Spring Security의 개념과 아키텍처 구조에 대한 이해가 필요합니다.
위 내용을 알고 싶으신 분들은 여기를 참고해주세요.
참고) Servlet 애플리케이션의 Spring Security v 5.7.9 기준입니다.
인증(Authentication) 아키텍처
Spring Security의 아키텍처 구성요소는 다음과 같습니다.
| 구성 요소 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| SecurityContextHolder | 인증된 사용자의 세부 정보를 포합합니다. |
| SecurityContext | SecurityContextHolder에서 얻을 수 있으며, 현재 인증된 사용자에 대한 Authentication을 포함합니다. |
| Authentication | 이미 인증되어 SecurityContext에 저장된 현재 사용자거나, 사용자가 인증을 위해 제공한 credential |
| GrantedAuthority | 인증 시 주체(principal)에게 부여되는 권한 또는 그룹(scope) |
| AuthenticationManager | Spring Security의 필터가 인증을 수행하는 방법을 정의한 API |
| ProviderManager | AuthenticationManager의 일반적인 구현체 |
| AuthenticationEntryPoint | 클라이언트가 접근 권한이 없는 리소스에 접근하려고 할 때, 클라이언트에게 credential을 요청하기 위해 사용됩니다. (로그인 페이지로 리다이렉션 등) |
| AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter | 인증에 사용되는 기본 필터로 전반적인 인증 로직을 수행합니다. |
SecurityContextHolder

Spring Security 인증 모델의 핵심 요소로, 인증된 사용자에 대한 세부 정보가 저장되어있으며, SecurityContext를 포함합니다. Spring은 SecurityContextHolder가 어떤 식으로 채워지는지 상관하지 않으므로, setContext()를 사용하여 임의로 현재 인증된 사용자를 만들 수 있습니다.
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
Authentication authentication =
new TestingAuthenticationToken("username", "password", "ROLE_USER");
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
SecurityContextHolder.setContext(context);참고) SecurityContextHolder는 SecurityContextHolderStrategy 를 가지며, SecurityContextHolderStrategy의 구현체들은 SecurityContext를 가집니다.
// SecurityContextHolder
public class SecurityContextHolder {
...
private static SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy;
...
private static void initializeStrategy() {
...
if (!StringUtils.hasText(strategyName)) {
// Set default
strategyName = MODE_THREADLOCAL;
}
...
}
}
// SecurityContextHolderStrategy
public interface SecurityContextHolderStrategy {
void clearContext();
SecurityContext getContext();
void setContext(SecurityContext context);
SecurityContext createEmptyContext();
}
//FilterChainProxy
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
...
finally {
//SecurityContext를 지운다.
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
}
}SecurityContextHolder의 기본 전략은 ThreadLocal을 사용하여 SecurityContext를 저장하는 MODE_THREADLOCAL입니다. 따라서 매개변수로 SecurityContext가 전달되지 않더라도 동일한 스레드라면 SecurityContextHolder.getContext()로 SecurityContext를 사용할 수 있습니다. 스레드풀 기반 환경에서 ThreadLocal을 사용하여 발생하는 memory leak 문제는 FilterChainProxy가 SecurityContext를 지우는 것으로 방지합니다.
SecurityContextHolder의 다른 전략들은 다음과 같습니다.
MODE_GLOBAL: 모든 스레드에서SecurityContext를 공유합니다.MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL: 현재 스레드에서 하위로 생성된 스레드와SecurityContext를 공유합니다.
SecurityContext
SecurityContextHolder에서 얻을 수 있으며, 현재 인증된 사용자에 대한 Authentication을 포함합니다.
public interface SecurityContext extends Serializable {
Authentication getAuthentication();
void setAuthentication(Authentication authentication);
}Authentication
Authentication은 Spring Security에서 두 가지 역할을 합니다.
- 사용자가 인증을 위해 제공한 credential
- 이 경우,
isAuthentication()은 false를 반환합니다.
- 이 경우,
- 이미 인증되어
SecurityContext에 저장된 현재 사용자- 이 경우,
isAuthentication()은 true를 반환합니다.
- 이 경우,
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
Object getCredentials();
//인증 요청의 세부 정보(ex. IP, certificate serial number)를 가져옵니다.
Object getDetails();
Object getPrincipal();
boolean isAuthenticated();
void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}Authentication은 다음 세 가지 요소를 포함합니다.
- principal: 인증되는 주체의 식별자입니다.
- 사용자 이름/비밀번호 인증의 경우 사용자 이름이 됩니다.
- credentials: 대부분의 경우 비밀번호이며, 유출되지 않도록 사용자가 인증된 후 지워집니다.
- authorities: 사용자에게 부여되는 권한입니다.
GrantedAuthority
GrantedAuthority는 Authentication.getAuthorities()을 통해 컬렉션 형태로 얻을 수 있습니다. 인증된 사용자에게 부여되는 권한이며, 일반적으로 “ROLE_ADMIN”과 같은 역할(role)을 가집니다.
public interface GrantedAuthority extends Serializable {
String getAuthority();
}AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager는 Spring Security의 필터가 인증을 수행하는 방법을 정의한 API입니다.
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
}인증이 성공하여 Authentication이 반환되면, AuthenticationManager를 호출한 메서드에서 SecurityContextHolder에 Authentication을 설정합니다. 인증이 실패할 경우 AuthenticationException를 발생시킵니다.
ProviderManager
가장 일반적인 AuthenticationManager 구현체입니다.
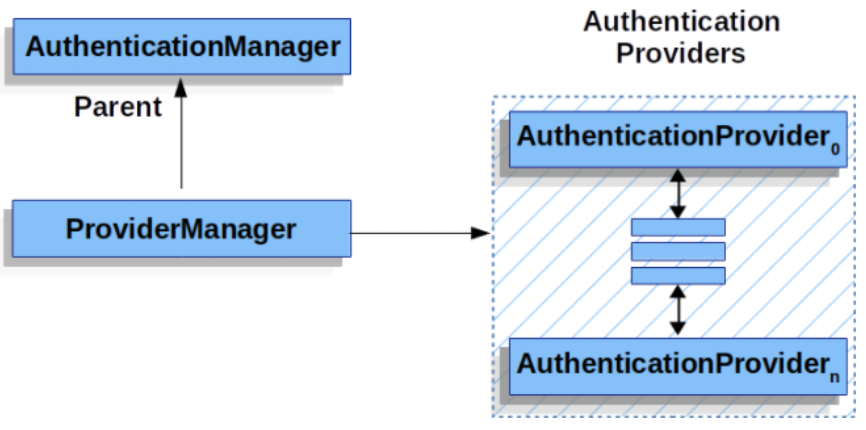
ProviderManager는 각 AuthenticationProvider들을 조회하며 인증을 시도하고, credential 기반으로 인증된 경우 credential을 지우고 반환합니다.
public class ProviderManager implements AuthenticationManager, MessageSourceAware, InitializingBean {
...
private List<AuthenticationProvider> providers = Collections.emptyList();
private AuthenticationManager parent;
private boolean eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication = true;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
...
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
...
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
...
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
...
}
...
if (result != null) {
if (this.eraseCredentialsAfterAuthentication && (result instanceof CredentialsContainer)) {
// Authentication is complete. Remove credentials and other secret data
// from authentication
((CredentialsContainer) result).eraseCredentials();
}
...
}
if (result == null && this.parent != null) {
// Allow the parent to try.
try {
parentResult = this.parent.authenticate(authentication);
result = parentResult;
}
...
}
}
return result;
}
...
}
}ProviderManager의 AuthenticationProvider들로 인증할 수 없는 경우, parent를 참조하여 인증을 수행할 수 있습니다. 한마디로, ProviderManager는 AuthenticationManager 타입으로 계층 구조를 가질 수 있고 여러 ProviderManager가 같은 parent를 가질 수도 있습니다. 이는 공통 인증 과정이 있고, 여러 SecurityFilterChain 인스턴스가 있는 경우 일반적인 구조입니다.
AuthenticationProvider
ProviderManager에게 호출되어 실제로 인증을 수행하며, 각 AuthenticationProvider 구현체들은 특정 유형의 인증을 처리할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 DaoAuthenticationProvider는 사용자 이름/비밀번호 기반 인증을 처리하며, RememberMeAuthenticationProvider는 RememberMeAuthenticationToken 기반 인증을 처리할 수 있습니다.
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}AuthenticationEntryPoint
AuthenticationEntryPoint는 클라이언트가 접근 권한이 없는 리소스에 접근하려고 할 때, credential을 요청하는 HTTP 응답을 보내는 데 사용됩니다.
AuthenticationEntryPoint 구현체인 LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint은 로그인 페이지로 리디렉션합니다.
public interface AuthenticationEntryPoint {
void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException)
throws IOException, ServletException;
}AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
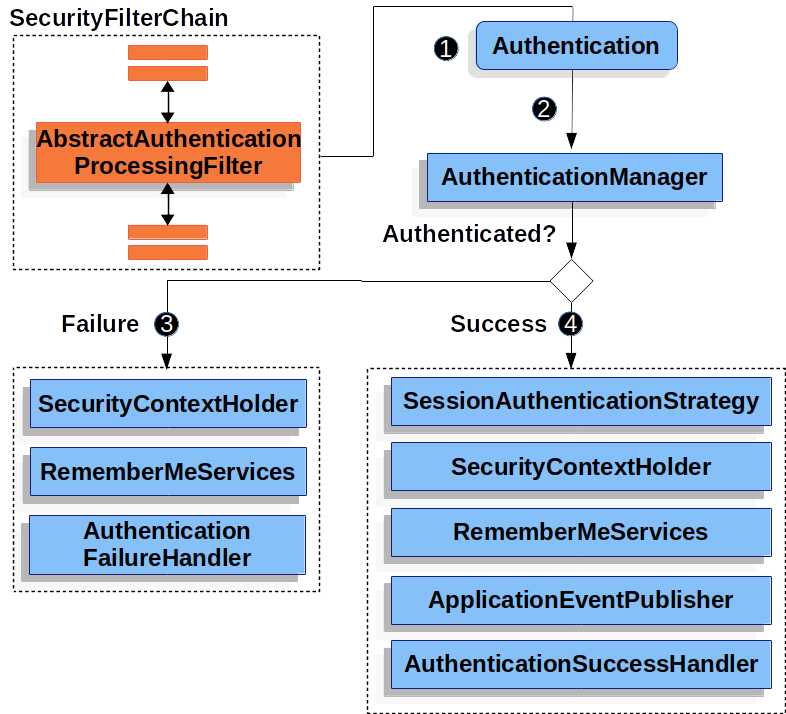
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter는 사용자를 인증하기 위한 필터로, SecurityFilterChain에 기본 등록됩니다. AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter는 Spring Security의 사용자 인증 시작점이라고 할 수 있습니다.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter부터 시작하는 사용자 인증 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.
//AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authenticationResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
return;
}
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);
// Authentication success
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex);
}
}SecurityFilterChain의 filter들이 순차적으로 실행되고,AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter을 실행합니다.AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.attemptAuthentication()는 요청의 인증 정보를 가져와Authentication을 만들고,AuthenticationManager로 인증을 수행합니다.- 성공한 경우 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.
- 세션 인증 전략에 따라 세션을 처리하고 응답에 설정합니다.
SecurityContextHolder를 통해SecurityContext에 인증된 사용자를 저장하고, 해당SecurityContext를 영속화합니다.- RemeberMeServices를 지원하는 경우,
RemeberMeServices.loginSuccess()을 실행합니다. - 새로운
InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent를 발생시킵니다. - 추가적인
AuthenticationSuccessHandler를 실행합니다.
- 실패한 경우 흐름은 다음과 같습니다.
SecurityContextHolder의 context를 비웁니다.- RemeberMeServices를 지원하는 경우,
RemeberMeServices.loginFail()을 실행합니다. - 추가적인
AuthenticationFailureHandler를 실행합니다.