💡 디자인 패턴을 적용하지 않고 개발을 하게 된다면, 액티비티가 무거워지거나 종속성이 너무 강해져 테스트가 힘들고 유지보수가 어려워짐
1️⃣ MVC 디자인 패턴
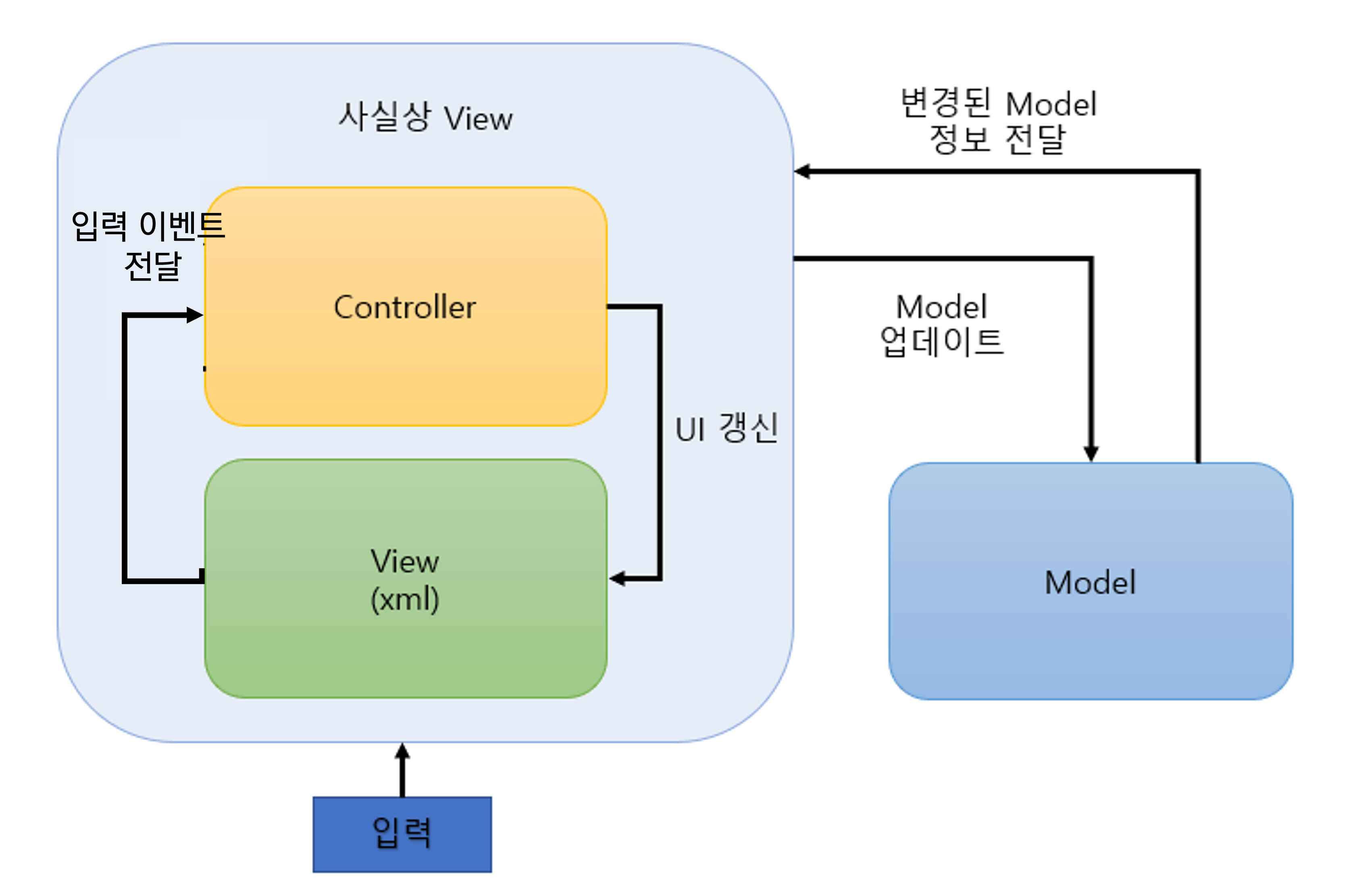
애플리케이션 구조를 모델, 뷰, 컨트롤러 세 가지 주요 측면으로 관심사를 분리함
- 웹에서 적용된 MVC는 View와 Control이 완전히 분리된 상태지만, 안드로이드에서는 View와 Control이 함께 공존함
- 가장 오래된 패턴이며 현재 안드로이드에서 잘 쓰이지 않음
Model
- 앱에서 사용하는 데이터(사용자의 이름, 상품의 가격 등)와 데이터를 처리하기 위한 비즈니스 로직을 포함함
- 사용자에게 보이지 않아 어떻게 보일지 신경 쓰지 않아도 됨
View
- 사용자가 보는 화면 (레이아웃 파일, activity_main.xml 등의 형태)
- 사용자의 입력에 대해 어떤 동작을 할지는 모름 -> 어떠한 데이터나 로직이 들어가 있으면 안됨
- Model이 처리한 데이터를 Controller를 통해 받아서 사용자에게 보여줌
- Activity, Fragment는 뷰와 컨트롤러의 역할을 동시에 함
* xml 레이아웃이 View 역할을 하고, Activity에 작성된 함수가 Controller의 역할을 하도록 분리했지만, 결국 xml의 View를 보여주는 방식은 Activity에서 정의해야 하기 때문
Controller
- Model과 View에 의존함 -> View가 사용자 입력을 받으면 Controller에게 알리고, Controller는 적절한 조치를 취하기 위한 동작을 함 (Model과 상호작용하여 UI 상태를 갱신하는 등)
👍 장점
- 구조가 단순하고 직관적임 -> 규모가 작고 간단한 앱에는 좋음
- 규모가 작은 애플리케이션에 적용 시 개발 기간이 짧아짐
- 거의 모든 코드가 액티비티나 프래그먼트 같은 컨트롤러에 작성되는 경향이 있어 코드를 파악하기 쉬움
👎 단점
- 액티비티 또는 프래그먼트가 뷰와 컨트롤러 역할을 겸하는 구조라 코드량이 점진적으로 증가할 수 밖에 없고, 그로 인해 하나의 액티비티 또는 프래그먼트 클래스에서 수천 줄이 넘는 코드가 작성되기도 함 → 유지보수 비용이 증가함
- 뷰와 모델의 결합도가 높아 유닛 테스트가 거의 불가능함
* 대부분의 코드가 뷰에서 모델을 직접 호출하여 사용하게 되기 때문 -> 테스트 코드를 작성하는 경우 UI 위주의 테스트코드를 작성해야 하는데, UI는 개발 중 변화가 자주 있는 곳이기 때문에 일이 매우 복잡해짐
2️⃣ MVP 디자인 패턴

애플리케이션 구조를 모델, 뷰, 프리젠터 세 가지 주요 측면으로 관심사를 분리함
- 뷰와 모델이 프리젠터를 통해서만 동작할 수 있도록 하여, 뷰와 모델의 의존성을 제거함
- 뷰는 모델을 직접 호출할 수 없고, 모델은 뷰에게 바로 데이터를 전달해줄 수 없음
Presenter
사용자가 뷰를 통해 어떤 이벤트를 일으키면 프리젠터가 모델에 접근해서 뷰 대신 데이터를 가져다줌 -> 뷰는 이 데이터를 통해 UI를 업데이트함
- 한 뷰에서 사용한 프리젠터를 다른 뷰에서 사용할 수 있게 만들기는 어렵거나 애매하기 때문에 보통 하나의 액티비티(프래그먼트)에서 프리젠터를 인스턴스화해서 사용함
- 뷰와 프리젠터는 1대1 대응 관계를 가지게 됨
❓ 예시
- Interface
interface ViewActionContract {
fun updateUI(message: String)
fun getUserInformation()
}
- Presenter
// 뷰마다 프리젠터를 따로 만들어줘야 함
class ViewActionPresenter(
private val context: Context
): ViewActionContract {
override fun updateUI(message: String) {
Toast.makeText(context, "updateUI() 호출. message : $message", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
override fun getUserInformation() {
Toast.makeText(context, "getUserInformation() 호출", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
- View
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".mvp.ViewActionActivity">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.AppCompatButton
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="버튼"
android:layout_marginBottom="40dp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>class ViewActionActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var presenter: ViewActionPresenter
private val binding: ActivityViewActionBinding by lazy {
ActivityViewActionBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(binding.root)
init()
}
private fun init() {
presenter = ViewActionPresenter(this)
presenter.getUserInformation()
binding.run {
button.setOnClickListener { // 1) 뷰 내부 버튼 클릭하면
presenter.updateUI("호출") // 2) 프리젠터 내부 함수 호출
}
}
}
}👍 장점
- View와 Model 간 결합도가 약해져 유닛 테스트가 MVC 패턴보다 상대적으로 수월해지고, 확장성이 개선됨
- UI, Data 파트가 나눠져 역할이 명확해지고, 코드가 깔끔해짐
👎 단점
- View와 Presenter가 1대1 관계이기 때문에 View가 많아질수록 Presenter도 많아지게 됨
- Presenter는 View와 Model을 연결시켜 주는 역할을 하기 때문에, 애플리케이션 기능이 추가될 때마다 Presenter 내 코드가 많아짐
3️⃣ MVVM 디자인 패턴
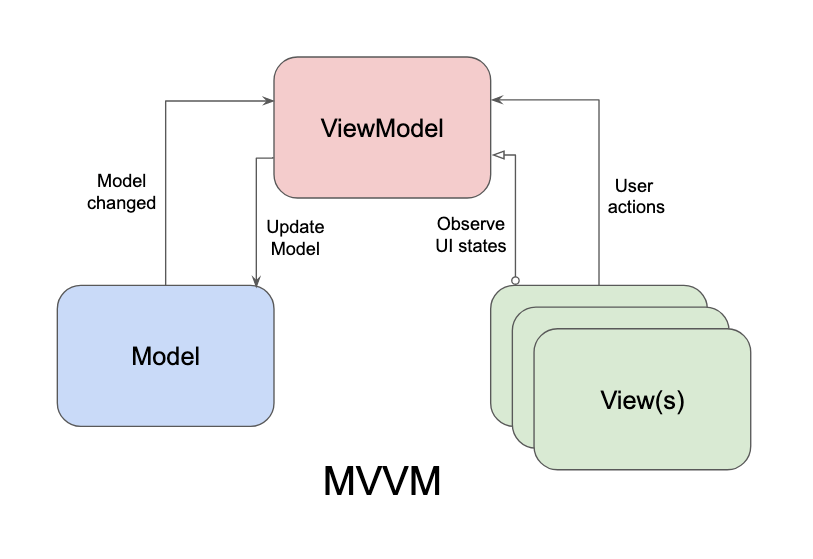
애플리케이션 구조를 모델(Repository, DB), 뷰, 뷰 모델 세 가지 주요 측면으로 관심사를 분리함
- Data Binding, LiveData, RxJava와 같은 Observable 타입을 이용하여 Presenter와 View 사이의 결합도를 끊는데 집중함
View Model
- View와 Model 사이의 매개체 역할을 함
- View와 View Model은 MVP와 다르게 1:n 관계를 가질 수 있음
* Data Binding 라이브러리를 사용하여 View Model이 View에 대한 의존성을 갖지 않고 느슨하게 연결되도록 할 수 있음 -> 특정 View에 의존적이지 않고 다른 View와도 연결될 수 있음
- ⁉️ Jetpack의 ViewModel도 있는데 둘의 차이는 나중에 공부하겠음
👍 장점
-
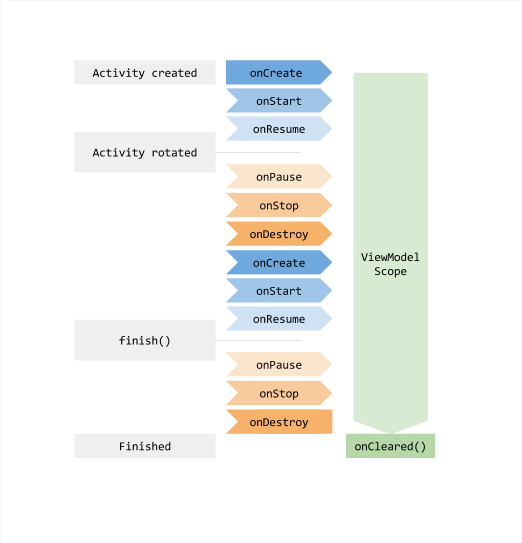
View Model은 생명주기로부터 안전하여 메모리 누수를 방지할 수 있음
* 액티비티가 화면의 회전으로 인해 소멸되었다가 다시 생성되어도 뷰 모델은 소멸되지 않고 그대로 유지됨
-
View와 View Model 사이의 결합도를 느슨하게 하여 유닛테스트가 수월함
-
View는 View Model을 알지만 View Model은 View를 알지 못하고, View Model은 Model을 알지만 Model은 View Model을 알지 못함 -> 한쪽 방향으로만 의존 관계가 있어서 각 모듈별로 분리하여 개발할 수 있음
👎 단점
- 간단한 사용자 인터페이스를 만들 때는 과함
- 비교적 구현 구조가 복잡한 편이고 설계가 쉽지 않음 -> 설계를 잘 못하는 경우 의미가 없어지며, Data Binding, LiveData 등 다른 라이브러리를 필수적으로 알아야 사용할 수 있음
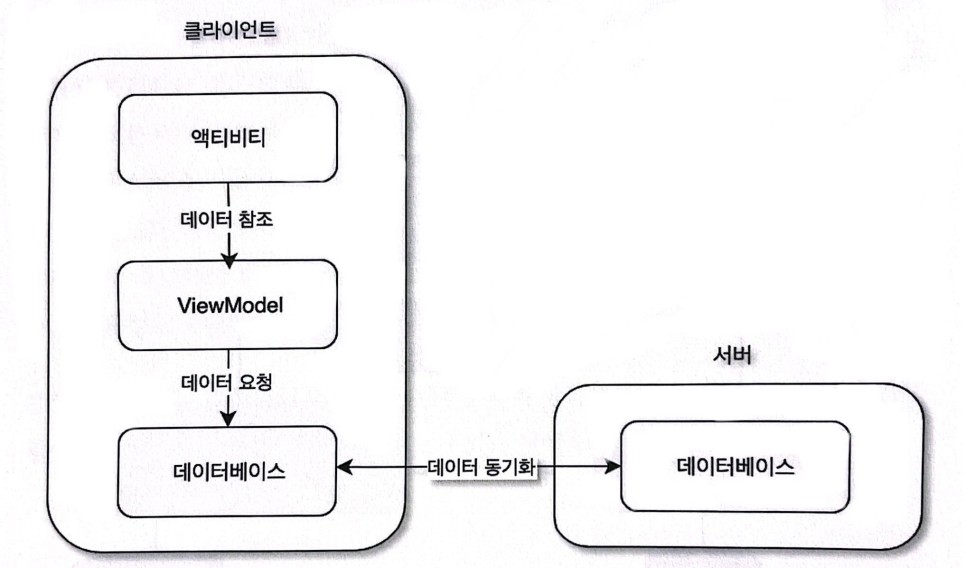
4️⃣ 구글에서 권장하는 애플리케이션 설계
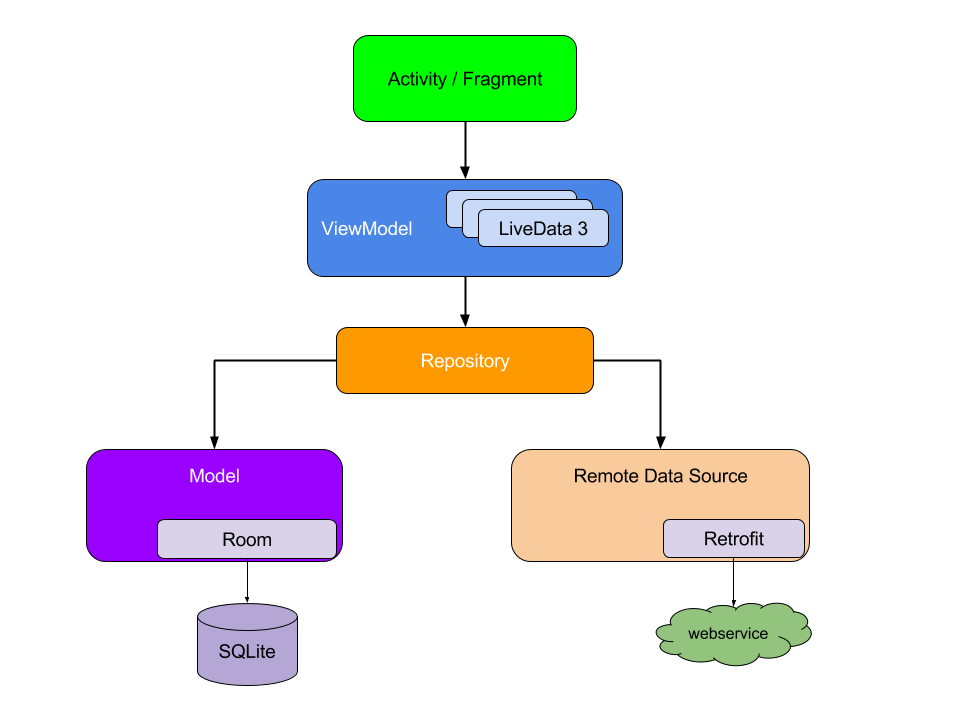
- 액티비티 또는 프래그먼트는 ViewModel만을 참조함
- ViewModel은 Repository라는 저장소를 참조하고 이 저장소로부터 UI 컴포넌트가 화면을 구성하는 데 필요한 데이터를 불러옴
- 데이터를 불러와 LiveData라는 데이터의 변화를 감지할 수 있는 형태로 관리함
- 저장소는 네트워크 연결이 필요 없는 내부 모델과, 서버에서 데이터를 불러오는 네트워크가 필요한 원격 모델로 분리함
- 내부 모델: 로컬 데이터베이스, 즉 SQLite나 SQLite 기반의 Room 또는 범용적으로 많이 사용되는 Realm 등
- 원격 모델: HTTP 통신, 즉 서버와의 통신에 사용되는 OkHttp 또는 Retrofit과 같은 라이브러리
- 내부 모델 또는 원격 모델을 통해 얻은 데이터는 ViewModel에 관리하며 데이터의 변경이 감지되는 대로 UI 컴포넌트의 바인딩된 뷰에 나타냄
- 사용자의 경험을 증대시키도록 일반적으로 서버에서 얻은 데이터는 내부 데이터베이스에 저장하여 불러옴
- ViewModel은 내부 데이터베이스만 항상 참조하고, 클라이언트의 데이터베이스와 서버의 데이터베이스가 요청을 통해 비동기적으로 동기화함
- 이를 통해, 전파 수신 약전계에서도 애플리케이션은 원활히 동작할 수 있고, 네트워크 상황이 좋아지는 대로 다시 최신의 데이터로 UI 컴포넌트를 갱신할 수 있음
참고자료
도서 '아키텍처를 알아야 앱 개발이 보인다 : Dagger2, Jetpack, RxJava를 통한 안드로이드 클린 코드 설계'
https://bj-turtle.tistory.com/106
https://salix97.tistory.com/205
https://onlyfor-me-blog.tistory.com/554
https://velog.io/@changhee09/%EC%95%88%EB%93%9C%EB%A1%9C%EC%9D%B4%EB%93%9C-ViewModel
