문제 설명
0 또는 양의 정수가 주어졌을 때, 정수를 이어 붙여 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 수를 알아내 주세요.
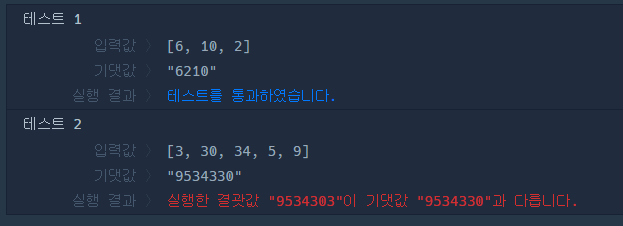
예를 들어, 주어진 정수가 [6, 10, 2]라면 [6102, 6210, 1062, 1026, 2610, 2106]를 만들 수 있고, 이중 가장 큰 수는 6210입니다.
0 또는 양의 정수가 담긴 배열 numbers가 매개변수로 주어질 때, 순서를 재배치하여 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 수를 문자열로 바꾸어 return 하도록 solution 함수를 작성해주세요.
제한 사항
numbers의 길이는 1 이상 100,000 이하입니다.
numbers의 원소는 0 이상 1,000 이하입니다.
정답이 너무 클 수 있으니 문자열로 바꾸어 return 합니다.
입출력 예
| numbers | return |
|---|---|
| [6, 10, 2] | "6210" |
| [3, 30, 34, 5, 9] | "9534330" |
풀어보자
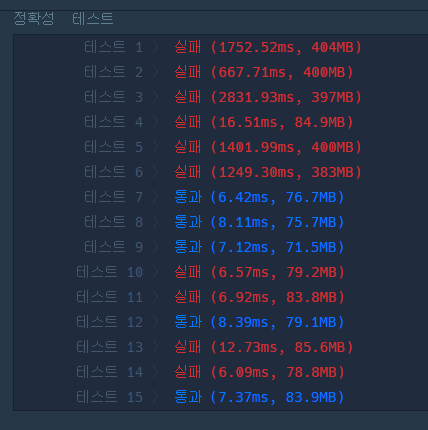
제일 먼저 드는 생각: 그냥 다 문자열로 바꾸고 sort 한 다음에 합치면 안되나?
-> 안 될 거라고 생각하긴 했지만 안됨
import java.util.Arrays;
class Solution {
public String solution(int[] numbers) {
String[] temp = new String[numbers.length];
String answer = "";
for (int i=0; i<numbers.length; i++){
temp[i] = "" + numbers[i];
}
Arrays.sort(temp);
for (int i=0; i<temp.length; i++){
answer += temp[temp.length-i-1];
}
return answer;
}
} |  |
|---|
- 뭐가 문제인가?
- 공개된 TC에서 뭐가 이상한지를 보면 3, 30, 34를 정렬할 때 34, 30, 3 순으로 정렬됨 (문자열이니까)
- 그치만 실제로는 34303보다 34330이 더 크기 때문에 34, 3, 30 순으로 정렬되어야 한다.
- 그러면 단순히 Arrays.sort() 하지 말고 맨 앞자리가 같은 elem끼리는 정렬을 다시 하고... 하면 어떨까.
- 만약 32, 3, 30이었다면 3, 32, 30이 되었어야 한다.
- 이거 또 뭔가 쓸데없는 부분에 꽂혀서 이상한 고민하고 있는 것 같긴 한데 계속해보자...
- Arrays.sort()를 쓰지 말고, 정렬을 직접 구현해 보자
- 일단 맨 앞자리가 크면 맨 앞으로 와야 한다
- 맨 앞자리(a)가 같을 때, 둘째 자리(b1, b2, ...)가 큰 순으로 정렬되어야 한다.
- a보다 b가 큰 수들은 한 자리 수 a보다 앞에, b가 a보다 작은 수들은 a보다 뒤로 가야 한다.
- 자릿수가 커지면 어떻게 해야 할지 잘 모르겠다...
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(int[] numbers) {
String[] temp = new String[numbers.length];
String answer = "";
String tmp;
// 배열을 int -> string으로 변경
for (int i=0; i<numbers.length; i++){
temp[i] = "" + numbers[i];
}
Arrays.sort(temp);
for (int i=0; i<temp.length-1; i++){
if (temp[i].charAt(0) == temp[i+1].charAt(0)){
if (temp[i].length() == temp[i+1].length() && Integer.valueOf(temp[i]).intValue() > Integer.valueOf(temp[i+1]).intValue()){
tmp = temp[i];
temp[i] = temp[i+1];
temp[i+1] = tmp;
}
else if (temp[i].length() )
}
}
return answer;
}
}뭔가 해보려고 했던 흔적...
(1) 일단 문자열 순으로 정렬하고,
(2) 맨 앞 글자가 같을 때
(3) 문자열의 길이가 같고 + 뒤에 있는 게 앞에 있는 것보다 작으면 자리 바꾸기 (뒤에서부터 합치려고 오름차순 정렬하는 중)
(4) 길이가 다르면...?
다른 사람의 코드를 보자...
- TC에 0이 포함된 경우도 있나 보다...
- StringBuffer라는 친구를 많이 쓰는군
- Arrays.sort(temp, (a, b) -> (b + a).compareTo(a + b));
- 정렬에 이런 것을 쓸 수 있다. (비교기, Comparator)
- A.compareTo(B)는 A==B이면 return 0
- 이외에는 return A-B인 듯
- b+a와 a+b를 비교해서, compareTo가 적절한 값을 return한다.
- sort의 두 번째 파라미터는 comparator를 지정한다.


- 람다식에서 도대체 무슨 일이 일어나는지 모르겠어서 gpt한테 좀 물어봄
- temp 안의 모든 (a, b)에 대해서 compare 하고, (a, b)가 (b, a) 보다 큰지 작은지 비교해서 a, b의 위치를 결정한다.
- ㄷ ㄷ
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(int[] numbers) {
String[] temp = new String[numbers.length];
String answer = "";
String tmp;
// 배열을 int -> string으로 변경
for (int i=0; i<numbers.length; i++){
temp[i] = "" + numbers[i];
}
Arrays.sort(temp, (a, b) -> (b + a).compareTo(a + b));
if (temp[0].equals("0")) return "0";
for (int i=0; i<temp.length; i++){
answer += temp[i];
}
return answer;
}
}통과하긴 함
람다식은 멋진 거구나
