1. 문제
133. Clone Graph
Medium
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
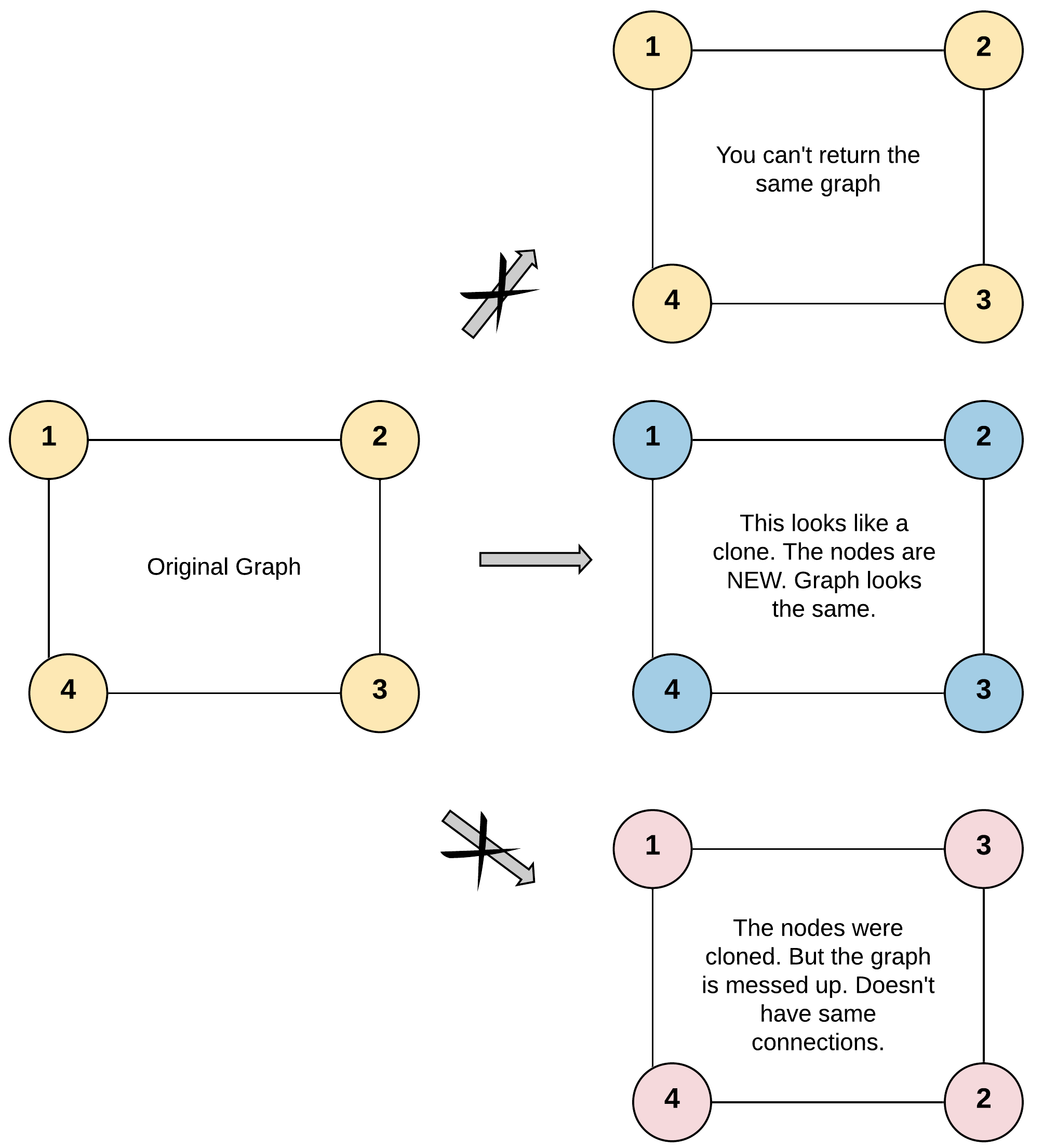
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
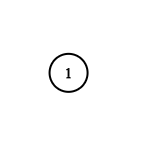
Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
2. 문제 풀이
연결된 방향이 없는 그래프에서 노드의 참조가 주어집니다.
그래프의 딥 카피(복제본)를 반환합니다.
그래프의 각 노드는 값(int)과 이웃 노드의 목록(List[Node])을 포함합니다.
Node class {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}테스트 케이스 형식:
간단하게 하기 위해 각 노드의 값은 노드의 인덱스(1-인덱스)와 동일합니다. 예를 들어 값이 1인 첫 번째 노드, 값이 2인 두 번째 노드 등이 있습니다. 테스트 케이스에서 그래프는 인접성 목록을 사용하여 표현됩니다.
인접성 목록은 유한 그래프를 표현하는 데 사용되는 정렬되지 않은 목록의 모음입니다. 각 목록은 그래프에서 노드의 이웃 집합을 설명합니다.
주어진 노드는 항상 val = 1인 첫 번째 노드입니다. 주어진 노드의 복사본을 복제된 그래프에 대한 참조로 반환해야 합니다.
Example 1:
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3. 접근 방법
그래프는 모두 이어여있으므로 순회하는 방법을 선택한다.
대표적인 그래프 순회 방법인 BFS로 구현한다.
복사하려는 node를 key로 사용하여 value 값에는 key의 노드를 복사하도록 한다.
4. 문제 풀이
class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
map.put(node, new Node(node.val));
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node currentNode = queue.poll();
Node cloneNode = map.get(currentNode);
for (Node n : currentNode.neighbores) {
if (!map.containsKey(n)) {
map.put(n, new Node(n.val));
queue.add(n);
}
cloneNode.neighbores.add(map.get(n));
}
}
return map.get(node);
}5. 개선 사항
class Solution {
public Node cloneGraph(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
// 루트 노드와 동일한 값으로 새 노드를 생성
Node copy = new Node(node.val);
// 해당 노드가 방문되면 인덱스에 해당 노드를 저장하고 쉽게 검색할 수 있다.
Node[] visited = new Node[101];
// 처음에는 모든 위치에 null을 저장한다.
Arrays.fill(visited, null);
// 루트 노드의 모든 정점을 통과하기 위해 DFS를 호출한다.
DFS(node, copy, visited);
return copy;
}
public void DFS(Node node, Node copy, Node[] visited) {
// 현재 노드를 val 인덱스에 저장하면 이 노드가 이제 방문되었음을 알 수 있다.
visited[copy.val] = copy;
// 루트 노드의 인접 노드에 대해 횡단
for (Node n : node.neighbores) {
// 해당 노드가 방문되었는지를 여부 확인
// 방문하지 않았ㅇ으면 null이 있어야 한다.
if (visited[n.val] == null) {
// 방문하지 않은 새 노드를 생성
Node newNode = new Node(n.val);
// 이 노드를 이전 복사된 노드의 인접 노드로 추가
copy.neighbores.add(newNode);
// 방문하지 않은 노드가 인접 노드를 탐색하는지 여부를 검색하도록 DFS를 호출한다.
DFS(n, newNode, visited);
} else {
// 해당 노드가 이미 방문된 경우, 방문한 배열에서 해당 노드를 검색하여 사전에 복사된 노드의 인접 노드로 추가한다.
copy.neighbores.add((visited[n.val]));
}
}
}
}