Lab_01 : JPA란?
- JPA는 java 진영에서 사용하는 ORM 기술의 표준 사양이다.
- 표준 사양이라는 의미는 다시 말하면 JAVA의 인터페이스로 사양이 정의되어 있기 때문에 JPA라는 표준 사양을 구현한 구현체는 따로 있다는 것을 의미
Hibernate ORM
JPA 표준 사양을 구현한 구현체는 바로 Hibernate ORM,Eclipse Link DataNucleus 등이 있다.
- JPA는 Java Persistence API의 약자이지만, 현재는 Jakarta Persistence라고 불린다.
데이터 액세스 계층에서의 JPA위치
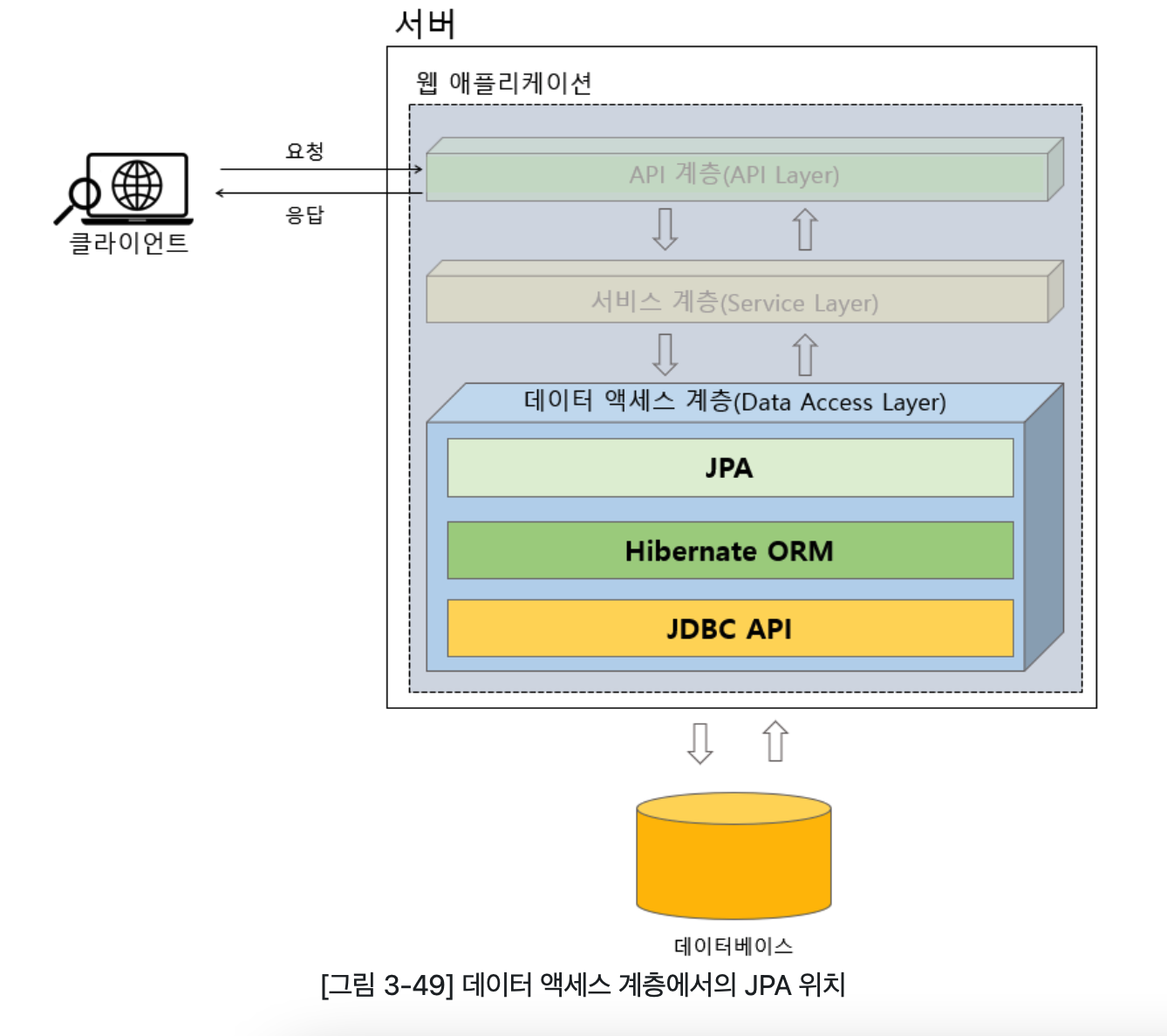
- 데이터 액세스 계층에서 JPA는 데이터 액세스 계층의 상단에 위치한다.
- 데이터 저장 , 조회 등의 작업은 JPA를 거쳐 JPA의 구현체인 HibernateORM을 통해서 이루어지며, Hibernate ORM은 내부적으로 JDBC API를 이용해서 데이터베이스에 접근한다.
JPA에서 P의 의미
Persistence는 영속성,지속성이라는 뜻을 가지고 있다. 즉, 무언가를 금방 사라지지 않고 오래 지속되게 한다라는 것이 Persistence의 목적이다
영속성 컨텍스트
- ORM은 객체와 데이터베이스 테이블의 매핑을 통해 엔티티 클래스 객체안에 포함된 정보를 테이블에 저장하는 기술이다.
- JPA에서는 테이블과 매핑되는 엔티티 객체 정보를 영속성 컨텍스트라는 곳에 보관해서 애플리케이션 내에서 오래 지속되도록 한다.
- 보관된 엔티티 정보는 데이터베이스 테이블에 데이터를 저장,수정,조회,삭제하는 데 사용된다.
- 영속성 컨텍스트를 관리하는 모든 엔티티 ㅐㅁ니저가 초기화 및 종료되지 않는 한 엔티티를 영구히 저장하는 환경이다.
영속성 컨텍스트를 그림으로 표현하면

그림과 같이 영속성 컨텍스트에는 1차 캐시라는 영역과 쓰기 지연 SQL저장소라는 영역이 있다.
JPA API중에서 엔티티 정보를 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장하는 API를 사용하면 영속성 컨텍스트의 1차 캐시에 엔티티정보가 저장된다.
Lab_02 JPA API영속성 컨텍스트 실습
라이브러리 설정
- JPA를 사용하기 위해서 의존 라이브러리를 build.gradle에 추가해야 한다.
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa' // (1)
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}[코드] 의존성 주입
JPA 설정
spring:
h2:
console:
enabled: true
path: /h2
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:test
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create # (1) 스키마 자동 생성
show-sql: true # (2) SQL 쿼리 출력[코드] JPA 설정 추가
- (1)과 같이 설정을 추가해 주면 우리가 JPA에서 사용하는 엔티티 클래스를 저으이하고 애플리케이션 실행시, 이 엔티티와 매핑되는 테이블을 데이터베이스에 자동으로 생성해 준다.
- 즉, Spring Data JDBC에서는 sql파일을 따로 설정하여 테이블을 생성해주었지만, JPA에서는 (1)의 설정을 추가하면 JPA가 자동으로 데이터베이스에 테이블을 생성해준다.
- (2)와 같이 설정을 추가하면, JPA의 동작 과정을 이해하기 위해 JPA API를 통해서 실행되는 SQL쿼리를 로그로 출력해 준다.
샘플 코드 생성
@Configuration
public class JpaBasicConfig {
private EntityManager em;
private EntityTransaction tx;
// (2)
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner testJpaBasicRunner(EntityManagerFactory emFactory) {
this.em = emFactory.createEntityManager();
this.tx = em.getTransaction();
return args -> {
// (3) 이 곳에 학습할 코드를 타이핑합니다.
};
}[코드] 샘플 코드 작성
-
@Configuration애너테이션을 추가하면 Srping에서 Bean에서 bean 검색 대상인 Configuration 클래스로 간주해서 (2)와 같이 @Bean 애너테이션이 추가된 메서들르 검색한 후, 해당 메서드에서 리턴하는 객체를 Spring Bean으로 추가해 준다. -
(3)과 같이
CommandLineRunner객체를 람다 표현식으로 정의해 주면 애플리케이션 부트스트랩 과정이 완료된 후에 이 람다 표현식에 정의한 코드를 실행해 준다.EntityManagerFactory
-
애플리케이션 로딩 시점에 DB당 딱 하나만 생성되어야 한다.
EntityManager
-
엔티티를 관리하는 역할을 수행하는 클래스
-
트랜잭션을 수행시키기 위해 EntityManagerFactory로부터 DB 커넥션을 하나 생성받는 개념
-
필요할 때마다 EntityManagerFactory로부터 발급받고, 사용 후에 close()를 호출해 반납한다.
-
쓰레드 간에 절대 공유하면 안된다.
-
- JPA는 EntityManager와 영속성 컨텍스트를 통해 데이터의 상태변홯를 감지하고 필요한 쿼리를 자동으로 수행한다.
EntityTransaction
-
JPA의 데이터를 변경하는 모든 작업은 반드시 트랜잭션 안에서 수행되어야 한다.
-
완료되면 commit을 해주고, 문제가 생기면 Rollback을 해줘야 한다.
엔티티 클래스 생성
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity // (1)
public class Member {
@Id // (2)
@GeneratedValue // (3)
private Long memberId;
private String email;
public Member(String email) {
this.email = email;
}[코드] JPA 동작 확인을 위한 Member 엔티티 클래스
-
@Entity,@Id애너테이션을 추가하면 JPA에서 해당 클래스를 엔티티 클래스로 인식한다. -
@GeneratedValue애너테이션은 식별자를 생성해 주는 전략을 지정할 때 사용한다. 즉, 식별자에 해당하는 맴버 변수에 사용할 시에 데이터베이스 테이블에서 기본키가 되는 식별자를 자동으로 설정해 준다.영속성 컨텍스트 Member 객체를 저장
@Configuration public class JpaBasicConfig { private EntityManager em; @Bean public CommandLineRunner testJpaBasicRunner(EntityManagerFactory emFactory) { // (1) this.em = emFactory.createEntityManager(); // (2) return args -> { example01(); }; } private void example01() { Member member = new Member("hgd@gmail.com"); // (3) em.persist(member); // (4) Member resultMember = em.find(Member.class, 1L); System.out.println("Id: " + resultMember.getMemberId() + ", email: " + resultMember.getEmail()); } }
[코드] Member엔티티를 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장하는 코드
- JPA의 영속성 컨텍스트는 EntityManager 클래스에 의해서 관리되는데 이 EntityManager 클래스의 객체는 (1)과 같이 EntityManagerFactory 객체를 Spring으로 부터 DI 받을 수 있다.
- (2)와 같이 EntityManagerFactory의 createEntityManager() 메서드를 이용해서 EntityManager 클래스의 객첼르 얻을 수 있다.
- (3)과 같이 persist(member) 메서들르 호출하면 영속성 컨텍스트에 member 객체의 정보들이 저장된다.
- (4)에서는 영속성 컨텍스트에 member 객체가 잘 저장되었는지 find(member.class,1L)메서드로 조회하고 있다.
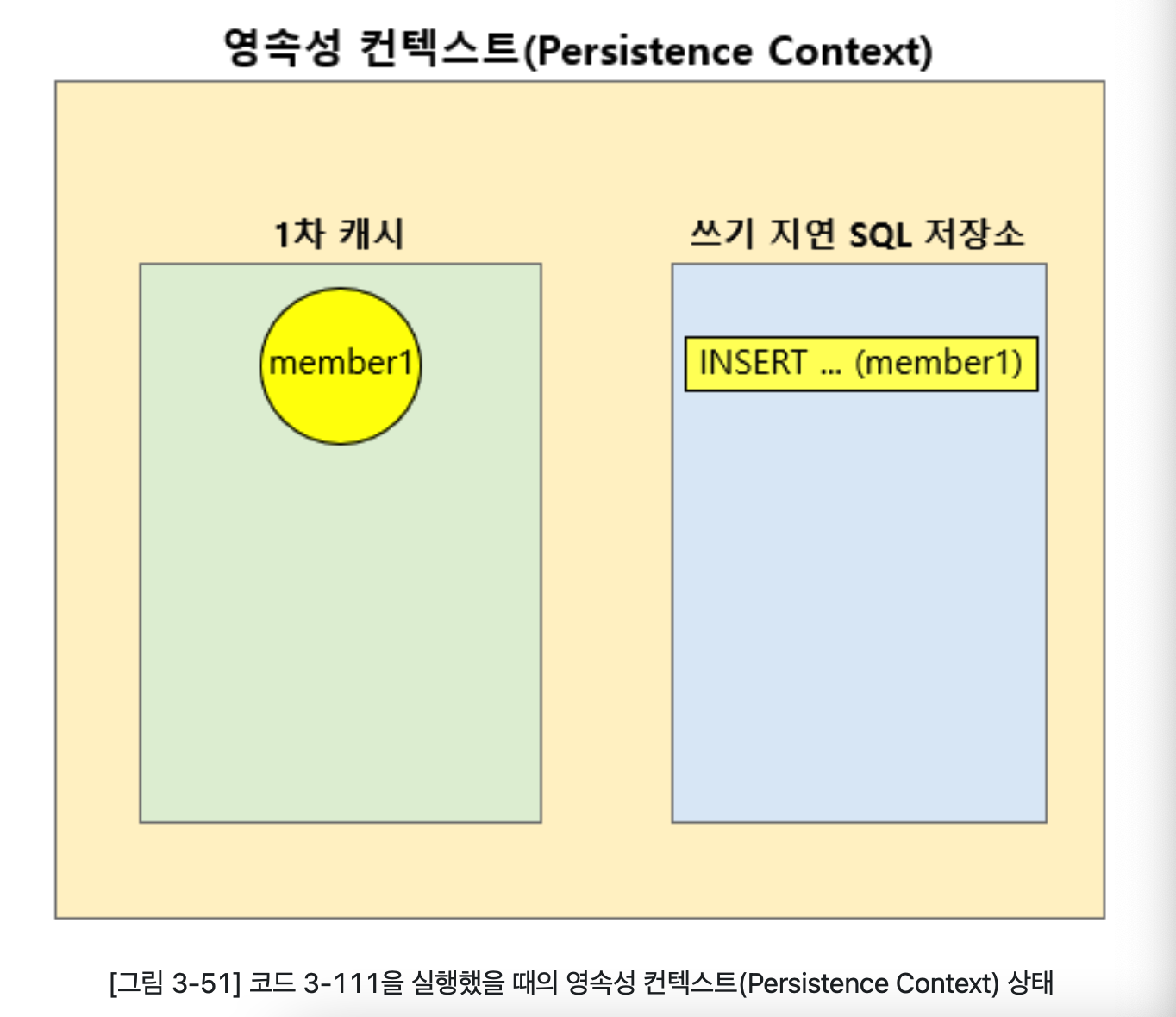
em.persist(member)를 호출하면 그림과 같이 1차캐시에 member 객체가 저장되고 이 member 객체는 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소에 INSERT쿼리 형태로 등록이 된다.
위 코드를 실행하면, 아래와 같은 출력 값을 얻을 수 있다.
Hibernate: drop table if exists member CASCADE
Hibernate: drop sequence if exists hibernate_sequence
Hibernate: create sequence hibernate_sequence start with 1 increment by 1
Hibernate: create table member (member_id bigint not null, email varchar(255), primary key (member_id))
2023-04-22 14:53:33.171 INFO 49271 --- [ main] o.h.e.t.j.p.i.JtaPlatformInitiator : HHH000490: Using JtaPlatform implementation: [org.hibernate.engine.transaction.jta.platform.internal.NoJtaPlatform]
2023-04-22 14:53:33.174 INFO 49271 --- [ main] j.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean : Initialized JPA EntityManagerFactory for persistence unit 'default'
2023-04-22 14:53:33.214 WARN 49271 --- [ main] JpaBaseConfiguration$JpaWebConfiguration : spring.jpa.open-in-view is enabled by default. Therefore, database queries may be performed during view rendering. Explicitly configure spring.jpa.open-in-view to disable this warning
2023-04-22 14:53:33.347 INFO 49271 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8083 (http) with context path ''
2023-04-22 14:53:33.353 INFO 49271 --- [ main] c.c.Section3Week2JpaApplication : Started Section3Week2JpaApplication in 1.298 seconds (JVM running for 1.539)
Hibernate: call next value for hibernate_sequence
Id: 1, email: hgd@gmail.com- 출력 결과를 보면 ID가 1인 Member의 email 주소를 영속성 컨텍스트에서 조회하고 있다.
- member 객체 정보를 출력하는 라인 위쪽 로그에서 JPA가 내부적으로 테이블을 자동 생성하고, 테이블의 기본키를 할당해 주는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- persist를 사용하여 영속성 컨텍스트에 Member 객체를 젖아하지만 실제 테이블에 회원 정보를 저장하지는 않는다. 실제 로그에서 insert쿼리가 보이지 않는다.
영속성 컨텍스트와 테이블에 엔티티 업데이트
테이블에 이미 저장되어 있는 데이터를 JPA를 이용해서 어떻게 업데이트 할 수 있는지에 대해 실습해보려 한다.
@Configuration
public class JpaBasicConfig {
private EntityManager em;
private EntityTransaction tx;
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner testJpaBasicRunner(EntityManagerFactory emFactory) {
this.em = emFactory.createEntityManager();
this.tx = em.getTransaction();
return args -> {
example04();
};
}
private void example04() {
tx.begin();
em.persist(new Member("hgd1@gmail.com")); // (1)
tx.commit(); // (2)
tx.begin();
Member member1 = em.find(Member.class, 1L); // (3)
member1.setEmail("hgd1@yahoo.co.kr"); // (4)
tx.commit(); // (5)
System.out.println(member1.getEmail());
}
}- (1)에서 새로운 Member개체를 email : "hdg1@gmail.com" 으로 초기화 및 생성하였다. 그 다음에 쓰기 지연sql 저장소, 1차캐시에 각각 sql insert,맴버 객체를 등록하였다.
- (2)에서 쓰기 지연sql 저장소에 저장된 sql insert문을 실행하여 데이블에 저장하였다.
- (3)에서 식별자 1L에 해당하는 데이터를 탐색한다.
- (4) setEmail 메서드를 사용하여 member1에 정의된 email을 "hgd1@yahoo.co.kr"로 수정한다.
- (5) 변경이 감지되어 쓰기 지연 sql저장소에 member1에 대한 update sql 문이 등록되어 있고 이 sql문을 실행해 테이블에 해당 데이터를 update 한다.
위 코드를 실행시키면 아래와 같은 결과가 출력된다.

Update 쿼리가 실행이 되는 과정
- 영속성 컨텍스트에 엔티티가 저장될 경우에는 저장되는 시점의 상태를 그대로 가지고 있는 스냅샷을 생성한다.
- 그 후 해당 엔티티의 값을 setter 메서드로 변경한 후, tx.commit()을 하면 변경된 엔티티와 이 전에 이미 떠 놓은 스냅샷을 비교한 후, 변경된 값이 있으면 쓰기 > 지연 sql 저장소에 update쿼리를 등록하고 update쿼리를 등록하고 update 쿼리를 실행한다.
영속성 컨텍스트와 테이블의 엔티티 삭제
@Configuration
public class JpaBasicConfig {
private EntityManager em;
private EntityTransaction tx;
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner testJpaBasicRunner(EntityManagerFactory emFactory) {
this.em = emFactory.createEntityManager();
this.tx = em.getTransaction();
return args -> {
example05();
};
}
private void example05() {
tx.begin();
em.persist(new Member("hgd1@gmail.com")); // (1)
tx.commit(); //(2)
tx.begin();
Member member = em.find(Member.class, 1L); // (3)
em.remove(member); // (4)
Member member2 = em.find(Member.class,1L);
System.out.printf("member is not exist : %b",member2==null);
}
}- (1)에서 Member클래스의 객체를 영속성 컨텍스트의 1차 캐시에 저장
- (2) tx.commit()을 호출해서 영속성 컨텍스트의 쓰기 지연 sql 저장소에 등록된 insert 쿼리를 실행
- (3)에서 식별자 1L 에 해당하는 데이터를 1차 캐시에서 찾음
- (4) 1차 캐시,쓰기 지연 sql저장소 에 저장된 데이터 삭제
해당 코드를 실행하게 되면 아래와 같은 결과를 출력받는다.
flush() :
tx.commit() 메서드가 호출되면 JPA 내부적으로 em.flush() 메서드가 호출되어 영속성 컨텍스트의 변경 내용을 데이터베이스에 반영
Lab_03 : EntityManager와 영속성 컨텍스트
생명주기
엔티티는 4가지 상태가 존재한다.
- 비영속
- 영속성 컨텍스트와 연관이 없는 상태
- 영속
- 영속성 컨텍스트에서 관리 중인 상태
- 준영속
- 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장되어 있으나 분리된 상태
- 삭제
- 영속성 컨텍스트에서 완전히 삭제된 상태
비영속
@Entity 어노테이션을 갖는 엔티티 인스턴스를 막 생성했을 때는 영속성 컨텍스트에서 관리하지 않는다.
EntityManger의 persist메소드를 사용하여 영속 상태로 변경할 수 있다.
em.persist(someEntity);영속
EntityManager 를 통해 데이터를 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장했다.
JPA는 일반적으로 id 필드가 존재하지 않으면 예외를 뱉어내는데, 영속 상태의 엔티티를 고나리하기 위해서다.
id로 데이터를 관리하기 때문에 꼭 필요하다
- 1차 캐시
em.find(key)를 호출하면 영속성 컨텍스트에 캐시된 데이터를 먼저 찾는다.- 캐시된 데이터가 없다면 DB에 접근하여 데이털르 로드하고 1차 캐시 데이터에 저장한다.
- 1차 캐시의 존재로 Java영역에서
REPEATABLE READ등급의 트랜잭션 격리 수준을 활용한다.
- 동일성 보장
- JPA를 통해 불러온 데이터는 모두 캐시 데이터에 저장되기 때문에 같은 id를 가진 데이터는 같은 데이터이다.
- Java에서 '같다'라는 기준은 identify(hashcode)/Equality(equals)이다.

- 트랜잭션 지원하는 쓰기 지연
- Transaction이 시작된 이후 JPA가 생성한 쿼리는 모두 쓰기 지연 저장소에 저장된다.
- commit이 수행되면 모든 쿼리를 실행한다.
- 변경 감지
- SQL을 직접 활용하여 개발하면 update문을 수행할 때 매우 귀찮은 점이 있다.
- 컬럼 1개, 2개,3개 ,...N개를 수정해야 할 때를 모두 쿼리로 작성해야 하는 것이다.
- 이렇게 되면 비즈니스 로직은 SQL에 의존할 수밖에 없다.
- JPA는 데이터를 저장하기 전 영속성 컨텍스트에 저장도니 데이터가 있는지 확인한다.
- 동일 데이터가 존재하면 update,없으면 insert를 수행한다.
- JPA가 실제로 수행하는 쿼리는 모든 컬럼을 변경한다.
- 지연 로딩
준영속
- 원래 영속 상태였으나 영속성 컨텍스트에서 분리되어 더 이상 관리하지 않는 데이터가 된 상태이다.
- 영속 상태의 엔티티를 dettach 시키거나 영속성 컨텍스트 자체가 초기화/종료되면 컨텍스트 내부의 모든 데이터는 준영속 상태가 된다.
- 관리되지 않는 상태이지만 JPA의 지원을 받지 못할 뿐, 정상적인 데이털르 갖는 인스턴스이다.
//1.
em.detach(someEntity);
//2.
em.close();
//3.
em.clear();삭제
- 엔티티를 영속성 컨텍스트와 DB 양쪽에서 모두 삭제한다.
em.remove(someEntity);플러시(flush)
- 영속성 컨테스트의 변경 내용을 DB에 반영하는 절차
- 플러시 수행 순서
- 데이터의 변경을 감지한다
- 생성된 쿼리를 쓰기 지연 저장소에 등록한다.
- commit되면 저장되어 있던 쿼리를 모두 수행한다.
em.flush()를 활용하면 직접 플러시할 수 있다.
플러시 모드
@FlushModeType.AUTO (default)
- commit이나 쿼리 실행할 때 플러시
@FlushModelType.COMMIT
- commit할 때만 플러시
종료
영속성 컨텍스트를 종료하려면 EntityManager의 close 메소드를 호출한다.
em.close();
병합
준영속 상태의 데이터는 병합 기능을 사용하여 다시 영속 상태로 돌릴 수 있다.
someEntity entity = em.find(key);
em.detach(entity);
em.merge(entity);
