
스프링 데이터 JPA의 공통 Interface의 구현체
@Repository
- JPA 예외를
스프링이 추상화한 예외로 변환 - 나중에 JDBC에서 JPA로 변경해도 service, controller에서의 exception 처리는 같음.
@Transactional
- jpa의
모든 변경은 트랜잭션 안에서동작 - 서비스 계층에서 트래잭션 시작하지 않아도 repository에서 트랜잭션 시작
- 서비스 계층에서 트랜잭션 시작했다면, repository는 해당 트랜잭션 전파 받아서 사용
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
- flush 생략
- 변경 감지 X, DB에 쿼리 날리지 않는다는 것
-> 아주 약간의 성능 최적화를 얻을 수 있음
- 변경 감지 X, DB에 쿼리 날리지 않는다는 것
- 원래는 transaction 끝날 때, 영속성 컨텍스트의 내용을 DB에 flush해서 쿼리 날리고, commit을 함.
save()
SimpleJpaRepository의 save() 코드
@Transactional
@Override
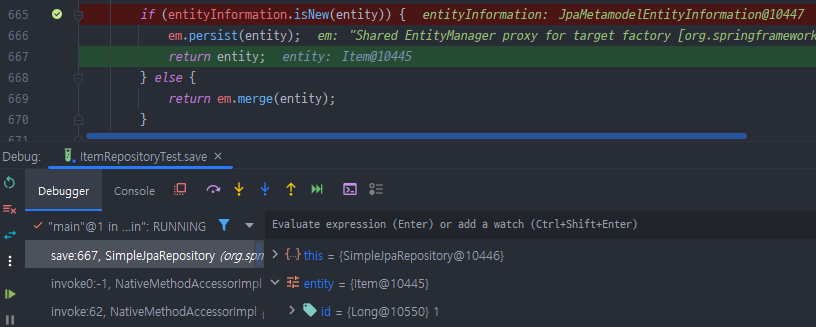
public <S extends T> S save(S entity) {
Assert.notNull(entity, "Entity must not be null.");
if (entityInformation.isNew(entity)) {
em.persist(entity);
return entity;
} else {
return em.merge(entity);
}
}- 새로운 Entity :
persist - DB에 한번 들어갔다가 나온 애 :
merge
merge 동작 방식
DB에서 엔티티를 조회해온 뒤 save의 파라미터로 넘어온 엔티티로 조회해온 것을 덮어버린다.
-> 단점 : DB에 select 쿼리 한 번 날려야한다.
데이터 변경은 변경 감지로!!
가급적이면 merge 사용 자제!!
데이터 변경을 merge로 하면 안된다!!
merge 사용은 언제?
영속 상태에 있던 엔티티가 어떠한 이유로 영속상태를 벗어난 다음, 다시 영속상태가 되어야할 때 사용
새로운 Entity 구별 방법
위의 save()함수에서 새로운 Entity면 persist, 아니면 merge를 호출한다고 하였다.
새로운 Entity인지 구별을 어떻게 하는지 알아보자.
기본 전략
식별자(pk)가 객체이면 null로 판단
식별자(pk)가 자바 기본 타입이면 '0'으로 판단
확인
Item Entity
Long 타입 id만 가지고 있는 Item 엔티티 생성
@Entity
@Getter
public class Item {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
}ItemRepository
ItemRepository는 JpaRepository extends
public interface ItemRepository extends JpaRepository<Item, Long> {
}Test
Item을 하나 생성해서 save하는 Test 작성
@SpringBootTest
class ItemRepositoryTest {
@Autowired ItemRepository itemRepository;
@Test
public void save() throws Exception {
Item item = new Item();
itemRepository.save(item); // 이때 item의 id = null
}
}id를 @GenerateValue로 설정
@GenerateValue는 JPA에 persist하면 그 때 값이 채워진다.
따라서, save를 호출하고 new Entity인지 확인할 때 까지는 item의 id = null 이다.
-> save() 함수를 보면, persist보다 isNew 검사가 먼저 진행됨!
참고
Long : Wrapper Class
long : 자바 순수 타입(primitive type)
null 확인
isNew() 라인 break point 찍고, 확인해보니 id = null임을 확인할 수 있었다.

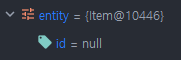
persist 호출 후 id 값 생성 확인
persist(entity)를 수행하고 다음 줄로 넘어가니, id가 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
참고!
@Test에 @Transactional 없어도 SimpleJpaRepository에 @Transactional 기본적으로 붙어있어서 save() 잘 작동한다!
문제 상황
@GenerateValue를 사용하지 않고 직접 pk를 설정한다면,
isNew() 검사할 때 pk != null 이라서 persist가 호출되지 않는다.
-> 대신 merge를 호출한다.
persist 대신 merge를 호출하는지 확인해보자.
Item 엔티티
id를 @GenerateValue가 아니고, String 타입으로 변경
@Entity
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class Item {
@Id
private String id;
public Item(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
}Test
@SpringBootTest
class ItemRepositoryTest {
@Autowired ItemRepository itemRepository;
@Test
public void save() throws Exception {
Item item = new Item("A");
itemRepository.save(item);
}
}결과
merge는 DB에 해당 객체가 있다고 생각하고 동작한다.
1) pk = 'A' 인 Item 엔티티를 DB에서 select하는 쿼리 날림.
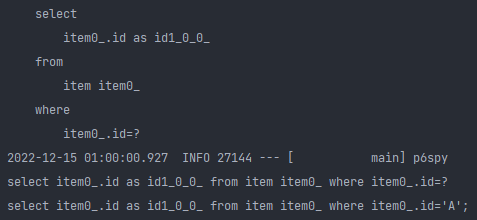
2) DB에 없으면 새거라고 판단하고 insert 쿼리 날림.
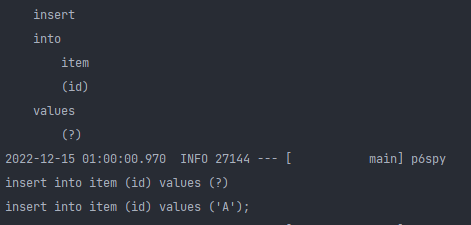
pk 값을 직접 넣고 싶을 때는 어떻게 하나요?
위와 같이 merge는 우선적으로 DB에서 select해서 값을 확인하고, DB에 값이 없으면 새로운 엔티티로 인지하므로 비효율적이다.
따라서, Persistable 인터페이스를 직접 구현해서 판단 로직 변경하면 된다.
Item Entity
단, String id 값을 가지고는 새로운 객체 판단하기가 쉽지 않다.
따라서,
생성일을 가지고 판단한다.
@CreateDate를 설정하면, persist 되기 전에 생성일값이 채워진다.
따라서, isNew() 검사를 할 때, 새로운 객체라면 생성일 = null 일 것이다.
@Entity
@Getter
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
@NoArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class Item implements Persistable<String> {
@Id
private String id;
@CreatedDate // persist 되기 전에 호출됨
private LocalDateTime createdDate;
public Item(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public boolean isNew() {// 새로운 객체 판단 로직 직접 작성
// String id 값으로 새로운 객체인지 판단은 어려움
// -> 생성일을 가지고 판단
return createdDate == null;
}
}결과
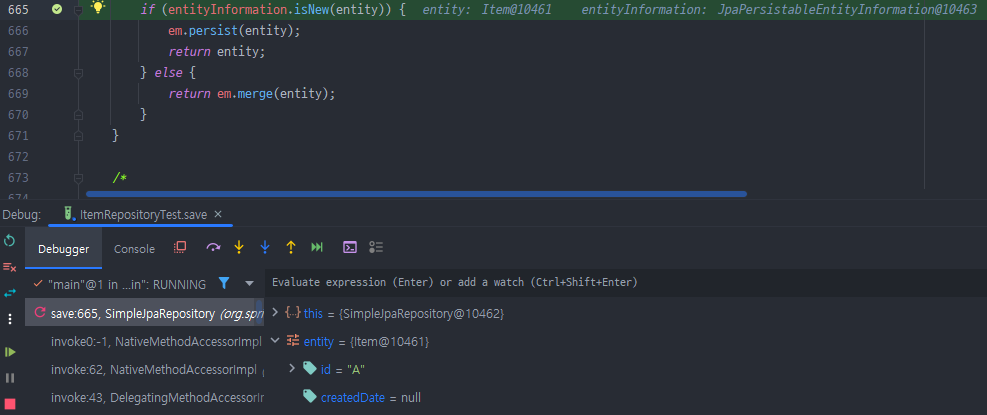
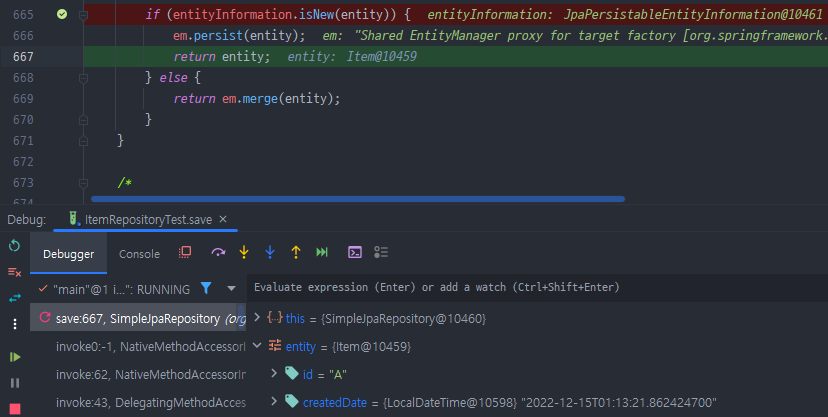
결론
저장 : persist
변경 : 변경 감지
-> merge는 사용 자제
