⌨️ 사용자에게 직접 입력받아 성적표 출력하기
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in); // 입력 작업 시작에 필수
input.close(); // 입력 작업 마지막에 필수 ( 코드의 맨 마지막에 넣기 )
input.nextInt(); // 입력 값을 받는 함수
public static void main(String[] args) {
//입력 작업 시작
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("국어 : ");
// 입력된 정수를 변수에 대입
int kor = input.nextInt(); //입력 받은 점수를 korean에 저장한다. input.nextInt(); -> 입력받는 함수
System.out.print("영어 : ");
int eng = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("수학 : ");
int math = input.nextInt();
// 총점 구하기
int sum = kor+eng+math;
// 평균 구하기
//double avg = sum / 3; -> 평균의 소수점 자리가 나타나지 않음, 형변환이 필요함
double avg = sum / 3.0;
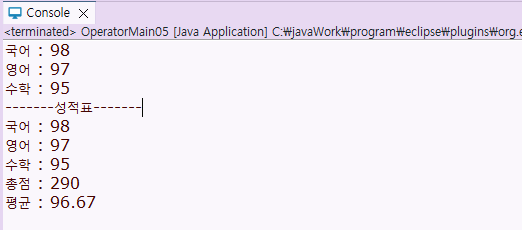
System.out.println("-------성적표-------");
System.out.printf("국어 : %d%n", kor);
System.out.printf("영어 : %d%n", eng);
System.out.printf("수학 : %d%n", math);
System.out.printf("총점 : %d%n", sum);
System.out.printf("평균 : %.2f%n", avg);
input.close();
//입력 작업 끝
}
}실행 결과
🟰 비교 (관계) 연산자
- 변수나 상수의 값을 비교할 때 쓰이는 연산자로서 결과가 항상 true 또는 false인 논리값
| 연산자 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| > | 크다 |
| < | 작다 |
| >= | 크거나 같다 |
| <= | 작거나 같다 |
| == | 같다 |
| != | 같지 않다 |
🟰 비교 (관계) 연산자 실습
public class OperatorMain06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("====비교 (관계) 연산자====");
boolean result;
int a =10;
double b = 10.5;
result = a < b;
System.out.println(" a < b : " + result); //비교 연산자는 boolean으로 나타냄
result = a > b;
System.out.println(" a > b : " + result);
result = a >= b;
System.out.println(" a >= b : " + result );
result = a <= b;
System.out.println("a <= b : " + result);
result = a == b; // 같다
System.out.println("a == b : " + result);
result = a != b; // 같지 않다
System.out.println(" a != b : " + result);
}
}⭕❌ 논리연산자
- 논리곱 && : 주어진 조건들이 모두 true 일 때 결과값이 true 가 된다.
- 선조건 : true 후조건 : true => 결과 : true
- 선조건 : true 후조건 : false => 결과 : false
- 선조건 : false ============> 결과 : false
- 선조건 : false ============> 결과 : false
선조건이 true일 때만 후조건을 실행하며 선조건이 false이면 후조건을 실행하지 않는다.
- 논리합 || : 주어진 조건 중 하나라도 true 이면 결과값이 true 가 된다.
- 선조건 : true ============> 결과 : true
- 선조건 : true ============> 결과 : true
- 선조건 : false 후조건 : true => 결과 : true
- 선조건 : false 후조건 : false => 결과 : false
선조건이 true이면 후조건을 실행하지 않으며 선조건이 false일 때만 후조건을 실행한다.
⭕❌ 논리연산자 실습
public class OperatorMain08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 논리곱(&&)
* 선조건 && 후조건 결과
* true true true
* true false false
* false 미실행 false
*
* 논리합(||)
* 선조건 || 후조건 결과
* true 미실행 true
* false true true
* false false false
*
* => 연산 속도를 빠르게 하기 위해서
*
*/
//증감연산자, 비교연산자, 논리연산자
int a, b;
a= b=10;
boolean c = a++ >= ++b && ++a > b++;
//10 //11
//false
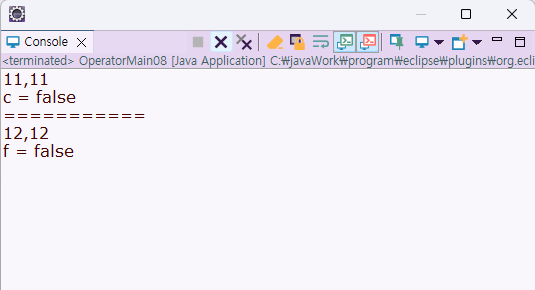
System.out.println(a + "," +b);
//11 //11
System.out.println("c = " +c);
//false
System.out.println("===========");
int d,e;
d = e = 10;
boolean f = ++d < e++ || d++ >= ++e;
//11 //10 //11 //12
//false //false
// 12 , 12 , false
System.out.println(d + "," +e);
System.out.println("f = " +f);
}
실행 결과
☑️ 조건 (삼항) 연산자
- 하나의 조건을 정의하여 만족 시에는 '참값'을 반환하고 만족하지 못할 시에는 '거짓값'을 반환한다.
| 연산자 | 의미 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| ?: | 조건을 만족하면 참값, 만족하지 못하면 거짓값 반환 | 조건 ? 참값 : 거짓값 |
☑️ 조건 (삼항) 연산자 실습 1
public class OperatorMain09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("===조건 (삼항) 연산자===");
int x = 10;
int y = -10;
// 조건 (삼항) 연산자
//조건 참값 : 거짓값
int absX = x >=0 ? x : -x;
//x = 10 => true
int absY = y >=0 ? y : -y;
//y= -10 => false
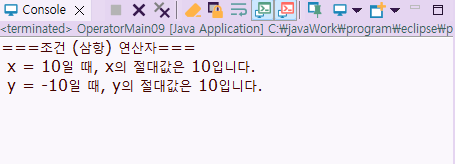
System.out.println(" x = 10일 때, x의 절대값은 " + absX +"입니다.");
System.out.println(" y = -10일 때, y의 절대값은 " + absY +"입니다.");
}
}
실행 결과
☑️ 조건 (삼항) 연산자 실습 2
public class OperatorMain10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("===조건 (삼항) 연산자===");
int a = 5, b = 10;
int max; //최대값을 저장하는 변수 선언
int min; //최소값을 저장하는 변수 선언
//최대값 구하기
max = a > b ? a: b ;
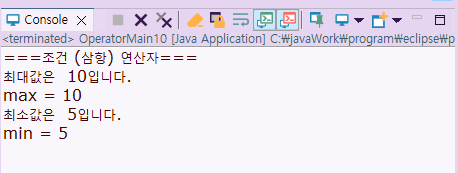
System.out.println("최대값은 " + max + "입니다.");
System.out.println("max = " + max);
//최소값 구하기
min = a < b ? a: b ;
System.out.println("최소값은 " + min + "입니다.");
System.out.println("min = " + min);
}
}실행 결과
☑️ 조건 (삼항) 연산자 실습 3
public class OperatorMain11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("===조건 (삼항) 연산자===");
char ch = 'M';
String str; //대문자인지 판단한 결과를 저장할 문자열 변수 선언
//str = ch>=65 && ch<=90 ? "대문자" : "소문자";
str = ch>='A' && ch<='Z' ? "대문자" : "소문자";
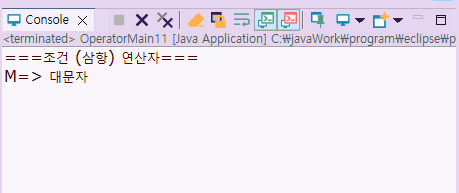
System.out.println(ch + "=> " + str );
}
}실행 결과
🟰 대입 연산자
| 연산자 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| = | 연산자를 중심으로 오른쪽 변수 값을 왼쪽 변수에 대입 |
| += | 연산자 완쪽 변수의 값과 연산자 오른쪽의 값(변수의 값)을 덧셈하여 왼쪽 변수에 대입 |
| -= | 연산자 왼쪽 변수의 값과 연산자 오른쪽의 값(변수의 값)을 뺄셈하여 왼쪽 변수에 대입 |
| * = | 연산자 왼쪽 변수의 값과 연산자 오른쪽의 값(변수의 값)을 곱하여 왼쪽 변수에 대입 |
| /= | 연산자 왼쪽 변수의 값과 연산자 오른쪽의 값(변수의 값)을 나누어 왼쪽 변수에 대입 |
| %= | 연산자 왼쪽 변수의 값과 연산자 오른쪽의 값(변수의 값)을 나누어 만들어진 나머지 값을 왼쪽 변수에 대입 |
🟰 대입 연산자 실습
public class OperatorMain12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("===대입연산자===");
int a = 5;
int b = 7;
a += b; //a = a+b
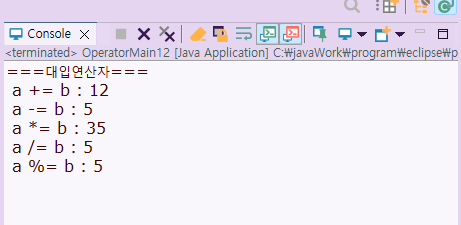
System.out.println(" a += b : " + a);
a -=b; // a = a - b
System.out.println(" a -= b : " + a);
a *= b; // a = a * b
System.out.println(" a *= b : " + a);
a /= b; // a = a / b
System.out.println(" a /= b : " + a);
a %= b; // a = a % b
System.out.println(" a %= b : " + a);
}
}실행 결과
📜 연산자 실습 1
[실습]
키보드에서 입력한 정수값에 마지막 자리수를 제외한 값과 마지막 자리 수를 표시하시오.
[입력 예시]
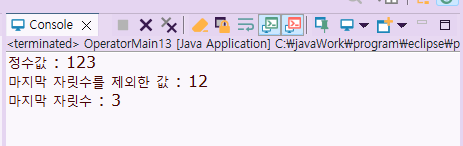
정수값 : 123
[출력 예시]
마지막 자릿수를 제외한 값 : 12
마지막 자릿수 : 3
public class OperatorMain13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수값 : ");
int num = input.nextInt();
System.out.println("마지막 자릿수를 제외한 값 : " + num/10);
System.out.println("마지막 자릿수 : " + num%10);
input.close();
}
}실행 결과
📜 연산자 실습 2
[실습]
A전자대리점에서는 그날 물건 판매액의 15%를 할인해주기로 했습니다.
판매한 상품명과 상품의 단가와 수량을 입력해서 지불 금액을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
(단, 출력 시에는 소수점 이하는 절삭하세요.)
[입력 및 출력 예시]
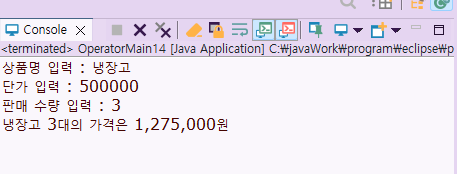
상품명 입력 : 냉장고
단가 입력 : 500000
판매 수량 입력 : 3
냉장고 3대의 가격은 1,275,000원
public class OperatorMain14 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("상품명 입력 : ");
String item = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("단가 입력 : ");
int price = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("판매 수량 입력 : ");
int quantity = input.nextInt();
int total = (int) (quantity * price * 0.85) ;
System.out.printf("%s %d대의 가격은 %,d원" , item, quantity, total);
input.close();
}
}실행 결과
📜 연산자 실습 3
[실습]
3개의 정수를 입력받아서 최대값, 최소값을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
[입력 예시]
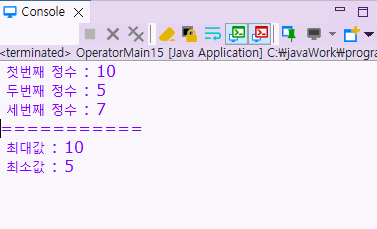
첫번째 정수 : 10
두번째 정수 : 5
세번째 정수 : 7
[출력 예시]
최대값 : 10
최소값 : 5
public class OperatorMain15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(" 첫번째 정수 : ");
int first = input.nextInt();
System.out.print(" 두번째 정수 : ");
int second = input.nextInt();
System.out.print(" 세번째 정수 : ");
int third = input.nextInt();
int max, min;
max = first > second ? first: second;
max = max > third ? max : third;
min = first < second ? first : second;
min = min < third ? min : third;
System.out.println("===========");
System.out.println(" 최대값 : " + max);
System.out.println(" 최소값 : " + min);
input.close();
}
}
실행결과
🛂 제어문
🛂 If문 실습 1
public class IfMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
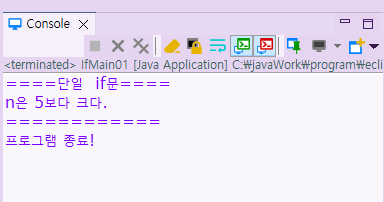
System.out.println("====단일 if문====");
int n = 10;
//단일 if 문: 조건이 true 이면 if 블럭 안의 수행문을 실행한다.
if(n > 5) {
System.out.println("n은 5보다 크다.");
}
System.out.println("============");
//if 문 블럭 내의 수행문이 한 줄이면 {} 생략이 가능하다.
if(n < 5)
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~");
System.out.println("프로그램 종료!");
}
}실행 결과
🛂 If문 실습 2
public class IfMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==== if ~ else ====");
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수형 데이터 한 개 입력 : ");
int a = input.nextInt();
// if ~ else
// 조건이 true 이면 if 블럭의 수행문을 실행
// 조건이 false 이면 else 블럭의 수행문을 수행
if(a % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("짝수입니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("홀수입니다.");
}
input.close();
}
}실행 결과
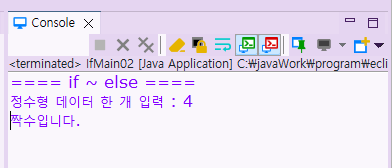
🛂 If문 실습 3
public class IfMain03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==== 다중 if문 ====");
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 한 개 입력 : ");
int a = input.nextInt();
//다중 if문
if (a > 0) {
System.out.println("양수입니다.");
}
else if(a < 0) {
System.out.println("음수입니다.");
}
else {
System.out.println("0 입니다.");
}
input.close();
}
}
실행 결과
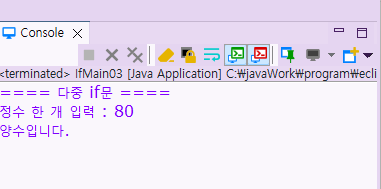
🛂 If문 실습 4
public class IfMain04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("성적을 입력하세요 : ");
int score = input.nextInt();
char grade;
if( score >= 90 && score <=100) {
grade = 'A';
}
else if (score >= 80 && score < 90) {
grade = 'B';
}
else if (score >= 70 && score < 80) {
grade = 'C';
}
else if (score >= 60 && score < 70) {
grade = 'D';
}
else if (score >= 0 && score < 60) {
grade = 'F';
}
else
{
grade = '?';
}
System.out.printf("성적 : %d%n", score);
System.out.printf("등급 : %c%n", grade);
input.close();
}
}실행 결과
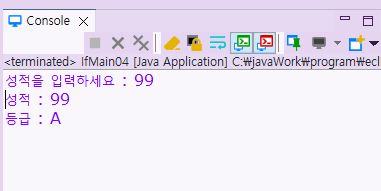
🛂 If문 실습 5
[실습]
정수 하나를 입력하여 짝수면 10을 더하고 홀수면 20을 더해서 결과값을 출력해라
[입력 예시]
정수 하나 입력: 5
[출력 예시]
결과 : 25
public class IfMain05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
*/
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
int result;
result = 0;
System.out.print("정수 하나 입력 : ");
int num = input.nextInt();
if( num %2 == 0 ) {
result = num + 10;
}
else if (num %2 == 1){
result = num + 20;
}
System.out.printf("결과 : %d%n" , result);
input.close();
}
}실행 결과
🛂 If문 실습 6
[실습]
정수 두 개를 입력 받아서 변수에 저장하고 두 값 중 최대값과 최소값을 구하여 최대값과 최소값을 출력하라
입력한 두 수가 같을 경우 "두 수는 같다"라고 출력하시오.
[입력 예시]
첫번째 정수 입력 : 3
두번째 정수 입력 : 2
[출력 예시]
최대값 : 3
최소값 : 2
public class IfMain06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("첫번째 정수 입력 : ");
int first = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("두번째 정수 입력 : ");
int second = input.nextInt();
if(first > second) {
System.out.println("최대값 : " + first);
System.out.println("최소값 : " + second);
}
else if(first < second) {
System.out.println("최대값 : " + second);
System.out.println("최소값 : " + first);
}
else {
System.out.println("두 수는 같다.");
}
input.close();
}
}실행 결과
📒 숙제 - 제출 완료
[숙제]
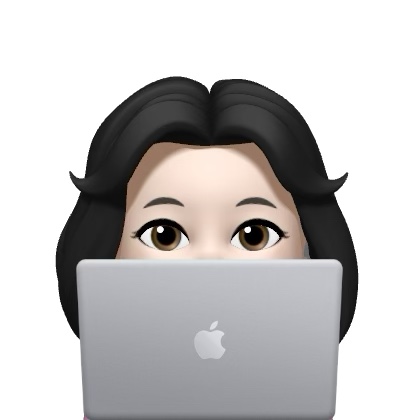
생년월일을 입력하고 만 나이를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
만 나이 = (현재 연도 - 태어난 연도) - (생일이 지났으면 0, 생일이 지나지 않았다면 1)
[입력 예시]
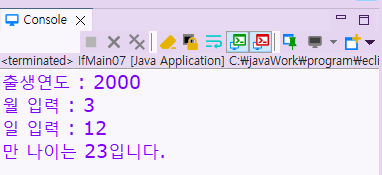
출생연도 : 2000
월 입력 : 3
일 입력 : 12
[출력 예시]
만 나이는 23입니다.
package kr.s03.operation;
public class IfMain07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//현재 날짜 정보
int nowYear = 2024;
int nowMonth = 2;
int nowDate = 20;
int age;
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("출생연도 : ");
int birthYear = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("월 입력 : ");
int birthMonth = input.nextInt();
System.out.print("일 입력 : ");
int birthDate = input.nextInt();
if (birthMonth < nowMonth || (birthMonth == nowMonth && birthDate <= nowDate)) {
age = nowYear - birthYear;
System.out.printf("만 나이는 %d입니다.", age);
}
else {
age = nowYear - birthYear - 1;
System.out.printf("만 나이는 %d입니다.", age);
}
input.close();실행 결과