1. 문제
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/49190
2. 풀이
너무나도 까다로웠던 문제...
핵심은 다시 원점으로 돌아온다면? -> 방이 1개 생성.
하지만 예외가 있다..
이미지 참고 링크
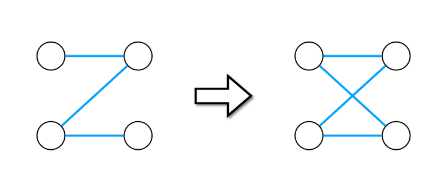
이러한 경우에는 대각선으로 한 번 이동하면 2개의 방이 생성된다. 따라서 교차점이 발생하는지 보아야 하기 때문에 하나의 입력이 들어와도 이를 2번 처리함으로써 해결해준다.
핵심 ✨Point
- HashMap을 사용하여 크게 정점의 객체를 관리해준다.
- 기존에 방문했던 정점을 새로운 간선을 통해 방문했을 때가 되는 것이다. 따라서 각 정점마다 Set을 만들어서 이 정점이 new 정점과 연결되었던 적이 있는지 파악하고 없으면 방을 생성해준다.
- Node class를 static으로, 그 안에있는 makeId 메소드도 static으로 만들어야한다. 그래야
String goId = Node.makeId(goX, goY);해당 코드를 접근할 수 있다.
3. 전체 코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int moveX[] = {-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1};
public int moveY[] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
public int solution(int[] arrows) {
int answer = 0;
HashMap<String, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
Node node = new Node(0, 0);
map.put(node.id, node);
for(int arrow : arrows){
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
int goX = node.x + moveX[arrow];
int goY = node.y + moveY[arrow];
//Node goNode = new Node(goX, goY);
String goId = Node.makeId(goX, goY);
if( !map.containsKey(goId) ){
map.put(goId, new Node(goX, goY));
} else if(!node.connectSet.contains(goId)){
answer++;
}
Node goNode = map.get(goId);
node.connectSet.add(goNode.id);
goNode.connectSet.add(node.id);
//node = goNode;
node = map.get(goId);
}
}
return answer;
}
public static class Node{
int x;
int y;
String id;
HashSet<String> connectSet;
public Node(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.id = makeId(x, y);
this.connectSet = new HashSet<>();
}
public static String makeId(int x, int y){
return String.format("(%d, %d)", x, y);
}
}
}