
[2941] 크로아티아 알파벳 (LJESNJAK)
난이도: ★★☆☆☆ • solved on: 2025-07-01
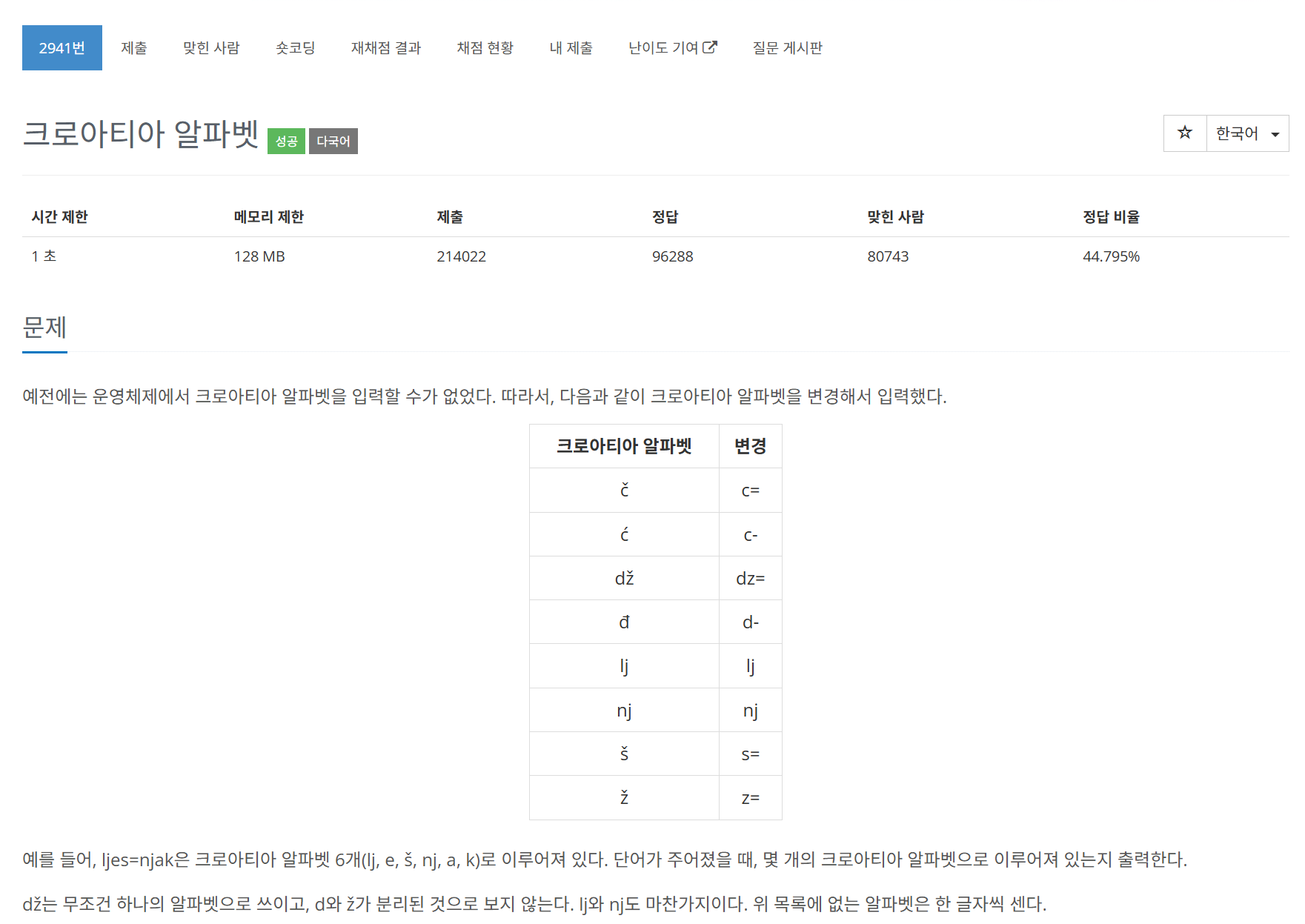

문제 요약
- 문제 유형: 문자열 처리
- 요구사항:
특정 크로아티아 알파벳 조합("c=", "c-", "dz=", "d-", "lj", "nj", "s=", "z=")을 하나의 문자로 간주하여 문자열의 총 문자의 수를 출력해야한다.
사용 개념
- 자료구조
- 없음 (단순 변수, 문자열)
- 알고리즘/기법
- 문자열 탐색 및 치환
- 핵심 키워드
- 크로아티아 알파벳
- 문자열 길이
풀이 아이디어 및 코드
- 문제 분해
- 문자열에 대한 순회 및 if 조건 처리
- 입력 문자열에서 크로아티아 알파벳 조합을 모두 먼저 치환
방법 1: char 배열 순회하며 카운트 조정
- 핵심 로직: 각 문자마다 이전 문자와 조합을 검사한 뒤, 특수 조합인 경우엔 카운트를 건너뛰거나 감소
- “dz=” 조합은 두 칸 전까지 검사하여 처리
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
char[] testString = sc.nextLine().toCharArray();
int totalWordNumber = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < testString.length; i++) {
if(i==0){
totalWordNumber += 1;
continue;
}
else{
if(testString[i]=='='){
if(i<=1){
continue;
} else if(testString[i-2]=='d'&&testString[i-1]=='z'){
totalWordNumber -= 1;
continue;
} else{
continue;
}
} else if(testString[i]=='-'){
continue;
} else if (testString[i]=='j'&&(testString[i-1]=='l'||testString[i-1]=='n')){
continue;
} else{
totalWordNumber += 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println(totalWordNumber);
}
}방법 2: while + 인덱스 점프 방식
- 핵심 로직: 길이가 긴 패턴("dz=")부터 검사하고, 매칭되면 인덱스를 해당 길이만큼 점프하여 한 글자로 카운트
- List.of(...)로 2글자 패턴을 간결하게 관리
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = br.readLine();
List<String> twoChar = List.of("c=", "c-", "d-", "lj", "nj", "s=", "z=");
int i = 0, count = 0;
while (i < s.length()) {
if (i + 2 < s.length() && s.startsWith("dz=", i)) {
count++;
i += 3;
} else if (i + 1 < s.length() && twoChar.contains(s.substring(i, i + 2))) {
count++;
i += 2;
} else {
count++;
i++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
시간·공간 복잡도
방법 1 :
- 시간 복잡도: O(N × M) (N: 문자열 길이, M: 치환 패턴 개수)
- 공간 복잡도: O(N)
방법 2 :
- 시간 복잡도: O(N)
- 공간 복잡도: O(1) (추가 배열 제외)
어려웠던 점
-
“dz=”와 “z=” 중첩 처리 순서
: "=", "-", "j"는 특수 문자를 표시하는 로직이 다르고, "j"의 경우 단일로 사용하면 알파벳이 되기 때문에 처리하는데 조금 어려움이 있었다. -
여러 패턴 치환 시 인덱스 보정 로직 관리가 생소했고, 실제로 처음에는 생각하지 못했다.
-
문자열 순회를 도는 것과 치환하여 인덱스 보정하는 것. 이 두가지 중 무엇이 시간 복잡도가 더 높은지 계산이 안됐다.
배운 점 및 팁
- startsWith와 substring을 활용하면 복잡한 조건문을 줄일 수 있음
- 긴 패턴(“dz=”)을 먼저 검사해야 중첩 오류를 방지할 수 있음
참고 및 링크
- 문제 링크: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/2941
- 참고 블로그/깃허브: 없음
