기본 스크롤 감지 훅
현재 작업 중인 프로젝트에서 상단의 nav 컴포넌트는 다음과 같이 동작한다.
- 스크롤이 맨 위에 있을 때는 배경이 투명함
- 스크롤을 내리면 배경이 검정색으로 바뀜
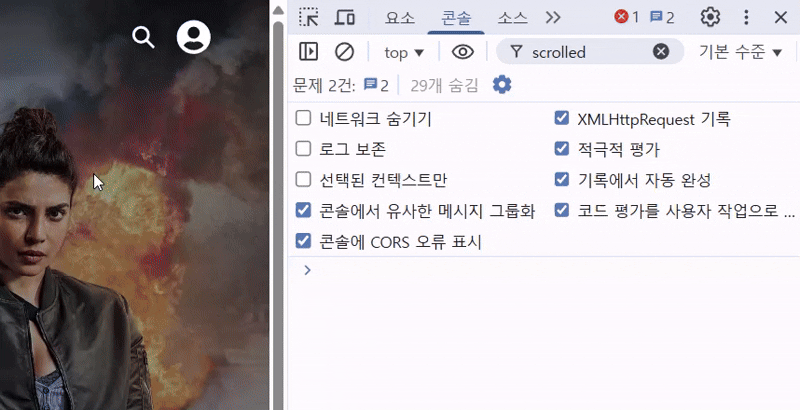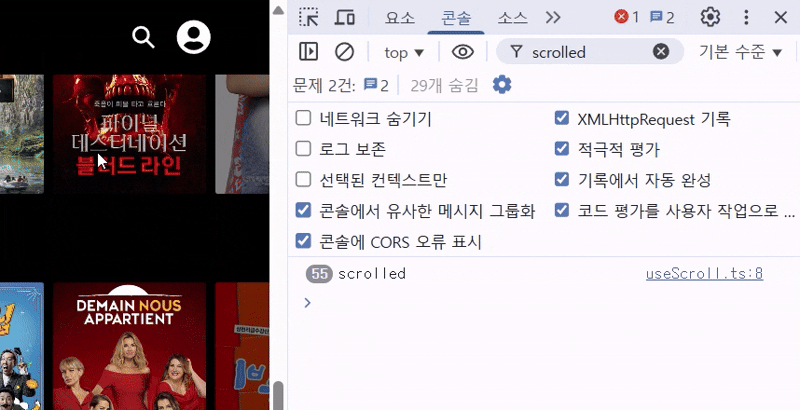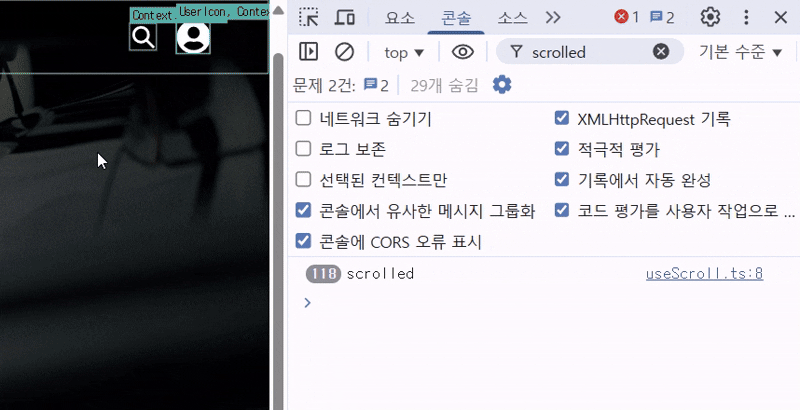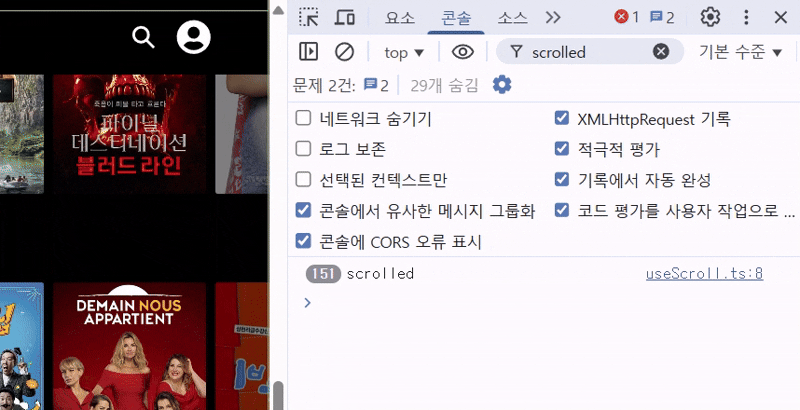
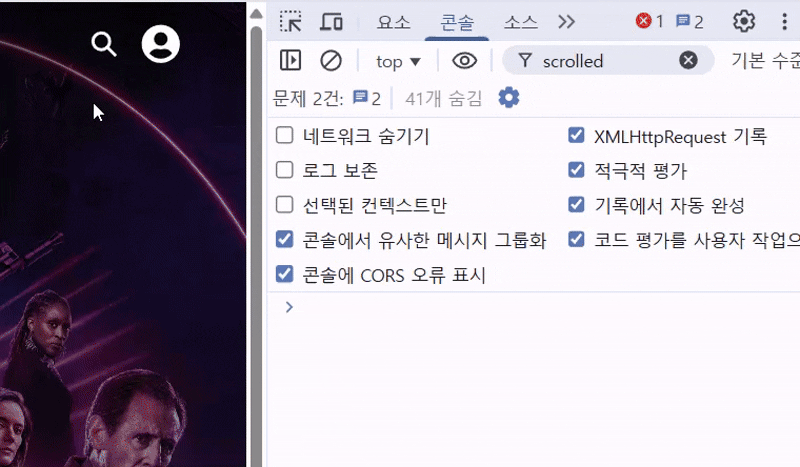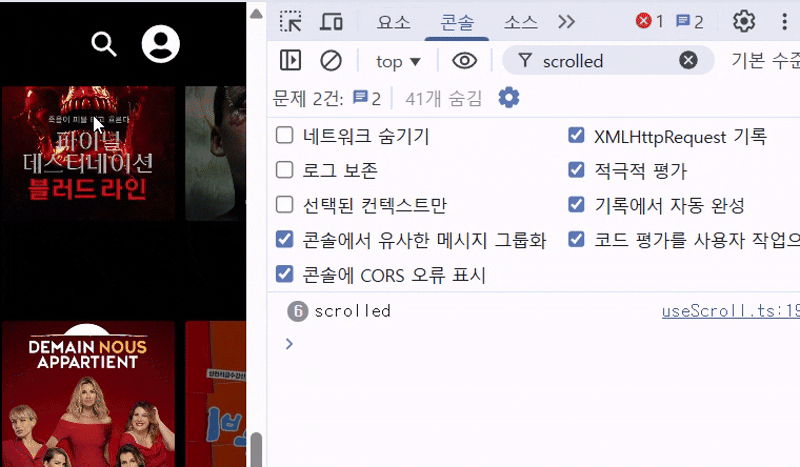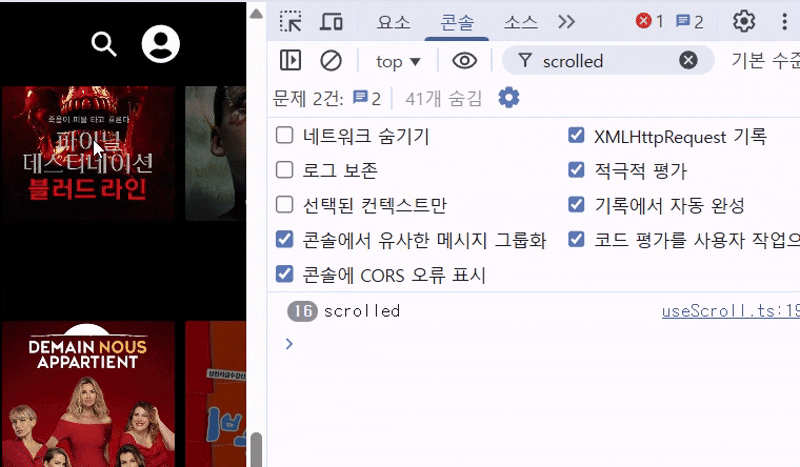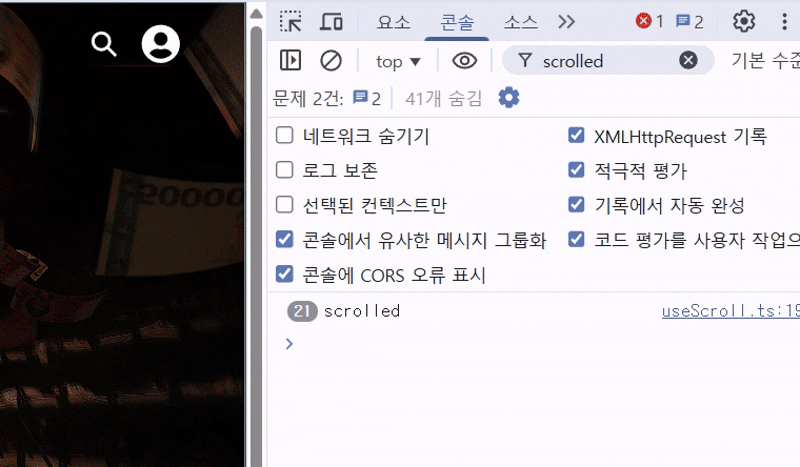
useScroll이라는 커스텀 훅을 만들어 window.scrollY 값을 감지하고, 그에 따라 nav의 배경색을 토글하도록 했다. useScroll 훅 로직은 다음과 같고, 콘솔을 찍어보면 스크롤 한 번에 스크롤 이벤트가 수십 번씩 호출되고 있다.
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
export default function useScroll(): boolean {
const [isScrolled, setIsScrolled] = useState<boolean>(false);
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
console.log('scrolled');
setIsScrolled(window.scrollY > 0);
};
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}, []);
return isScrolled;
}
그래서 스크롤 이벤트에 throttle을 적용시켜 최적화를 진행하려 한다. 학습을 위해 lodash는 사용하지 않고 직접 구현해보기로 했다.
⚙️ Throttle 적용
스크롤 이벤트가 짧은 시간 내에 여러 번 발생해도 일정 시간 동안에는 하나의 이벤트만 처리되도록 제한한다.
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from 'react';
const THROTTLE_DELAY = 200;
export default function useScroll(): boolean {
const [isScrolled, setIsScrolled] = useState<boolean>(false);
const throttleInProgress = useRef<boolean>(false);
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
if (throttleInProgress.current) {
return;
}
throttleInProgress.current = true;
console.log('scrolled');
setIsScrolled(window.scrollY > 0);
setTimeout(() => {
throttleInProgress.current = false;
}, THROTTLE_DELAY);
};
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}, []);
return isScrolled;
}throttleInProgress.current === true이면 현재 타이머가 실행 중이므로 즉시 리턴하여 이벤트를 실행시키지 않는다.
THROTTLE_DELAY 후 throttleInProgress.current 값을 false로 바꾸어 이벤트 실행 가능 상태로 만든다.
[사용자 스크롤 ↓↓↓↓↓↓]
이벤트 발생
→ 실행 가능 상태? → YES → 실행 + 잠금
→ 실행 가능 상태? → NO → 무시
→ 실행 가능 상태? → NO → 무시
[200ms 후] → 잠금 해제 → 다음 이벤트 가능❌ 문제
throttle은 잘 적용되었지만 스크롤을 다시 맨 위로 올렸을 때 nav의 배경이 투명해지지 않는다. 200ms(THROTTLE_DELAY) 안에 스크롤을 맨 위로 올리면 handleScroll의 로직이 실행되지 않고 isScrolled가 true인 상태로 유지되기 때문이다.
🛠️ 마지막 스크롤 위치 기억하기
throttle 타이머 내에서 항상 마지막 스크롤 위치를 반영하도록 수정했다.
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from 'react';
const THROTTLE_DELAY = 200;
export default function useScroll(): boolean {
const [isScrolled, setIsScrolled] = useState<boolean>(false);
const throttleTimeout = useRef<NodeJS.Timeout | null>(null);
const lastScrollY = useRef<number>(0);
useEffect(() => {
const handleScroll = () => {
lastScrollY.current = window.scrollY;
if (throttleTimeout.current) {
return;
}
throttleTimeout.current = setTimeout(() => {
console.log('scrolled');
setIsScrolled(lastScrollY.current > 0);
throttleTimeout.current = null;
}, THROTTLE_DELAY);
};
window.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => window.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
}, []);
return isScrolled;
}throttleTimeout은setTimeout()의 핸들을 저장해서 throttle 타이머 상태를 추적한다.lastScrollY은 마지막으로 감지한scrollY값을 저장한다.
현재 throttle 중이라면 리턴하여 이벤트를 실행하지 않고, 아니라면 타이머를 설정하고 THROTTLE_DELAY 후에 setIsScrolled를 실행한다.
실행이 끝난 뒤 throttleTimeout.current를 다시 null로 만들어 다음 이벤트 실행이 가능하게 한다.
이전 코드와의 차이
항목 첫 번째 코드 (throttleInProgress) 두 번째 코드 (throttleTimeout, lastScrollY) throttle 구현 방식 플래그 기반 setTimeout 핸들 직접 사용 스크롤 위치 저장 즉시 window.scrollY 사용 마지막 scrollY를 따로 저장해 반영
✨ 결과
참고
https://dev.to/andreyen/how-to-use-throttle-and-debounce-in-react-app-13af
