🤔예시 데이터를 참고해 타입 생성 vs 명세를 참고해 타입 생성
- 예시 데이터를 참고해 타입 생성
- 눈 앞에 있는 데이터들만 고려하게 되므로 예기치 못한 오류가 발생 할 수 있다.
- 명세를 참고해 타입 생성
- 타입스크립트는 사용자가 실수를 줄일 수 있게 도와준다.
- DefinitelyTyped(아주 큰 깃허브 레퍼지토리)에 정의된 것을 활용하는 방법이 있다.
// Feature 타입이 정의된 적이 없다.
// focusOnFeature 함수로 Feature 타입을 작성해 볼 수 있다.
// 하지만 공식 GeoJSON 명세가 있으니 명세를 사용하자.
function focusOnFeature(f: Feature) {
const bounds = calculateBoudingBox(f);
const camera = viewportForBounds(bounds);
setCamera(camera);
const {center: {lat, lng}, zoom} = camera;
zoom;
window.location.search = `?v=@${lat},${lng}z${zoom}`;
}function calculateBoundingBox(f: Feature): BoundingBox | null {
let box: BoundingBox | null = null;
const helper = (coords: any[]) => {
// ...
};
const {geometry} = f;
if(geometry) {
helper(geometry.coordinates);
}
return box;
}🔍DefinitelyTyped는 무엇이고 어떻게 사용하는 걸까?
- DefinitelyTyped : 아주 큰 깃허브 레퍼지토리로, 모든 유명한 npm 라이브러리를 가지고 있는 저장소이다. 여기서 TypeScript로 작업할 때 필요한 대부분의 라이브러리나 패키지의 type definition을 얻을 수 있다.
- DefinitelyTyped로 geojson 설치 :
$ npm install --save-dev @types/geojson - DefinitelyTyped로 geojson의 Feature 타입 사용 :
import { Feature } from 'geojson';
👀DefinitelyTyped로 확인하는 명세 기반 타입 작성이 좋은 이유
import { Feature } from 'geojson';
function calculateBoundingBox(f: Feature): BoundingBox | null {
let box: BoundingBox | null = null;
const helper = (coords: any[]) => {
//...
};
const { geometry } = f;
if(geometry) {
// geometry가 GeometryCollection 타입이 될 수도 있는데
// GeometryCollection에는 coordinates 속성이 없기 때문에 에러 발생.
helper(geometry.coordinates); // 에러 발생.
}
return box;
}
/** DefinitelyTyped로 확인하는 Feature 타입 정의 */
// Feature 타입 정의
export interface Feature<G extends Geometry | null = Geometry, P = GeoJsonProperties> extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'Feature';
geometry: G;
id?: string | number | undefined;
properties: P;
}
// Geometry 타입 정의
export type Geometry = Point | MultiPoint | LineString | MultiLineString | Polygon | MultiPolygon | GeometryCollection;
// Geometry에서 언급된 타입 정의
export interface Point extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'Point';
coordinates: Position;
}
export interface MultiPoint extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'MultiPoint';
coordinates: Position[];
}
export interface LineString extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'LineString';
coordinates: Position[];
}
export interface MultiLineString extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'MultiLineString';
coordinates: Position[][];
}
export interface Polygon extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'Polygon';
coordinates: Position[][];
}
export interface MultiPolygon extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'MultiPolygon';
coordinates: Position[][][];
}
export interface GeometryCollection<G extends Geometry = Geometry> extends GeoJsonObject {
type: 'GeometryCollection';
geometries: G[];
// GeometryCollection에서는 coordinates 속성이 없다.
}에러를 해결해보자
// 타입을 체크하는 방법 이용
// 하지만 특정 타입 차단보다는 모든 타입을 지원하는 방법이 더 좋다.
const { geometry } = f;
if(geometry) {
if(geometry.type === 'GeometryCollection') {
throw new Error ('GeometryCollections are not supported');
}
helper(geometry.coordinates); // 정상
}모든 타입을 지원하는 방법으로 수정해보자
const geometryHelper = (g: Geometry) => {
if(geometry.type === 'GeometryCollection') {
geometry.geometries.forEach(geometryHelper);
} else {
helper(geometry.coordinates); // 정상
}
}
const { geometry } = f;
if(geometry) {
geometryHelper(geometry); // 정상
}- 직접 타입을 선언해 작성했다면
GeometryCollection같은 예외 상황이 포함되지 않았을 것. - 명세 기반으로 타입 작성을 하면 현재까지 경험한 데이터 + 사용 가능한 모든 값에 대해서 작동한다는 확신을 가질 수 있다.
👍API도 명세로부터 타입을 생성하는 것이 좋다.
- GraphQL API : 타입스크립트와 비슷한 타입 시스템을 사용하여, 가능한 모든 쿼리와 인터페이스를 명세하는 스키마로 구성.
- Apollo : GraphQL 쿼리를 타입스크립트 타입으로 변환해 주는 도구 중 하나.
- 자동으로 타입 정보를 생성해주는 기능인 듯 하다.
- 쿼리 변경 → 타입도 자동으로 변경 / 스키마 변경 → 타입도 자동으로 변경 (항상 일치)
- 타입 정보를 자동으로 생성해 주어 API를 정확히 사용할 수 있도록 도와준다.
```tsx
$ apollo client:codegen \
--endpoint https://api.github.com/graphql \
--includes license.graphql \
--target typescript
```🚨명세 정보나 공식 스키마가 없다면?
- 데이터로부터 타입을 생성해야 한다.
- 생성된 타입이 실제 데이터와 일치하지 않을 수 있다는 점 주의.
quicktype같은 도구가 있다.
quicktype은 JSON 객체를 입력하면 그 객체의 interface를 자동으로 만들어준다. ( https://velog.io/@code-bebop/quicktype-TypeScript의-매우-유용한-도우미 )
😮우리는 이미 자동 타입 생성의 이점을 누리고 있다?
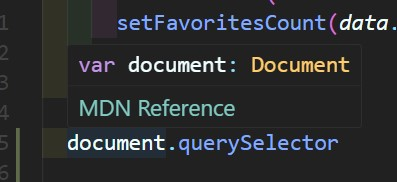
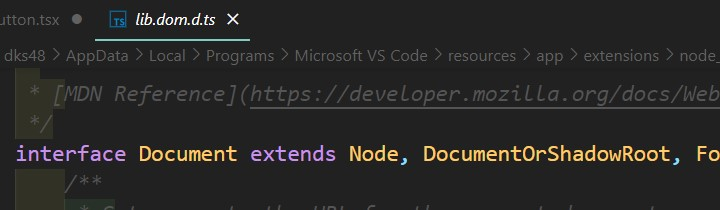
- 브라우저 DOM API에 대한 타입 선언은 공식 인터페이스로부터 생성.
- 복잡한 시스템을 정확히 모델링하고 타입스크립트가 오류나 코드상의 의도치 않은 실수를 잡을 수 있게 한다.
- DOM API 타입 선언은 IDE에 포함되어 있기 때문에 잘 사용하면 됩니다!
- DOM API) document.querySelector(), addEventListener() 등
💡결론
- 코드의 구석 구석까지 타입 안정성을 얻기 위해 API 또는 데이터 형식에 대한 타입 생성을 고려해야 한다.
- 데이터에 드러나지 않는 예외적인 경우들이 문제가 될 수 있기 때문에 데이터보다는 명세로부터 코드를 생성하는 것이 좋다.
