ControllerAdvice
🧩 @ExceptionHandler
@Controller, @RestController가 적용된 Bean에서 발생된 예외를 잡아서 하나의 메서드에서 처리해주는 기능입니다.
(@Service나 @Repository 등 다른 Bean에서는 사용할 수 없습니다.)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface ExceptionHandler {
Class<? extends Throwable>[] value() default {};
}value 설정을 통해서 어떤 예외를 처리할지 설정할 수 있습니다.
(주의사항은 value를 지정하지 않으면 모든 예외를 처리하기 때문에 설정을 해주어야 합니다!)
@ExceptionHandler({Exception.class, RuntimeException.class})와 같이 2개 이상도 등록 가능합니다.
하지만 이를 @Controller단에 정의하게 된다면, 다른 Controller의 예외는 처리할 수 없으므로 각각의 Controller에 정의해줘야 합니다.
그렇게 되면 같은 예외처리임에도 불구하고 각각의 Controller의 정의해줘야 하는 코드의 중복이 발생하게 됩니다.
이를 한번에 처리할 수 있게 해주는 것이 @ControllerAdvice 입니다.
🔖 @ControllerAdvice
@Controller 애노테이션이 있는 모든 곳에서의 예외를 잡을 수 있도록 해줍니다.
@ControllerAdvice 안에 있는 @ExceptionHandler는 모든 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 예외상황을 잡을 수 있습니다.
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface ControllerAdvice {
@AliasFor("basePackages")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] basePackages() default {};
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {};
}속성 설정을 통해서 원하는 컨트롤러나 패키지만 선택 할 수 있고, 선택하지 않는다면 모든 패키지에 있는 컨트롤러를 담당하게 됩니다.
👀 @RestControllerAdvice
| @ControllerAdvice + @ResponseBody → @RestControllerAdvice
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestControllerAdvice {
@AliasFor(
annotation = ControllerAdvice.class
)
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ControllerAdvice.class
)
String[] basePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ControllerAdvice.class
)
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ControllerAdvice.class
)
Class<?>[] assignableTypes() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ControllerAdvice.class
)
Class<? extends Annotation>[] annotations() default {};
}🏃 @ControllerAdvice 실행 순서
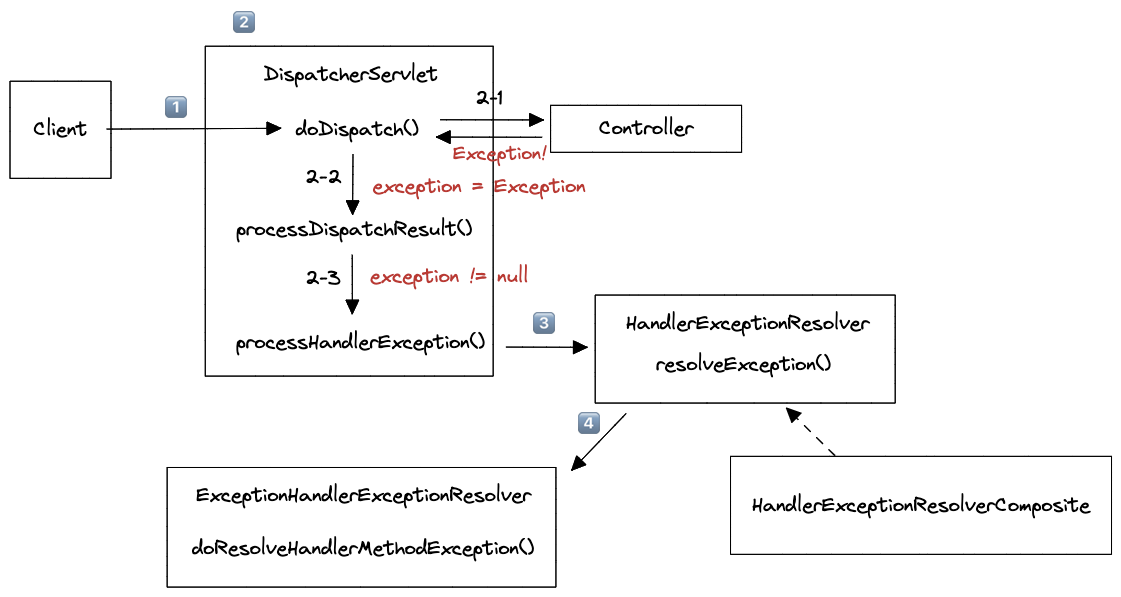
-
Controller단에서 오류가 발생하도록 Request 요청했습니다.
-
DispatcherServlet → 서블릿에서 요청을 처리합니다.
2-1.
doDispatch()에서 Controller 실행 → 오류 발생 →processDispatchResult()protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { ... HandlerAdapter ha = this.getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); ... **// ✨ 1. 실제로 여기서 컨트롤러단으로 넘어가 처리를 하게 됩니다. // → 하지만 오류가 발생 하겠죠?** mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); ... } catch (Exception var20) { **// ✨ 2. Catch 부분에서 해당 오류를 세팅합니다.** dispatchException = var20; } catch (Throwable var21) { dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", var21); } **// ✨ 3. 여기서 오류를 가지고 처리를 하게 됩니다.** this.processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, (Exception)dispatchException); ... }2-2.
processDispatchResult(): 오류가 있다면processHandlerException()구문을 실행!private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; **// ✨ exception이 1-1 메서드에서 넘어 왔기 때문에, 이 구문을 진행하게 됩니다.** if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { this.logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException)exception).getModelAndView(); } else { **// ✨ 이 구문을 진행하게 됩니다. → processHandlerException()** Object handler = mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null; mv = this.processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = mv != null; } } ... }2-3.
processHandlerException()에서 실제로 오류를 처리합니다.@Nullable protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE); ModelAndView exMv = null; if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) { Iterator var6 = this.handlerExceptionResolvers.iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { HandlerExceptionResolver resolver = (HandlerExceptionResolver)var6.next(); **// ✨ 이 구문을 진행하게 됩니다.** exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (exMv != null) { break; } } } ... }var6에는 총 2개의 객체가 있습니다.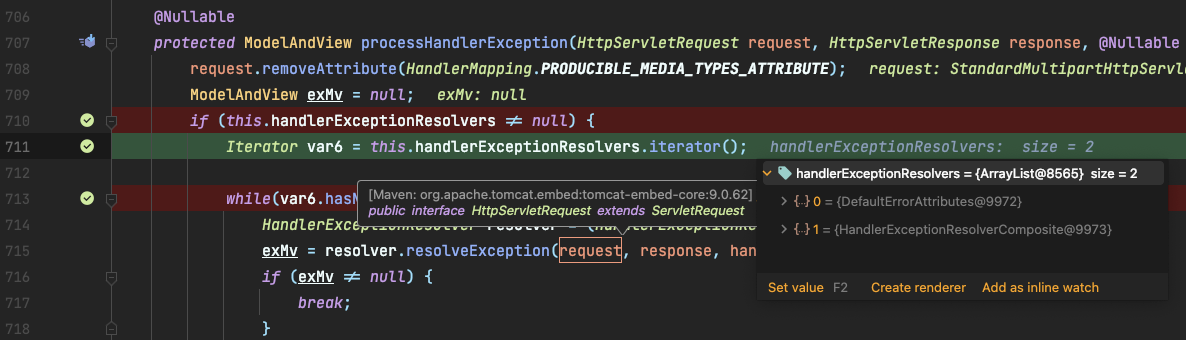
- DefaultErrorAttributes
- HandlerExceptionResolverComposite
-
HandlerExceptionResolverComposite 이 클래스에서 처리를 하게 됩니다.
var5에는 총 3개의 객체가 있습니다.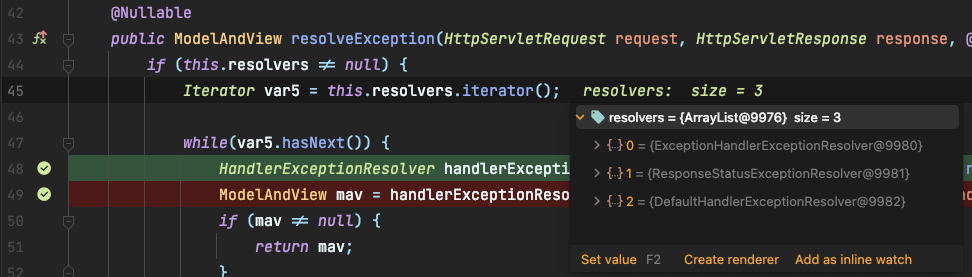
- ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
- ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
- DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
-
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver에서 실행할 핸들러를 찾아서 오류를 처리하게 됩니다.1-1. 결과적으로 여기서 1) ControllerAdvice를 찾아서 2) invoke를 통해 오류를 처리합니다.
@Nullable protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) { **// ✨ 1. getExceptionHandlerMethod() 메서드를 통해서 어디서 처리를 할건지 찾아냅니다.** // (ControllerAdvice 클래스를 생성했다면, 그 설정된 빈을 가져오게 되겠죠?) ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = this.getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception); ... **// ✨ 2. invoke를 통해서 이제 ControllerAdvice로 가서 처리를 하게 됩니다.** exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, arguments); ... }↑
✨
getExceptionHandlerMethod()→ ControllerAdivce 객체를 찾는 메서드 입니다.@Nullable protected ServletInvocableHandlerMethod getExceptionHandlerMethod(@Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) { Class<?> handlerType = null; if (handlerMethod != null) { **// ✨ 1. 해당 Controller ExceptionHandler가 있다면 이 구문에서 처리된다.** handlerType = handlerMethod.getBeanType(); ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = (ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver)this.exceptionHandlerCache.get(handlerType); if (resolver == null) { resolver = new ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(handlerType); this.exceptionHandlerCache.put(handlerType, resolver); } Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception); if (method != null) { **// ✨ <1> 에 해당한다면 여기서 Ealry Return!** return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod.getBean(), method, this.applicationContext); } if (Proxy.isProxyClass(handlerType)) { handlerType = AopUtils.getTargetClass(handlerMethod.getBean()); } } **// ✨ 2. 여기서 ControllerAdvice를 찾게 됩니다.** Iterator var9 = this.exceptionHandlerAdviceCache.entrySet().iterator(); while(var9.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<ControllerAdviceBean, ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver> entry = (Map.Entry)var9.next(); ControllerAdviceBean advice = (ControllerAdviceBean)entry.getKey(); if (advice.isApplicableToBeanType(handlerType)) { ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver resolver = (ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver)entry.getValue(); Method method = resolver.resolveMethod(exception); if (method != null) { return new ServletInvocableHandlerMethod(advice.resolveBean(), method, this.applicationContext); } } } return null; }-
해당 Controller에 ExceptionHandler 정의 된것과 매칭된다면 그것을 실행하게 됩니다!
-
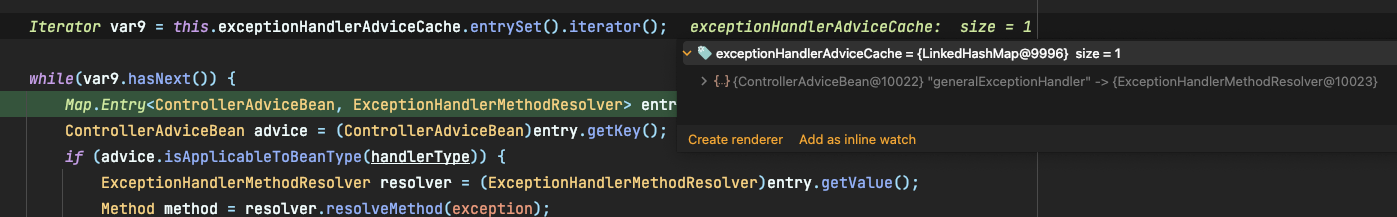
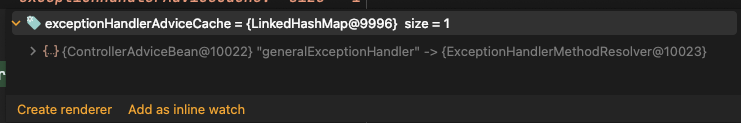
ControllerAdvice를 지정한 클래스 빈을 찾아서 실행하게 됩니다.
(저는 GeneralExceptionHandler 클래스 정의 → generalExceptionHandler가 보이시죠?)
-
🤔 질문 & 의문사항
-
RestControllerAdvice도 똑같은가? -병연님 질문-

변경을 하고 진행을 해보았습니다.
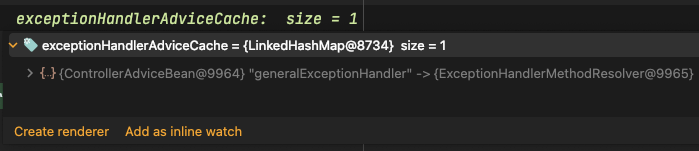
✨ 똑같은 ControllerAdviceBean으로 등록되어 사용되는걸 확인할 수 있었습니다.
-
Controller 자체에 ExceptionHandler가 있을 경우, 우선 처리가 되는가? → 어디서? 👀
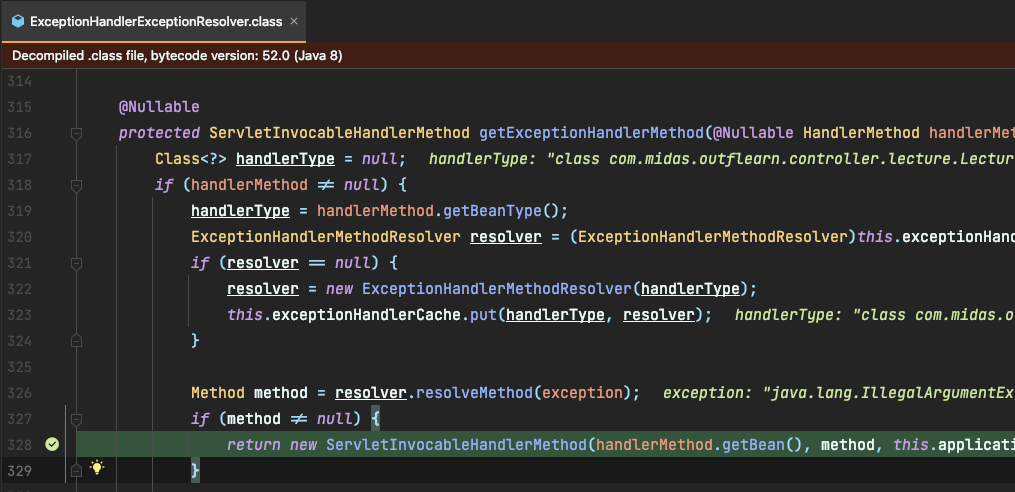
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver-getExceptionHandlerMethod()에서 Ealry return!(
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver에서 실행할 핸들러를 찾아서 오류를 처리하게 됩니다. )
-
ControllerAdvice - package를 지정한다면 우선적으로 실행 되는가?
@Slf4j @ControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.midas.outflearn.controller.lecture") public class TestExceptionHandler { ... }패키지를 지정하여 임시 ControllerAdvice 클래스를 지정해보았습니다.
그럼
GeneralExceptionHandlervsTestExceptionHandler무엇이 실행 될까요?🤔 얼레리오? 순서는 그대로 였고, 처리도
GeneralExceptionHandler여기서 처리 되었습니다.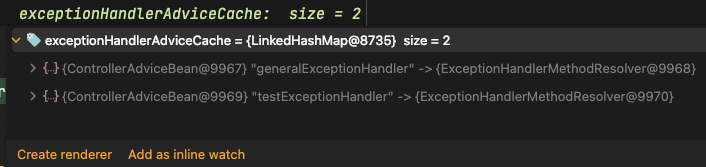
✨ basePackages 설정이 우선순위와는 상관이 없다는것을 알게되었습니다.
그러다가 블로그를 하나를 발견하게 됩니다.
@Order/@Priority를 이용해서 우선순위를 지정할 수 있다는 글이었습니다.위의 블로그 글처럼
@Order를 설정해보니...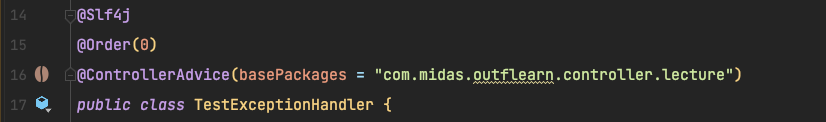
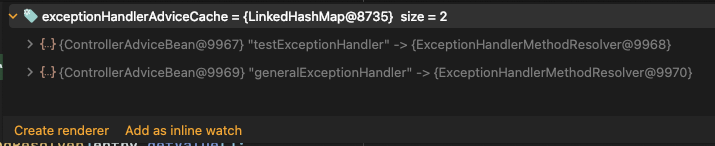
순서가 바뀌는 것을 확인할 수 있었습니다. 😳
⚡️ 참고 사이트
ExceptionHandler 와 ControllerAdvice
[Spring] ControllerAdvice는 AOP로 구현되어 있을까? ControllerAdvice의 동작 과정 소스 코드로 살펴보기
