🧱 String Buffer
- 문자열 버퍼 객체
- 문자열 추가 변경 가능
- append () 메소드 이용하여 문자(열) 추가
🧱 String Buffer 실습
public class StringBufferMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("여름 덥다!!");
System.out.println("1 : " + sb);
// 지정한 인덱스에 문자 삽입
sb.insert(2, '이');
System.out.println("2 : " + sb);
// 문자열 뒤에 문자열 붙이기
sb.append(" 가을은 ");
System.out.println("3 : " + sb);
sb.append("시원하다.");
System.out.println("4 : " + sb);
//시작인덱스부터 끝 인덱스 전까지 문자열 대체
sb.replace(0, 3, "여행가자!!");
System.out.println("5 : " + sb);
//지정한 인덱스의 문자를 삭제
sb.deleteCharAt(0);
System.out.println("6 : " + sb);
// 시작 인덱스부터 끝 인덱스 전까지 문자열 삭제
sb.delete(0, 3); //=> 2인덱스까지 삭제한다는 뜻
System.out.println("7 : " + sb);
//StringBuffer -> String 으로 변환
String str = sb.toString() ;
System.out.println("str = " + str);
}
}➕➖➗✖️ Math 실습
public class MathMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//절대값 구하기
int a = Math.abs(-10);
System.out.println("a 절대값 : " + a);
//소수점 자리수 올림 처리
double b = Math.ceil(3.3);
System.out.println("b 소수점 자리 올림 : " + b);
//소수점 자리 버림 처리
double c = Math.floor(3.7);
System.out.println("c 소수점 자리 버림 : " + c );
//소수점 자리 반올림 => 정수로 반환하기 때문에 정수의 결과값을 냄
int d = Math.round(3.7f);
System.out.println("d 소수점 자리 반올림 : " + d );
//최대값 구하기
int e = Math.max(3, 5);
System.out.println("최대값 구하기 : " + e);
//최소값 구하기
int f = Math.min(4, 7);
System.out.println("최소값 구하기 : " + f);
}
🔀 Random 실습
import java.util.Random;
public class MathMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String [] gift = {"스마트폰" , "TV" , "냉장고" , "X 꽝 X"};
//index 0 1 2 3
// 난수 발생 : 0 ~ 1 미만의 실수
double ran = Math.random();
System.out.println("발생한 난수 : " + ran);
/*
* 0 ~ 0.9999999999
* ----------------------
* *4
* 0 ~ 3.99999999999 => 4 곱하기 후 난수 발생 범위
* ================ > 소수점 날리기 -> double 형 .... > int 형으로 바꾸기
*/
int index = (int) (ran * 4); // 0 ~ 3 범위
System.out.println("정수로 변환한 난수 : " + index);
System.out.println("오늘의 선물 : " + gift[index]);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
String [] luck = {"귀인을 만납니다." , "사랑이 찾아옵니다." , "재물이 들어옵니다." , "별 소득이 없습니다."};
//index 0 1 2 3
Random r1 = new Random();
// 0부터 인자로 전달된 값의 전까지의 범위로 난수를 발생 0 ~ 3
index = r1.nextInt(4) ;
System.out.println("발생한 난수 : " + index);
System.out.println("오늘의 운세 : " + luck[index]);
}가위 바위 보 게임 실습
🗞️ Wrapper
- primitive 타입을 객체로 표현하는데 사용되는 다음 클래스들의 통칭
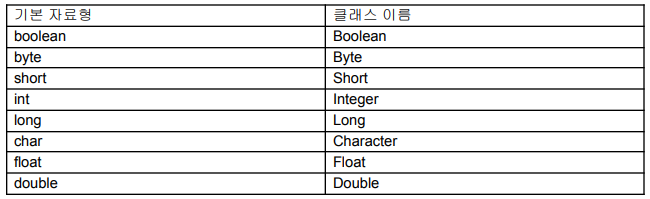
- primitive 타입 데이터를 감싸는 역할
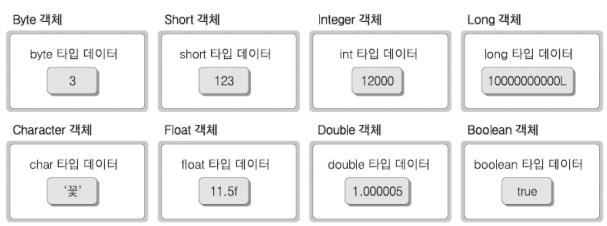
🗞️ Wrapper 실습 1
public class WrapperMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = true; // 기본 자료형
Boolean wrap_b = new Boolean(b);
//참조 자료형 데이터 -> 기본 자료형 데이터로 전환 시킴
boolean b2 = wrap_b.booleanValue() ;
System.out.println(b2);
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
char c = 'A'; // 기본 자료형
Character wrap_c = c ; //기본 자료형 데이터 -> 참조 자료형 데이터
//auto boxing
//참조 자료형 데이터 -> 기본 자료형 데이터
//auto unboxing
System.out.println(wrap_c);
}
}🗞️ Wrapper 실습 2
public class WrapperMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer obj1 = new Integer(12);
Integer obj2 = new Integer(7);
// 참조 자료형 데이터 - > 기본 자료형 데이터 : unboxing
int result = obj1.intValue() + obj2.intValue();
System.out.println("result : " + result );
System.out.println("------------------------------");
//auto boxing / auto unboxing
Integer obj3 = 10;
Integer obj4 = 20;
Integer result2 = obj3 + obj4;
System.out.println("result2 : " + result2);
}
}📅 Date
- 현재 날짜와 시간을 알 수 있는 객체
📅 Date 실습
import java.util.Date;
import java.text.*;
public class DateMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date now = new Date ();
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(now.toString());
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//deprecated 되어 사용하지 않음
//System.out.println(now.toLocaleString());
//연도 - 2자리 출력 , 시, 분까지 출력
DateFormat df = DateFormat.getInstance() ;
String today = df.format(now);
System.out.println(today);
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//연도 - 4자리 출력 , 시. 분. 초 모두 출력
df = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance() ;
String today2 = df.format(now);
System.out.println(today2);
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//날짜만 출력 , 연도 - 4자리
df = DateFormat.getDateInstance();
String today3 = df.format(now);
System.out.println(today3);
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
//시간만 출력, 시. 분. 초 모두 출력
df = DateFormat.getTimeInstance();
String today4 = df.format(now);
System.out.println(today4);
System.out.println("-----------------------------");
}
}📆 Calendar 실습 1
package kr.s21.object.util;
import java.util.*;
public class CalendarMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar today = Calendar.getInstance() ;
//System.out.println(today);
System.out.println("======================");
int year = today.get(Calendar.YEAR); // 연도
int month = today.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1; //기본값으로 0 ~ 11로 반환하기 때문에 +1을 해줘야 현재 달에 맞게 출력된다.
int date = today.get(Calendar.DATE) ;
System.out.printf("%d년 %d월 %d일 ", year , month, date);
int day = today.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK); //요일 반환 1 ~ 7로 반환
String [] days = {"일" , "월" , "화" , "수" , "목", "금" , "토"}; //인덱스는 0 ~ 6
// 그래서 요일 반환 값에서 - 1 을 해야 인덱스 값과 같아짐
System.out.print(days[day - 1] + "요일");
int amPm = today.get(Calendar.AM_PM); // 오전 0 , 오후 1 반환
String str = amPm == Calendar.AM ? "오전" : "오후" ; //0과 같다면 오전 반환, 다르면 오후 반환
int hour = today.get(Calendar.HOUR); //(12시 표기) //HOUR_OF_DAY(24시 표기)
int min = today.get(Calendar.MINUTE); // 분
int sec = today.get(Calendar.SECOND); // 초
System.out.printf(" %s %d시 %d분 %d초", str , hour, min, sec);
}
}📆 Calendar 실습 2
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalendarMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 현재 날짜와 시간을 구한다
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance() ;
System.out.println("희망 연도와 월을 입력하세요. (ex . 연도 : 2024 , 월 : 3)");
System.out.print("연도 > ");
int year = input.nextInt() ;
System.out.print("월 > ");
int month = input.nextInt() ;
System.out.println(" [ " + year + "년 " + month + "월 ]");
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println(" 일 월 화 수 목 금 토");
//희망 연도, 월, 일
// 월의 범위는 0 ~ 11 이기 때문에 입력월 -1
//일은 달력이 1부터 시작하기 때문에 1일로 셋팅
cal.set(year, month-1 , 1);
//1일의 요일 구하기, 1 일요일, 2 월요일 ... , 7 토요일
int week = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
//마지막 날짜 구하기
int lastOfDate = cal.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DATE);
//1일 전 공백 만들기
for(int i = 1; i < week; i++) {
System.out.printf("%4s" ," ");
}
//1일 ~ 마지막 날까지 반복s
for (int i = 1; i <= lastOfDate; i++) {
System.out.printf("%4d" , i);
if(week % 7 == 0) //토요일되면 줄바꿈
System.out.println();
week ++;
}
System.out.println("\n----------------------------------");
input.close();
}
🪙 String Tokenizer
- 문자열 분리 객체
- nextToken() 메소드 이용하여 문자(열)분리
🪙 String Tokenizer 실습 1
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String source = "100,200,300,400";
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(source,",");
//구분자를 통해서 잘려진 문자열이 있는지 검증
while(st.hasMoreTokens()) {
// 잘려진 문자열 반환
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
}
}
}🪙 String Tokenizer 실습 2
import java.util.*;
public class StringTokenizerMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String source = "2024-03-04 16:03:20";
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(source , "- :");
while(st.hasMoreTokens()) {
System.out.println(st.nextToken());
}
}
}
문자열 실습
아래 문자열의 대문자 -> 소문자 , 소문자 -> 대문자
public class StringMain05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcMDye-4W?EWzz";
String result = "" ;
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i ++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
if ( 64 < c && c < 91 ) { //대문자 구간
// char --> String 변환 후 소문자로 변환
result += String.valueOf(c).toLowerCase();
}
else if ( 96 < c && c < 123) { //소문자 구간
// char --> String 변환 후 대문자로 변환
result += String.valueOf(c).toUpperCase();
}
else { //대.소문자가 아닌 문자들
result += c;
}
}
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
String result2 = "";
// String - > char []
for(char c : str.toCharArray()) {
// 대문자이면 true 반환
if (Character.isUpperCase(c)) {
// 대문자 ---> 소문자
result2 += Character.toLowerCase(c);
}
// 소문자이면 true 반환
else if (Character.isLowerCase(c)) {
// 소문자 ---> 대문자
result2 += Character.toUpperCase(c);
}
else
// 대.소문자 아닌 문자들
result2 += c;
}
System.out.println(result2);
System.out.println("------------------------------");
String result3 = "";
for (int i = 0; i<str.length(); i ++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
if ( 64 < c && c < 91 ) { //대문자 구간
result3 += (char) ( c + 32 ); // 아스키코드 대문자와 소문자의 간격이 32 , 아스키코드 --> char로 형변환
}
else if ( 96 < c && c < 123) { //소문자 구간
result3 += (char) ( c - 32 );
}
else { //대.소문자가 아닌 문자들
result3 += c;
}
}
System.out.println(result3);
}
}추상 클래스
- 추상화라는 것은 구체적인 개념으로부터 공통된 부분들만 추려내어 일반화 할 수 있도록 하는 것을 의미한다. 다
시 말해서 일반적으로 사용할 수 있는 단계가 아닌 아직 미완성(未完成)적 개념인 것이다.
추상클래스는 일반클래스와 달리 미완성되어 있는 클래스이기 때문에 객체 생성이 불가능하고 상속관계를 맺은 자식 클래스가 객체 생성되어야 사용이 가능하다.
추상 메소드
- 추상클래스는 일반적으로 한 개이상의 추상메서드를 갖는다. 추상메서드는 일반메서드와 다르게 메서드가 수행할 코드를 갖고 있지 않다. 따라서 추상메서드는 상속시 자식 클래스에 반드시 구현되어야 자식클래스가 객체 생성될 수 있다.
추상 클래스의 상속 관계
- 추상 클래스들간에도 상속이 가능하다. 일반 클래스들간의 상속과 유사하지만 추상 클래스들간의 상속에서는 상속 받은 추상 메서드들을 꼭 재정의할 필요는 없다. 그냥 상속만 받아두고 있다가 언제가 일반 클래스와 상속관계가 이루어 질 때가 있을 것이다. 이때 재정의 하지 못했던 상속 받은 추상 메서드들을 모두 일반 클래스 내에서 재정의해도 되기 때문이다.
추상 클래스 실습 1
package kr.s22.object.abs;
// 추상 클래스
// 미완성된 개념으로 단독으로 객체 생성이 불가능하고 일반적으로 자식클래스에 상속되어져서 사용한다.
abstract class A {
private int x;
public void setX (int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getX () {
return x;
}
}
// 자식 클래스
class B extends A {
int b = 200;
}
public class AbstractMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 추상 클래스는 객체 생성이 불가능하다.
// A ap = new A ();
B bp = new B();
bp.setX(100);
System.out.println(bp.getX());
System.out.println(bp.b);
}
}
추상 클래스 실습 2
package kr.s22.object.abs;
// 추상 클래스
abstract class A2 {
private int x ;
public void setX ( int x ) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getX () {
return x;
}
// 추상 메소드
public abstract void make();
}
// 자식 클래스
class B2 extends A2 {
// 부모 클래스의 추상메소드를 구현
public void make() {
System.out.println("make");
}
}
public class AbstractMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
B2 bp = new B2();
bp.make();
}
}
추상 메소드 실습 3
package kr.s22.object.abs;
abstract class Animal {
public void breathe() {
System.out.println("숨을 쉬다.");
}
//추상 메소드
public abstract void sound();
}
// 자식 클래스
class Dog extends Animal {
// Animal의 추상메소드 sound 구현
@Override
public void sound () {
System.out.println("강아지는 멍멍!");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
// Animal의 추상메소드 sound 구현
@Override
public void sound() {
System.out.println("고양이는 미야옹");
}
}
public class AbstractMain03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog ();
d.breathe();
d.sound();
System.out.println();
Cat c = new Cat();
c.breathe();
c.sound();
}
}
추상 클래스& 메소드 실습 4
package kr.s22.object.abs;
// 추상 클래스
abstract class AbsEx {
int a = 100;
public int getA() { //일반 메소드
return a;
}
// 추상 메소드
abstract public int getB();
abstract public int getC();
}
//추상 클래스
abstract class AbsEx2 extends AbsEx {
// 추상클래스를 추상클래스에 상속하면 추상메소드 구현의 의무가 없음
String msg = "신세계";
//추상 메소드
public abstract String getMsg();
// 부모클래스의 추상메소드 구현
@Override
public int getB() {
return 200;
}
}
public class AbstractMain04 extends AbsEx2 {
// 부모클래스의 추상메소드를 구현한다
@Override
public int getC() {
return 300;
}
@Override
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractMain04 am = new AbstractMain04 ();
System.out.println(am.getA());
System.out.println(am.getB());
System.out.println(am.getC());
System.out.println(am.getMsg());
}
}

