스택을 간단한 연결리스트의 개념으로 구현해본 코드 입니다
interface Stack<T> {
readonly size: number;
push(num: T): void;
pop(): T;
}
type StackNode<T> = {
readonly value: T;
readonly next?: StackNode<T>;
};
class StackImpl<T> implements Stack<T> {
private _size: number = 0;
private head?: StackNode<T>;
//스택의 전체 크기
constructor(private capacity: number) {}
//외부에서 접근하는 용도로 getter 생성
get size() {
return this._size;
}
push(value: T) {
if (this.size === this.capacity) {
throw new Error('Stack is full');
}
// node : StackNode<T> 을 써도 되지만 추론 사용
const node = {
value,
next: this.head,
};
// head는 새로 들어온 것을 가리키고 있어야 함
this.head = node;
this._size += 1;
}
pop(): T {
if (this.head == null) {
throw new Error('Stack is empty');
}
// 제거하고자 하는 노드 (현재 head가 가리키고 있는)
const node = this.head;
this.head = node.next;
this._size -= 1;
return node.value;
}
}
// 숫자를 담는 스택
// const stack2: Stack<number> = new StackImpl<number>(10);
const stack2 = new StackImpl(10);
stack2.push(1);
stack2.push(2);
stack2.push(3);
// stack2.push('4'); // 문자열이므로 error
while (stack2.size !== 0) {
console.log(stack2.pop());
}여기서 사용된 클래스를 사용할 때
const stack2 = new StackImpl(10);이렇게 사용합니다
(선언한 클래스에다가 , , either변수에다가 각각 타입을 지정해 줘야 하지만 일부러 생략합니다)
이렇게 되면 unknown 형태로 타입이 지정되게 됩니다

unknown은 TS에서 매우 지양되는 타입입니다
그렇지만, 객체를 선언할때 타입을 선언해주지 않으면 무조건 unknown이 된다라고 이해하면 안 됩니다
다른 예제입니다
// 인터페이스에 제네릭 선언
interface Either<L, R> {
left: () => L;
right: () => R;
}
// SimpleEither클래스에 제네릭 , 인터페이스 구현에 제네릭
class SimpleEither<L, R> implements Either<L, R> {
// 생성자의 타입도 제네릭
constructor(private leftValue: L, private rightValue: R) {}
// number타입을 리턴하는 것으로 작성하게 되면
// 사용자가 작성하는 것에 따라 leftValue의 타입이 바뀌는 것인데
// number만 리턴하고 있는 것이므로 에러가 발생
left = (): L => {
//리턴 타입 제네릭
return this.leftValue;
};
right = (): R => {
//리턴 타입 제네릭
return this.rightValue;
};
}
// 객체의 타입을 인터페이스로 해주면 인터페이스의 메소드만 사용이 가능
const either= new SimpleEither(4, 5);
console.log(either.left());
console.log(either.right());
const either2 = new SimpleEither('a', 3);
console.log(either2.left());
console.log(either2.right());
클래스를 사용할 때 이렇게 사용하고 있으며 마찬가지로 모든 타입을 생략했습니다
const either= new SimpleEither(4, 5);
그렇지만 여기선 각각 타입이 알아서 명시되어 집니다
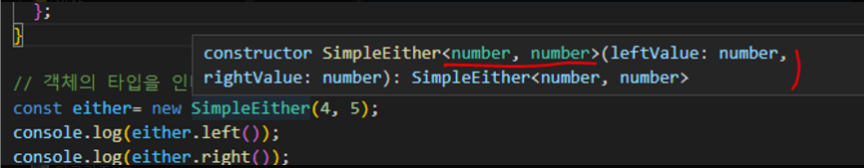
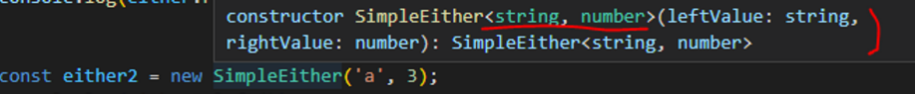
이렇게 되는 이유는 바로 생성자 입니다
이 코드의 생성자를 보면
constructor(private leftValue: L, private rightValue: R) {}이렇게 생성자의 타입이 제네릭으로 되어 있습니다
그러므로 처음에 new SimpleEither(4, 5) , new SimpleEither('a', 3) 로
생성자에 값을 넘겨주게 되면
이 클래스에서 사용되는 제네릭 L , R 에 자동으로 해당 값들이 들어가서 제네릭 타입이 지정되는 것입니다
만약 생성자에서 제네릭 R을 사용하지 않는다면
constructor(private leftValue: L, private rightValue: number) {}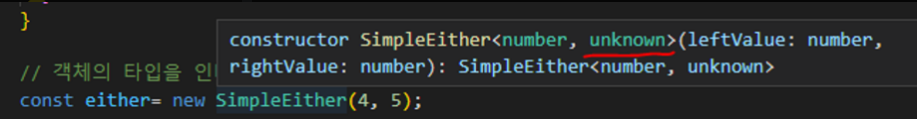
이렇게 unknown이 발생하는 것을 볼 수 있습니다
