1. 메시지 큐(Messague Queue)란?
메시지 큐는 메시지 지향 미들웨어(Message Oriented Middleware, MOM)의 한 형태로, 애플리케이션 간 비동기적으로 데이터를 주고받는 시스템입니다.
우체통처럼 메시지를 보관하고 전달하는 중간 저장소 역할을 수행합니다.
생산자(Producer)가 메시지를 발행하면 중간에 큐에 저장되고, 소비자(Consumer)가 필요할 때 꺼내 처리합니다.
1-1) 비동기
메시지 큐는 본질적으로 비동기입니다.
장점
- 빠른 응답: Producer는 메시지 전송 후 즉시 다른 작업을 수행
- 시스템 안정성: Consumer 장애가 Producer에 영향을 끼치지 않음
- 확장성: Consumer 수를 자유롭게 조절 가능
- 부하 분산: 메시지를 여러 Consumer가 나눠서 처리
고려사항
- 즉시 응답 불가: 처리 결과를 바로 알 수 없음
- 복잡성 증가: 에러 처리, 모니터링이 복잡
- 데이터 일관성: Eventually Consistent 모델
- 순서 보장: 경우에 따라 메시지 순서가 중요할 수 있음
1-2) Producer와 Consumer의 차이
Producer
- 역할: 메시지를 생성하고 큐에 전송
- 특징: 메시지를 보낸 후 응답을 기다리지 않음
- 장점: 빠른 처리, 시스템 부하 분산
Consumer
- 역할: 큐에서 메시지를 수신하고 처리
- 특징: 자신의 처리 속도에 맞춰 메시지 소비
- 장점: 안정적 처리, 부하 조절 기능
2. RabbitMQ란?
RabbitMQ는 AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) 기반의 오픈소스 메시지 브로커입니다. Erlang으로 개발되었으며, 엔터프라이즈급 메시징 솔루션으로 널리 사용됩니다.
안정성, 유연성, 사용 편의성이 높다고 알려져 있습니다.
2-1) RabbitMQ의 장점과 단점
장점
- 신뢰성: 메시지를 디스크에 저장/복제하고 ACK 기반 삭제로 메시지 손실 방지
- 안정성: 메시지 지속성, 클러스터링 지원
- 유연한 라우팅: Exchange를 통한 라우팅 규칙
- 관리 편의성: 웹 기반 관리 인터페이스 제공
- 다양한 프로토콜: AMQP, STOMP, MQTT 지원
- 플러그인 시스템: 확장 가능한 아키텍처
- 강력한 커뮤니티: 풍부한 문서 지원 처리량 한계: 초당 수만 메시지 처리(Kafka 대비 낮음)
단점
- 메모리 사용량: Erlang VM으로 인한 높은 메모리 사용
- 복잡성: Exchange, Binding 등 개념 학습 필요
- 단일 장애점: 클러스터 설정 없이는 SPOF 위험
2-2) RabbitMQ의 핵심 특징
RabbitMQ 아키텍처 구성요소
[Producer]
|
v
+-----------+
| Exchange |
+-----------+
/ | \
v v v
[Q1] [Q2] [Q3]
| | |
v v v
[Con1] [Con2] [Con3]- Producer는 Exchange로 메시지를 보냄.
- Exchange는 Binding 조건에 따라 메시지를 Q1, Q2, Q3 중 하나(또는 여러 개)에 보냄.
- 각 Queue는 연결된 Consumer에게 메시지를 전달.
1) Producer(메시지 생성자)
- 메시지를 발행하는 주체.
- Exchange에 메시지를 전달.
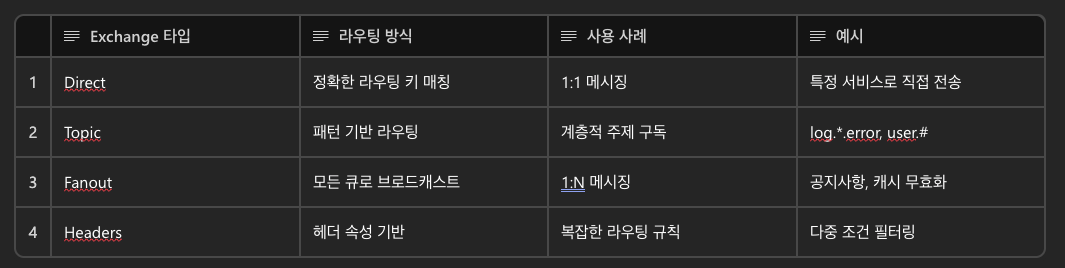
2) Exchange(메시지 라우터/교환기)
- Producer로부터 받은 메시지를 어떤 Queue로 보낼지 결정.
- Exchange 타입에 따라서 라우팅 전략이 달라짐.
3) Binding(연결 설정)
- Exchange와 Queue를 연결하는 규칙 또는 링크.
- "어떤 조건일 때 이 Queue로 보내라" 설정.
예) Direct Exchange에서 "error"라는 Routing key에 대해서만 errorLogsQueue에 전달하라.
4) Queue(메시지 큐)
- Exchange에서 라우팅된 메시지가 실제로 저장되는 공간.
- 여러 Consumer가 연결될 수 있으며 메시지는 FIFO 순서로 하나씩 처리됨.
- 큐는 메시지를 임시로 저장하며, Consumer가 ACK를 보낼 때까지 유지됨
5) Consumer(소비자)
- 큐로부터 메시지를 받아 처리하는 주체.
- 메시지를 수신하면 보통 ACK 응답을 보내 큐로부터 제거되도록 함.
- 비동기로 처리될 수 있으며, 다수의 Consumer가 하나의 Queue를 구독할 수 있음.
Exchange 타입별 특징
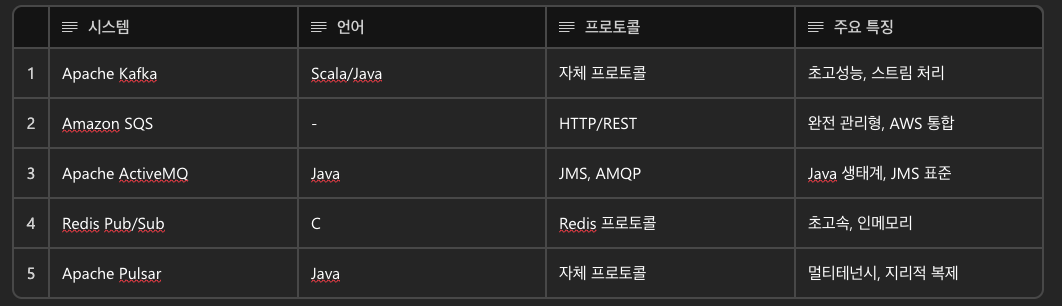
2-3) 타 메시지 큐
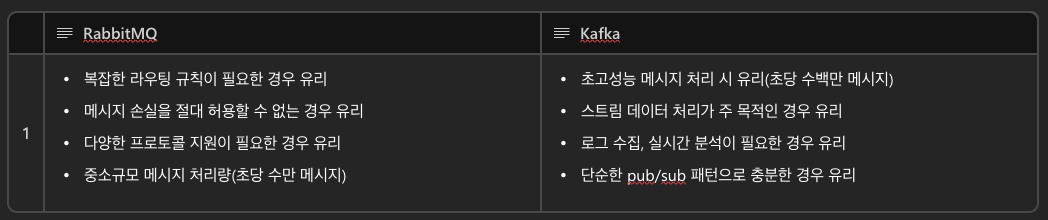
2-4) RabbitMQ vs Kafka?
2-5) 메시지 손실 방지를 위한 세팅
- 내구성 큐 생성(durable = true): 서버 재시작 후에도 큐 유지
@Bean
public Queue durableQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("my-queue").build();
}- Publisher Confirms 설정: 메시지가 브로커에 안전하게 도달했는지 확인
application.yml
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
publisher-confirm-type: correlated # 또는 simple
publisher-returns: true// Confirm Callback 등록
@Bean
public RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RabbitTemplate template = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
// 메시지 성공/실패 확인
template.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> {
if (ack) {
System.out.println("✅ 메시지 전송 성공");
} else {
System.err.println("❌ 메시지 전송 실패: " + cause);
}
});
// 메시지가 라우팅되지 못할 경우 처리
template.setReturnsCallback(returned -> {
System.err.println("❌ 라우팅 실패 메시지: " + new String(returned.getMessage().getBody()));
});
return template;
}
- 수동 ACK 활용: 처리 중 실패 시 메시지를 다시 큐에 넣기
application.yml
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
acknowledge-mode: manual # 수동 ack 설정@RabbitListener(queues = "my-queue")
public void receiveMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
try {
String msg = new String(message.getBody());
System.out.println("수신된 메시지: " + msg);
// 비즈니스 로직 처리...
// 성공 시 ack
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 실패 시 메시지를 다시 큐에 넣거나 폐기
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
}
}