Entity Manger Factory, Entity Manger
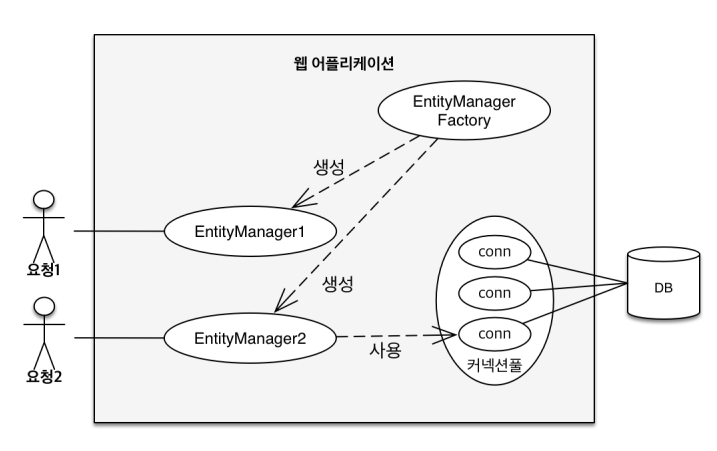
아래 그림과 같이 웹 어플리케이션은 EntityManber Factory는 고객의 요청에 따라 EntityManager를 생성한다. 이 EntityManager는 Connection을 통해 DB에 접근하게 된다.
Persistence Context
- Persistence Context : Entity를 영구 저장하는 환경이다.
- Persistence Context는 논리적인 개념으로 Entity Manager를 통해 접근 가능하다. 따라서 Entity Manager가 생성될 때 Persistence Context도 생성되어 Mapping된다.
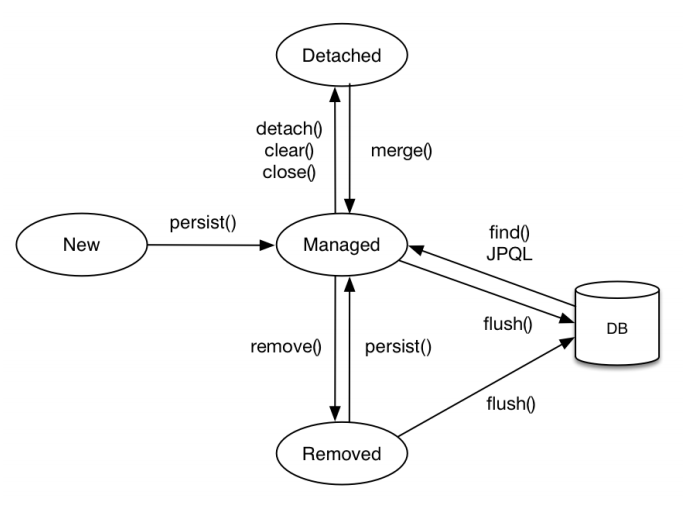
Entity의 생명 주기
- 비영속(new/transient) : Persistence Context와 관계없는 새로운 상태
- 영속(managed) : Persistence Context에 관리되는 상태
- 준영속(detached) : Persistence Context에 저장되었다가 분리된 상태
- 삭제(removed) : 삭제된 상태
비영속 상태
객체가 생성만 되고 Persistence Context에 저장되지 않은 상태이다.
//객체 생성
Member member = new Member();
member.setId("member1");
member.setUsername("회원1");
영속 상태
생석된 객체가 Persistence Context에 저장된 상태. 하지만 이때 DB에 저장되는 것은 아니다 DB에 저장되는 시점은 Transaction에 Commit되는 시점이다.
...
EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager();
em.getTransaction().begin();
//객체를 저장
em.persist(member);
준영속과 삭제
준영속은 객체를 Persistence Context에서 분리시킨 상태이고, 삭제는 말 그대로 삭제된 상태이다.
...
//객체 분리
em.detach(member);
//객체 삭제
em.remove(member);Persistence Context의 이점
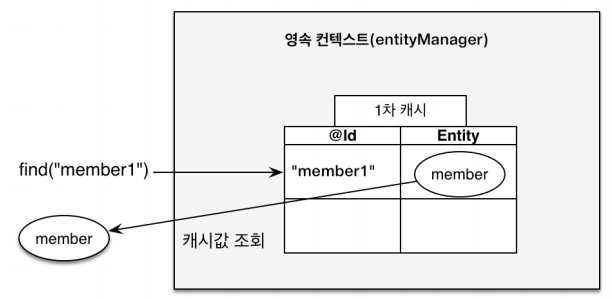
1. 1차 캐시
Entity Manager가 조회를 요청할 때 먼저 Persistence Context의 1차 캐시에서 조회한다.
Member member = new Member();
member.setId("member1");
member.setUsername("회원1");
//1차 캐시에 저장
em.persist(member)
//1차 캐시에서 조회
Member findMember = em.find(Member.class, "member1");
만약 1차 캐시에 없는 값을 조회하는 경우 DB에서 조회하여 1차 캐시에 저장한 후 값을 반환하게 된다.
...
Member findMember2 = em.find(Member.class, "member2");
...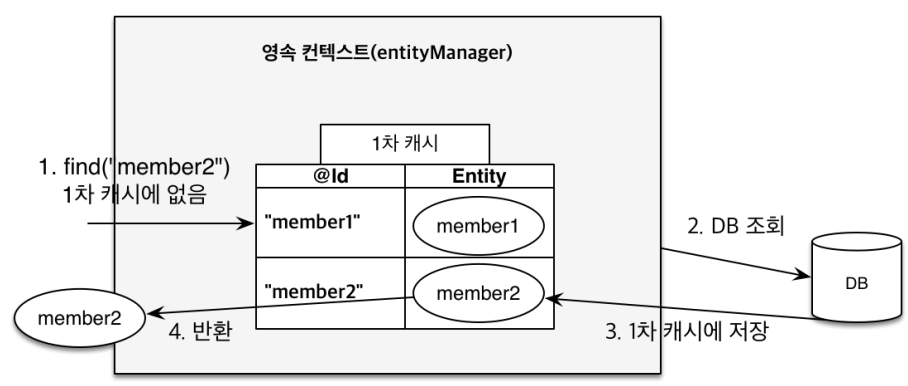
하지만 고객의 요청이 종료될때 Entity Manager는 삭제되기 때문에 1차 캐시가 성능상 큰 이점을 주지는 않는다.
2. 동일성 보장
같은 영속 Entity를 읽어올 경우 그것에 대한 동일성을 보장한다.
...
Member a = em.find(Member.class, "member1");
Member b = em.find(Member.class, "member1");
//동일성 비료 : true
System.out.printIn(a === b);
...3. Entity 등록시 Transaction을 지원하는 쓰기 지연(Transactional write-behind)
JPA는 Commit을 하기 전까지는 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소에 쿼리들을 저장하고, Transaction Commit과 함께 밀린 쿼리들을 DB에 전송하게 된다.
...
//Transaction 시작
transcation.begin();
em.persist(memberA);
em.persist(memberB);
//현재까지 INSERT SQL을 DB에 보내지 않았다.
//Commit하는 순간 DB에 INSERT SQL을 보낸다.
transaction.commit();
...4. 변경 감지 (Dirty-Check)
JPA는 Persistence Context 안의 1차 캐시에 Entity의 스냅샷을 저장한다. 이 스냅샷은 DB에서 최초로 읽어온 시점의 상태를 저장한 것이다.
...
Member memberA = em.find(Member.class, "member1");
//Entity Data 수정
memberA.setUsername("회원2");
memberA.setAge(10);
transaction.commit();
...변경 후 Commit 하는 시점에 현재 Entity와 스냅샷을 비교하여 UPDATE SQL을 생성하여 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소에 저장 후 DB에 전송하게 된다.
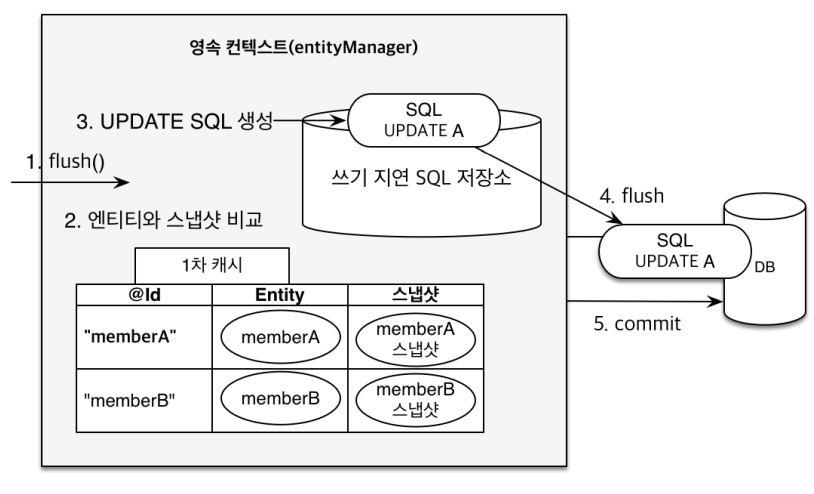
Flush
Persistence Context의 변경 내용을 DB에 반영하는 작업이다.
Flush 발생 시
- 변경 감지
- 수정된 Entity를 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소에 등록
- 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소의 쿼리를 DB에 전송 (등록, 수정, 삭제 쿼리)
- 1차 캐시의 내용이 삭제되지는 않는다.
Persistence Context를 Flush 하는 방법
- em.flush() : 직접 호출
- Transaction Commit : Flush 자동 호출
- JPQL 쿼리 실행 : Flush 자동 호출
유의할 것!
- Persistence Context를 비우지 않는다.
- Persistence Context의 변경 내용을 DB에 동기화한다.
- Transaction이라는 작업 단위가 중요하다. 즉 Commit 직전에만 동기화 하면 된다.
준영속 상태
영속에서 준영속으로 바뀐 상태로 영속 상태의 Entity가 Persistence Context에서 분리(detached)되어 Persistence Contest가 제공하는 기능(Dirty Check 등)을 사용하지 못한다.
준영속 상태로 만드는 방법
- em.detach(entity) : 특정 Entity만 준영속 상태로 전환
- em.clear() : Persistence Context를 완전히 초기화
- em.close() : Persistence Context를 종료
[Reference]
Inflearn 김영한 님의 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍 - 기본편 : https://www.inflearn.com/course/ORM-JPA-Basic/dashboard
