⌨️ 입출력 스트림
- 스트림(Stream)이란?
- 데이터를 목적지로 입출력하기 위한 방법이다.
- 스트링에 데이터를 쓸 수 있고, 스트림에서 데이터를 읽을 수 있다.
- 스트림에 데이터를 쓸 경우에는 출력 스트림이라고 한다. [output stream]
- 스트림에서 데이터를 읽을 경우에는 입력 스트림이라고 한다. [input stream]
- 스트림의 특징
- 스트림은 FIFO 구조이다. (선입선출 ---> 데이터의 순서가 바뀌지 않음)
- 스트림은 단방향이다. (읽기, 쓰기가 동시에 불가능하여 읽는 스트림 쓰는 스트림 하나씩 열어 사용해야 한다.)
- 스트림은 지연될 수 있다. (스트림은 넣어진 데이터가 처리되기 전까지는 스트림에 사용되는 스레드는 지연상태에 빠진다.)
- 스트림 분류
- 용도에 의한 분류
1) 1차 스트림 : 디바이스에 직접 연결되는 스트림
2) 2차 스트림 : 1차 스트림과 연결을 통해 디바이스에 연결되는 스트림 - 전송 방향에 의한 분류
1) 입력 스트림 : 디바이스에 직접 연결되는 스트림
2) 출력 스트림 : 디바이스로 데이터를 출력하는 스트림 - 전송 단위에 의한 분류
1) 바이트스트림 : 1 Byte 단윌 입력, 출력하는 스트림
2) 문자스트림 : 한 문자 (2 Byte) 단위로 입력, 출력하는 스트림 - 보조 스트림
- 스트림의 기능을 향상시키거나 새로운 기능을 추가시킴 직접적인 데이터 입출력은 불가능하다.
- 용도에 의한 분류
⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 1
입력하면서 enter을 누르게 되면 문자열로 인식하기 때문에 저장된 값을 지워줘야 한다.
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class InputStreamMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("영문자 1개 입력 : ");
try {
//문자 하나를 입력 받아서 아스키 코드로 반환
int a = System.in.read();
System.out.println(a + "," + (char)a);
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \r : 13
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \n : 10
System.out.print("숫자 1개 입력 : ");
int b = System.in.read();
System.out.println("입력한 숫자의 아스키 코드 : " + b);
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \r : 13
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \n : 10
System.out.print("숫자 1개 입력 : ");
int c = System.in.read() - 48 ;
System.out.println("입력한 숫자 : " + c);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 2
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class InputStreamMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int input = 0;
try {
// 명시적으로 -1을 만들려면 ctrl + Z
while ( (input = System.in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(input + " , " + (char)input);
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 3
----> 영문만 출력
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileInputStreamMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
int readbyte;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt"); // file.txt 를 읽기
// 파일의 정보를 한 문자씩 읽어 들여 아스키 코드로 반환
// 영문 이외의 문자는 깨짐
while( (readbyte = fis.read()) != -1 ) {
System.out.print((char)readbyte);
}
}
// 파일 찾을 수 없음
catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리 ---> 작업을 하지 못하게 함
if ( fis != null) {
try { fis.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
} //end of if
} // end of finally
}
}
----> 영문이외의 문자도 출력
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileInputStreamMain1_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
byte[] readbyte2;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt");
//영문 이외의 문자도 처리 가능
readbyte2 = new byte[fis.available()];
//파일로부터 읽은 데이터들을 byte[]에 저장
fis.read(readbyte2);
//byte [] -> String 변환
System.out.println(new String(readbyte2));
}
// 파일 찾을 수 없음
catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리 ---> 작업을 하지 못하게 함
if ( fis != null) {
try { fis.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
} //end of if
} // end of finally
}
}⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 4
파일 생성에는 덮어쓰기 모드와 이어쓰기 모드가 있다.
덮어쓰기 모드는 기존에 있던 데이터 위에 다시 덮는 것이고 이어쓰기는 기존에 있던 데이터에 이어간다.
이어쓰기에서 다시 덮어쓰기 모드로 변경을 하면 이어썼던 내용들 모두에 새로운 데이터를 덮는다.
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//파일 생성 ----> 덮어쓰기 모드
//fos = new FileOutputStream("fileout.txt");
//파일 생성 ----> 이어쓰기 모드 , 기존에 있던 데이터를 이어간다.
fos = new FileOutputStream("fileout.txt" , true);
String message = "Hello File! 파일에 내용 기술";
//파일에 데이터 기록
// String --> byte[]
fos.write(message.getBytes());
System.out.println("파일을 생성하고 내용을 기술했습니다.");
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(fos != null) { try {fos.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
}
}
}⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 5
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("bufferOut.txt");
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
String str = "BufferedOutputStream Test 입니다.";
//String --> byte []
bos.write(str.getBytes());
//버퍼를 비우고 버퍼에 있는 데이터를 파일에 출력
//플러시하지 않으면 버퍼에 담겨있는 데이터를 파일에 저장하지 않음
//bos.flush();
System.out.println("파일을 생성하고 파일에 내용을 기술함");
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리
/*
* BufferedOutputStream 의 close 매소드는 자원정리하기 전에
* buffer를 체크해서 남아있는 데이터가 있으면 flush 처리한다.
*/
if(bos != null) { try {bos.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
if(fos != null) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { } }
}
}
}
⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 6
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedReaderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
// 문자스트림 <-- 표준입력
br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("당신의 이름 > ");
String name = br.readLine();
System.out.println("당신의 이름은 " + name + "입니다.");
System.out.print("당신의 나이 > ");
// Strign --> int
int age = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("당신의 나이는 " + age + "살 입니다.");
}
catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자를 입력하세요");
}
catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("입력시 오류 발생");
}
finally {//자원정리
if ( br != null) { try {br.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
}
}
}⌨️ 입출력 스트림 실습 7
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileReaderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
int readChar;
try {
fr= new FileReader("file.txt");
//파일로부터 데이터를 한 문자씩 읽어들여 유니코드로 반환
while((readChar = fr.read()) != -1 ) {
System.out.print((char)readChar);
}
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리
if(fr != null) { try {fr.close();} catch(IOException e ) { } }
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스
- 시스템에 있는 파일이나 디렉토리를 추상화한 클래스이다.
- File 클래스를 이용한 파일의 크기, 생성, 삭제, 변경 및 마지막 수정날짜 등 다양한 정보를 알 수 있는 메서드를 제공하고 있다.
📂 File 클래스 실습 1
디렉토리와 파일 정보 반환하기
import java.io.*;
public class FileMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:\\";
File f = new File(path);
if(!f.exists() || !f.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("유효하지 않은 디렉토리입니다.");
System.exit(0); // 프로그램 종료
}
// 지정한 디렉토리의 하위 디렉토리와 파일 정보 반환
File [] files = f.listFiles();
for (int i = 0 ; i < files.length; i++) {
File f2 = files[i];
if (f2.isDirectory()) { // 디렉토리인 경우
System.out.println("[" + f2.getName() + "]");
}
else {//파일
System.out.print(f2.getName());
System.out.printf("(%,dbytes)%n", f2.length());
} // end of else
} //end of for
}📂 File 클래스 실습 2
파일 생성하기 , 파일 정보 확인하기
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 절대 경로
//String path = "C:\\javaWork\\sample.txt";
// 상대 경로
String path = "sample.txt";
File f1 = new File (path);
System.out.println("---- 파일 생성 ----");
try {
/*
* 제공된 경로를 기반으로 파일을 생성, 파일이 생성되면 true 반환,
* 생성되지 않으면 false 반환 경로가 잘못되면 IOException 발생
*/
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("---- 파일 정보 ----");
System.out.println("절대 경로 : " + f1.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("상대 경로 : " + f1.getPath());
System.out.println("디렉토리명 : " + f1.getParent());
System.out.println("파일명 : " + f1.getName());
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 3
파일명 변경하기
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileMain03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 상대 경로
String path = "sample.txt"; // 원래 파일명
String new_path = "example.txt"; // 새 파일명
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("---- 파일명 변경 ----");
File f2 = new File (new_path);
// 파일명을 변경할 수 있으면 변경하고 true 반환
// 변경이 불가능하면 false를 반환
System.out.println(f1.renameTo(f2));
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 4
파일 삭제하기
delete() : 삭제할 수 있으면 삭제 후 true 반환 , 삭제 불가능하면 false 반환
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileMain04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 상대 경로
String path = "example.txt";
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("---- 파일 삭제 ----");
if(f1.delete()) {
System.out.println(f1.getName() + " 파일 삭제");
}
else {
System.out.println("파일 삭제에 실패하였습니다.");
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 5
디렉토리 생성하기
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileMain05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 절대 경로
String path = "C:\\javaWork\\javaSample";
File f1 = new File(path);
System.out.println("---- 디렉토리 생성 -----");
//디렉토리를 생성할 수 있으면 true 반환
//디렉토리를 생성할 수 없으면 false 반환
System.out.println(f1.mkdir());
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 6
디렉토리 삭제하기
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileMain06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//절대 경로
String path = "C:\\javaWork\\javaSample";
File f1 = new File (path);
System.out.println("---- 디렉토리 삭제 ----");
if(f1.delete()) {
System.out.println(f1.getName() + " 디렉토리 삭제");
}
else {
System.out.println("디렉토리 삭제에 실패하였습니다.");
}
}
}
바이트 스트림
-
바이트 스트림은 1 byte를 입출력 할 수 있는 스트림이다.
일반적으로 바이트로 구성된 파일, 즉 동영상 파일, 이미지 파일, 음악 파일을 처리하기에 적합한 스트림이다. -
바이트 스트림의 종류
InputStream과 OutputStream으로 구성되어 있다.
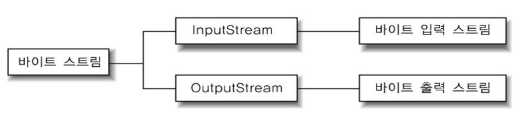
-
바이트 입력 스트림(InputStream)
InputStream은 바이트 입력을 수행하는 데 필요한 메서드를 정의하는 추상 클래스이다.
자바 프로그램은 객체를 생성하고 생성된 객체와 바이트 스트림과 연결함으로써 파일을 연다.
자바는 다른 장치들과도 바이트 스트림을 연결할 되어 있는고 프로그램이 시작되면 장치들과 연결된 세 개의 객체(System.in, System.out, System.err)를 생성한다.
System.in 객체는 키보드로 바이트를 입력할 수 있는 InputStream 객체이다. -
바이트 출력 스트림(OutputStream)
OutputStream은 바이트 출력을 수행하는 필요한 메서드를 정의한 추상 클래스이다.
프로그램이 시작 되면 장치와 연결된 두 개의 출력 스트림은 System.out, System.err를 생성한다.
System.out 객체는 화면에 데이터를 출력 한다.
System.err 객체는 화면에 오류 메시지를 출력하게 된다
문자 스트림
-
문자 스트림의 특징
바이트 스트림에 추가하여 Reader와 Writer 클래스를 제공하는데, 이것은 2 바이트를 입출력 할 수 있는 문자 기반 스트림이다.
바이트 스트림은 1바이트를 입출력하기 때문에 일반적으로 영문자로 구성된 파일, 동영상 파일, 음악 파일의 입출력 등에 적합한 스트림이다.
문자 스트림은 2바이트를 입출력하기 때문에 세계 모든 언어로 구성된 파일을 입출력 하기에 적합하다. -
문자 스트림의 구조
문자 스트림은 Reader와 Writer로 나눈다.
문자 입력 스트림 – Reader
문자 출력 스트림 - Writer
📂 File 클래스 실습 8
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileInputStreamMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
int readbyte;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("file.txt"); // file.txt 를 읽기
// 파일의 정보를 한 문자씩 읽어 들여 아스키 코드로 반환
// 영문 이외의 문자는 깨짐
while( (readbyte = fis.read()) != -1 ) {
System.out.print((char)readbyte);
}
}
// 파일 찾을 수 없음
catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리 ---> 작업을 하지 못하게 함
if ( fis != null) {
try { fis.close(); } catch(IOException e) {}
} //end of if
} // end of finally
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 9
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//파일 생성 ----> 덮어쓰기 모드
fos = new FileOutputStream("fileout.txt");
//파일 생성 ----> 이어쓰기 모드 , 기존에 있던 데이터를 이어간다.
//fos = new FileOutputStream("fileout.txt" , true);
String message = "Hello File! 파일에 내용 기술";
//파일에 데이터 기록
// String --> byte[]
fos.write(message.getBytes());
System.out.println("파일을 생성하고 내용을 기술했습니다.");
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(fos != null) { try {fos.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 10
버퍼를 비우고 버퍼에 있는 데이터를 파일에 출력한다. flush하지 않으면 버퍼에 담겨있는 데이터를 파일에 저장하지 않는다.
BufferedOutputStream 의 close 매소드는 자원정리하기 전에 buffer를 체크해서 남아있는 데이터가 있으면 flush 처리한다.
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileOutputStream fos = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream("bufferOut.txt");
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
String str = "BufferedOutputStream Test 입니다.";
//String --> byte []
bos.write(str.getBytes());
//bos.flush();
System.out.println("파일을 생성하고 파일에 내용을 기술함");
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리
if(bos != null) { try {bos.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
if(fos != null) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { } }
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 11
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedReaderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
// 문자스트림 <--표준입력
br = new BufferedReader ( new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("당신의 이름 > ");
String name = br.readLine();
System.out.println("당신의 이름은 " + name + "입니다.");
System.out.print("당신의 나이 > ");
// Strign --> int
int age = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("당신의 나이는 " + age + "살 입니다.");
}
catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자를 입력하세요");
}
catch(IOException e) {
System.out.println("입력시 오류 발생");
}
finally {//자원정리
if ( br != null) { try {br.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 12
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileReaderMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader fr = null;
int readChar;
try {
fr= new FileReader("file.txt");
//파일로부터 데이터를 한 문자씩 읽어들여 유니코드로 반환
while((readChar = fr.read()) != -1 ) {
System.out.print((char)readChar);
}
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//자원 정리
if(fr != null) { try {fr.close();} catch(IOException e ) { } }
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 13
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class FileWriterMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//파일 생성 ----> 덮어쓰기
//fw = new FileWriter("FileWriter.txt");
//파일 생성 ----> 이어쓰기
fw = new FileWriter("FileWriter.txt" , true);
String message = "안녕하세요 FileWriter 테스트.";
fw.write(message); // 버퍼 출력
fw.flush();
System.out.println("파일을 생성하고 내용을 기술");
}
catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if (fw != null) { try { fw.close();} catch (IOException e) {} }
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 14
package kr.s28.iostream;
public class Movie {
private String name; // 영화 제목
private String create_year; // 제작연도
private String director; // 감독
private String actor; //배우
private int time; //상영시간
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\t%d\n", name, create_year, director, actor, time);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getCreate_year() {
return create_year;
}
public void setCreate_year(String create_year) {
this.create_year = create_year;
}
public String getDirector() {
return director;
}
public void setDirector(String director) {
this.director = director;
}
public String getActor() {
return actor;
}
public void setActor(String actor) {
this.actor = actor;
}
public int getTime() {
return time;
}
public void setTime(int time) {
this.time = time;
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 15
메뉴 : 영화 정보 입력 / 영화 정보 출력 / 파일 생성 / 파일 일기 / 종료
callMenu /inputMovie / printMovie / createFile / readFile
조건 체크 : 0분 이상, 음수 불가, 숫자만 사용 가능함
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class MovieMain {
ArrayList<Movie> list ;
BufferedReader br;
public MovieMain() {
list = new ArrayList<Movie> () ;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
callMenu();
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(br != null) { try {br.close();} catch(IOException e) { } }
}
}
public void callMenu() throws IOException {
while (true) {
System.out.print(" 1. 영화 정보 입력 | 2. 영화 정보 출력 | 3. 파일 생성 | 4. 파일 열기 | 5. 종료 > ");
try {
int num = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()) ;
if ( num == 1) {
inputMovie();
}
else if (num == 2) {
printMovie();
}
else if (num == 3) {
createFile();
}
else if (num == 4) {
readFile();
}
else if (num == 5) {
System.out.println("프로그램을 종료하겠습니다. 다음에 또 이용해주세요.");
break;
}
else {
System.out.println("메뉴 번호를 정확히 입력해주세요.");
}
}
catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자만 입력해주세요.");
}
}
}
public void inputMovie() throws IOException {
Movie m = new Movie() ;
System.out.print("영화 제목 > ");
m.setName(br.readLine());
System.out.print("영화 제작연도 > ");
m.setCreate_year(br.readLine());
System.out.print("영화 감독 > ");
m.setDirector(br.readLine());
System.out.print("영화 출연 배우 > ");
m.setActor(br.readLine());
m.setTime(parseInputData("영화 상영 시간 > "));
list.add(m) ;
System.out.println("영화 정보가 등록되었습니다.");
}
public int parseInputData (String time) throws IOException {
while (true) {
System.out.println(time);
try {
int num = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if (num <= 0) {
System.out.println("상영 시간은 0분보다 길어야 합니다. 다시 입력해주세요.");
continue;
}
return num;
}
catch(NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("숫자만 입력해주세요.");
}
}
}
public void printMovie() {
if(list.size() > 0) {
System.out.printf("등록된 영화의 개수는 %d편 입니다.%n" , list.size());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("영화제목\t제작연도\t감독\t출연배우\t상영시간");
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");
for( Movie m : list) {
// System.out.printf("%s\t" , m.getName());
// System.out.printf("%s\t" ,m.getCreate_year());
// System.out.printf("%s\t" , m.getDirector());
// System.out.printf("%s\t" , m.getActor());
// System.out.printf("%d%n" ,m.getTime());
// System.out.println();
System.out.print(m.toString());
}
}
else {
System.out.println("등록된 영화 정보가 없습니다. 영화 정보 등록 후 다시 이용해주세요.");
System.out.println();
}
}
public void createFile( ) {
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fw = new FileWriter("movie.txt");
fw.write("-------------------------------------------\n");
fw.write("영화제목\t제작연도\t감독\t배우\t상영시간\n");
fw.write("-------------------------------------------\n");
for (Movie m : list) {
fw.write(m.toString());
}
fw.flush();
System.out.println("파일에 영화 정보를 저장했습니다.");
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("파일에 영화 정보 저장 오류가 발생했습니다.");
}
finally {
if(fw != null) try {fw.close();} catch(IOException e) { }
}
}
public void readFile() {
FileReader fr = null;
int readChar;
try {
fr = new FileReader("movie.txt");
while ( (readChar = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) readChar);
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("생성된 파일이 없습니다.");
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("파일을 읽어오는데 오류가 발생했습니다.");
}
finally {
if(fr != null) {
try {fr.close();} catch(IOException e) { }
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MovieMain() ;
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 16
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class InputStreamMain01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("영문자 1개 입력 : ");
try {
//문자 하나를 입력 받아서 아스키 코드로 반환
int a = System.in.read();
System.out.println(a + "," + (char)a);
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \r : 13
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \n : 10
System.out.print("숫자 1개 입력 : ");
int b = System.in.read();
System.out.println("입력한 숫자의 아스키 코드 : " + b);
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \r : 13
System.in.read(); //enter 처리 \n : 10
System.out.print("숫자 1개 입력 : ");
int c = System.in.read() - 48 ;
System.out.println("입력한 숫자 : " + c);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
📂 File 클래스 실습 17
package kr.s28.iostream;
import java.io.*;
public class InputStreamMain02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int input = 0;
try {
// 명시적으로 -1을 만들려면 ctrl + Z
while ( (input = System.in.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(input + " , " + (char)input);
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

