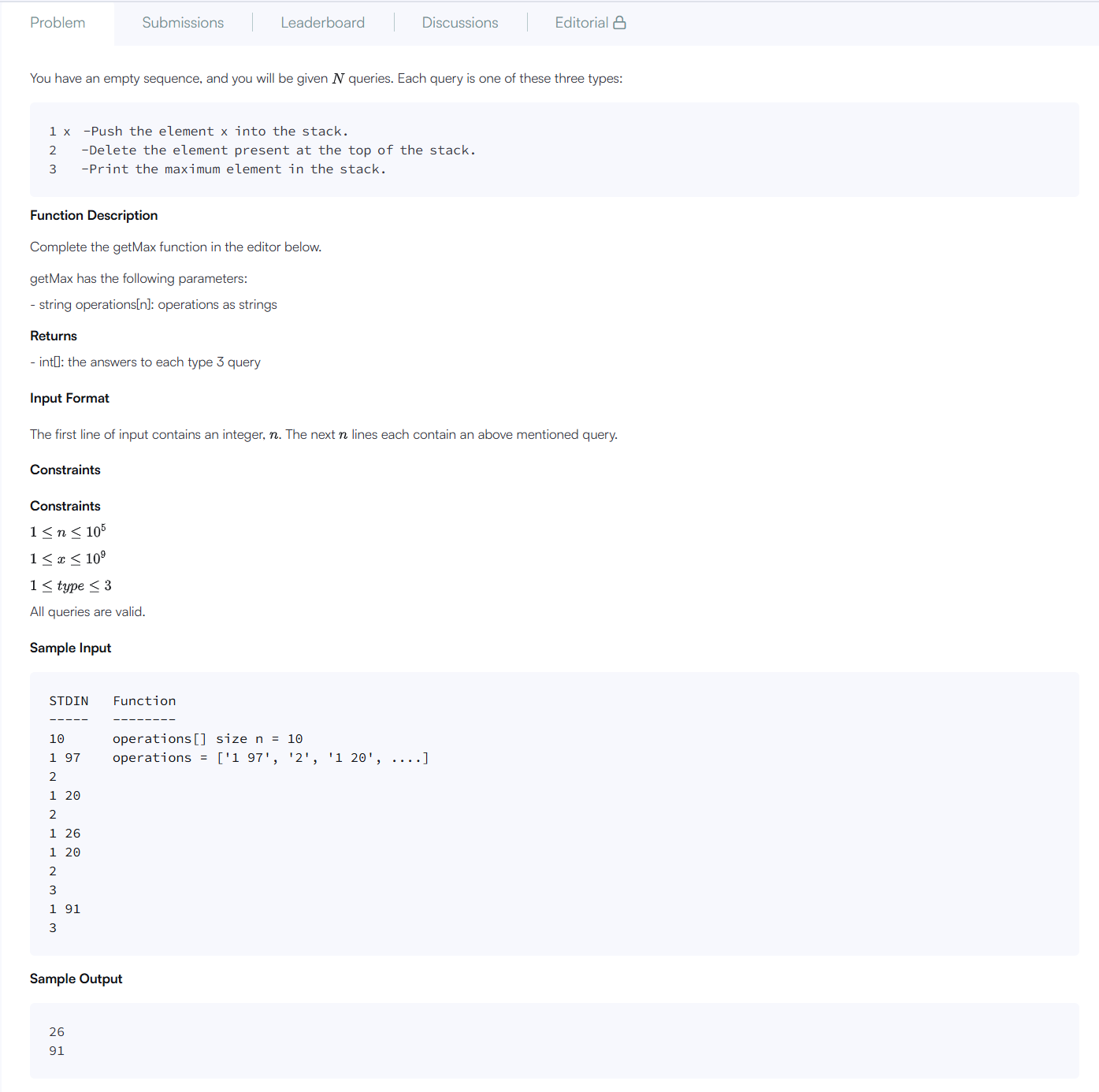
문제 요약
- 문제 유형: Stack, 자료구조
- 요구사항:
주어진 명령어 목록에 따라 스택을 조작하고, 명령어3이 주어질 때마다 스택 내 최댓값을 출력해야 한다.
사용 개념
-
자료구조
Stack<Integer>: push/pop 연산으로 데이터 관리List<Integer>: 출력값(최댓값) 저장
-
알고리즘/기법
- Stack 조작 (LIFO)
- 실시간 최댓값 관리
-
핵심 키워드
- 최대값 추적(max tracking)
- 스택의 상태 변화
- 명령어 기반 조건 분기
풀이 아이디어 및 코드
방법 1 : 단일 스택 + 현재 최댓값 갱신 방식
- 문제 분해
- 명령어를 파싱해
1 x,2,3으로 구분한다.1 x: 스택에x를 추가하며, 현재max보다 크면max갱신.2: 스택의 맨 위 요소를 제거하며, 만약 제거된 값이max라면 스택 전체를 순회하여 새 최대값 재탐색.3: 현재max를result리스트에 저장.
핵심 로직 흐름
for each operation: if push: stack.push(x) if x > max: max = x if pop: top = stack.pop() if top == max: max = 0 for each item in stack: if item > max: max = item if print: result.add(max)예외 처리
operations에 숫자 없이 명령만 존재하는 경우("2","3") →split결과 길이 확인- 첫 입력을 스택 크기가 아닌 실제 명령으로 처리해야 함 (문제 조건 주의)
public static List<Integer> getMax(List<String> operations) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
int[] arr = new int[2];
String[] arrString;
int max = 0;
int value;
for (int i = 0; i < operations.size(); i++) {
arrString = operations.get(i).split(" ");
arr[0] = Integer.valueOf(arrString[0]);
if (arrString.length > 1) arr[1] = Integer.valueOf(arrString[1]);
if (arr[0] == 1) { // push
if (max < arr[1]) max = arr[1];
stack.add(arr[1]);
}
else if (arr[0] == 2) { // pop
if (stack.peek() == max) {
stack.pop();
max = 0;
for (int v : stack)
if (v > max) max = v;
} else stack.pop();
}
else if (arr[0] == 3) result.add(max); // print max
}
return result;
}방법 2 : 두 개의 스택을 이용한 효율적 최대값 관리
- 핵심 아이디어
mainStack은 실제 데이터를 저장.maxStack은 각 시점의 “현재까지의 최댓값”만 저장.
- 삽입(
1) 시:
maxStack이 비어있거나 현재 값이maxStack.peek()보다 크면maxStack.push(x)- 아니면 기존 최댓값(
maxStack.peek())을 그대로 다시 push.
- 삭제(
2) 시:
- 두 스택을 동시에 pop하여 동기화 유지.
- 출력 시(
3):
maxStack.peek()이 곧 현재 최댓값.
시간 복잡도 개선
- 모든 연산이 O(1)로 해결 (최대값 탐색 반복 제거)
구현 로직
for each operation: if push: mainStack.push(x) if maxStack empty or x >= maxStack.peek(): maxStack.push(x) else: maxStack.push(maxStack.peek()) if pop: mainStack.pop() maxStack.pop() if print: result.add(maxStack.peek())
public static List<Integer> getMax(List<String> operations) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> maxStack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String op : operations) {
String[] parts = op.split(" ");
int cmd = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
if (cmd == 1) {
int val = Integer.parseInt(parts[1]);
stack.push(val);
if (maxStack.isEmpty() || val >= maxStack.peek())
maxStack.push(val);
else
maxStack.push(maxStack.peek());
}
else if (cmd == 2) {
stack.pop();
maxStack.pop();
}
else if (cmd == 3) {
result.add(maxStack.peek());
}
}
return result;
}시간·공간 복잡도
방법 1 :
- 시간 복잡도: O(N × M) (M은 스택의 최대 길이, pop 시 최대값 재탐색 때문)
- 공간 복잡도: O(N)
방법 2 :
- 시간 복잡도: O(N)
- 공간 복잡도: O(N) (보조 스택 추가 사용)
어려웠던 점
-
Stack과 List의 인스턴스화 문법을 혼동 (
List는 인터페이스이므로 직접 생성 불가)
- ArrayList로 인스턴스화한뒤 List로 변환해주어야 한다.
-
입력 첫 줄을 명령어 수가 아니라 명령 자체로 잘못 해석 (처음
n또한 operations에 추가되는 구조인줄로 오해했다.) -
명령어
3을 스택에서 최상단을 제거한뒤 출력하는 것으로 잘못 이해했다. -
“값 없는 명령어” (
"2","3") 처리의 경우split(" ")을 진행하면 명령어만 나오기 때문에size = 1이었는데 처음에는 빈칸으로 아이템이 추가되는size = 2인것으로 오해해 index 에IndexOutOfBoundsException이 발생했다. -
초기 구현 (방법1) 에서 명렁어
3발생시 매번 현재 스택 전체를 순회해 최대값을 구하느라 타임아웃 발생
배운 점 및 팁
-
List는new ArrayList<>()처럼 구현 클래스로 인스턴스화해야 함. -
maxStack 병행 관리 방식을 사용하면 모든 연산을 O(1)에 처리 가능. (그때마다 순회를 통해 최댓값을 찾는 방식은 비효율적)
-
Stack 순회 대신, 삽입 시점에서 “최댓값”을 함께 관리하는 것이 효율적.
참고 및 링크
- 문제 링크: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/maximum-element/problem
- 참고 블로그:
1. 자바 Stack 구조 & 사용법 정리
2. [Java] 리스트 (List) 정리
추가 연습 문제
-
비슷한 유형 (GPT 추천):
-
확장 문제 (GPT 추천):
- 큐에서 최대값을 O(1)에 반환하는 구조 설계 (Max Queue)
