식사하는 철학자 문제
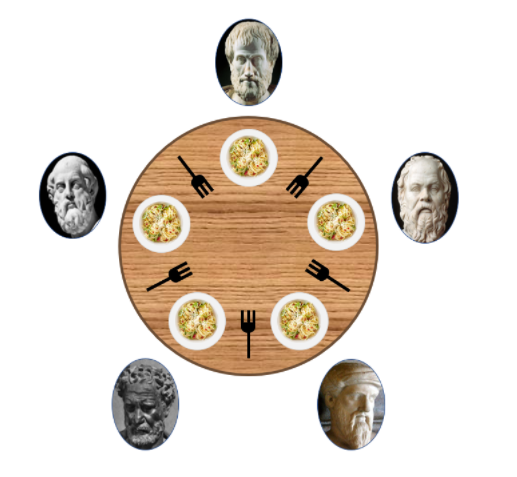
5명의 철학자가 원탁에 앉아서 식사를 한다. 철학자들 사이에는 포크가 하나씩 놓여 있고, 철학자들은 다음의 과정을 통해 식사를 한다.
1. 일정 시간 생각을 한다.
2. 왼쪽 포크가 사용 가능해질 때까지 대기한다. 만약 사용 가능하다면 집어든다.
3. 오른쪽 포크가 사용 가능해질 때까지 대기한다. 만약 사용 가능하다면 집어든다.
4. 양쪽의 포크를 잡으면 일정 시간만큼 식사를 한다.
5. 오른쪽 포크를 내려놓는다.
6. 왼쪽 포크를 내려놓는다.
7. 다시 1번으로 돌아간다.
간단하게 생각해, 만약 모든 철학자들이 동시에 자신의 왼쪽 포크를 잡는다면, 모든 철학자들이 자기 오른쪽의 포크가 사용 가능해질 때까지 기다려야 한다. 그런데 모든 철학자들이 그러고 있다. 이 상태에서는 모든 철학자가 영원히 3번 상태에 머물러있어 아무것도 진행할 수가 없게 되는데, 이것이 교착(Deadlock)상태이다. 출처
식사하는 철학자 문제 상황
초기 상태: 사람 5명, 젓가락 5개
실행 과정: 5명의 사람이 순차적으로 사용하지 않은 젓가락을 1개씩 집으면서 2개의 쌍을 맞춘다. 그리고 밥을 먹은 후 젓가락을 내려 놓는다. 이 과정을 무수히 빠르게 진행한다.
문제 발생 시점: 5명의 사람 모두 젓가락을 1개씩 집은 상황에서 젓가락 5개를 모두 사용했지만 5명 누구도 식사를 하지 못한다. 여기서 젓가락을 나눠주지도 못하므로 5명이 젓가락 1개씩 들고 하루 종일 밥만 구경하는 교착(Deadlock)상태에 걸려 무한히 대기한다. 이렇게 한번 교착상태에 빠진 철학자들은 계속 고뇌만 하다가 기아현상(Starvation)으로 굶어 죽는다.
식시하는 철학자 문제 코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM_PHILOSOPHER 5
#define HUNGRY 0;
#define THINKING 1;
int state[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
typedef struct _chopstick_t {
int value;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
} chopstick_t;
chopstick_t chopstick[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
void chopstick_init(chopstick_t *c, int value) {
c->value = value;
pthread_mutex_init(&c->lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&c->cond, NULL);
}
void chopstick_wait(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
while(c->value <= 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&c->cond, &c->lock);
}
c->value--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void chopstick_post(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
c->value++;
pthread_cond_signal(&c->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void get_chopstick(int philosopher) {
printf("philosopher %d waits for the left chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[philosopher]);
printf("philosopher %d waits for the right chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
printf("philosopher %d gets the chopsticks. \n", philosopher);
}
void put_chopstick(int philosopher) {
chopstick_post(&chopstick[philosopher]);
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
}
void *philosopher(int *number) {
while(1) {
printf("philosopher %d thinks \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
get_chopstick((int *) number);
printf("philosopher %d eats \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
put_chopstick((int *) number);
loop(1000000);
}
}
void test(int i) {
if(state[i+1]==0 && state[i]!=1 && state[i+2]!=1) {
state[i+1]=1;
}
}
void loop(int count) {
for(int i=0; i<count; i++);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
chopstick_init(&chopstick[i], 1);
}
pthread_t p[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
printf("[main begin] \n");
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, philosopher, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
pthread_join(p[i], NULL);
}
printf("[main end] \n");
return 0;
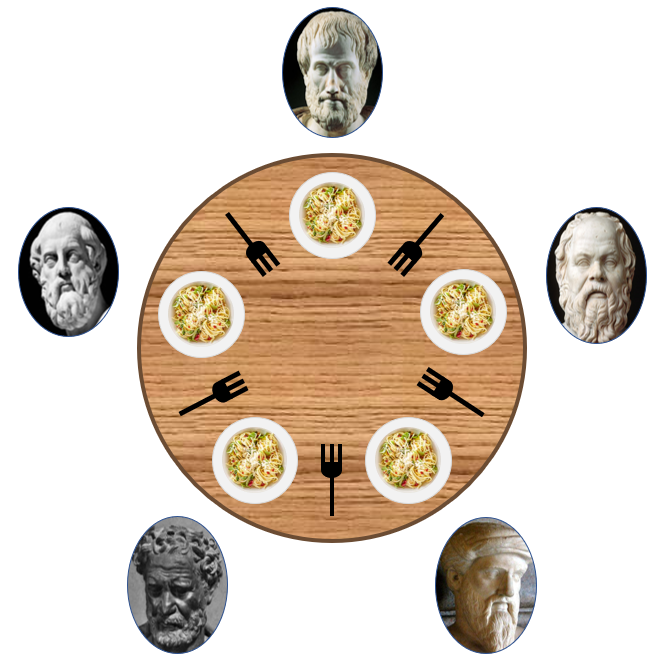
}방법 1. 젓가락 개수 늘리기
젓가락 개수를 5개에서 6개로 늘려 최악의 경우 5명이 젓가락 하나씩 집어도 1명은 2개의 젓가락으로 식사를 마치고 이 과정을 반복한다.
코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM_PHILOSOPHER 6
typedef struct _chopstick_t {
int value;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
} chopstick_t;
chopstick_t chopstick[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
void chopstick_init(chopstick_t *c, int value) {
c->value = value;
pthread_mutex_init(&c->lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&c->cond, NULL);
}
void chopstick_wait(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
while(c->value <= 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&c->cond, &c->lock);
}
c->value--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void chopstick_post(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
c->value++;
pthread_cond_signal(&c->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void get_chopstick(int philosopher) {
printf("philosopher %d waits for the left chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[philosopher]);
printf("philosopher %d waits for the right chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%6]);
printf("philosopher %d gets the chopsticks. \n", philosopher);
}
void put_chopstick(int philosopher) {
chopstick_post(&chopstick[philosopher]);
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%6]);
}
void *philosopher(int *number) {
while(1) {
printf("philosopher %d thinks \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
get_chopstick((int *) number);
printf("philosopher %d eats \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
put_chopstick((int *) number);
loop(1000000);
}
}
void loop(int count) {
for(int i=0; i<count; i++);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
chopstick_init(&chopstick[i], 1);
}
pthread_t p[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
printf("[main begin] \n");
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER-1; i++) {
pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, philosopher, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER-1; i++) {
pthread_join(p[i], NULL);
}
printf("[main end] \n");
return 0;
}방법 2. 철학자 위치 구분(홀짝)
1. 홀수 번 철학자, 짝수 번 철학자를 구분한다.
2. 홀수 번 철학자 인 경우는 젓가락을 왼쪽, 오른쪽 순으로 집어서 밥을 먹고 젓가락을 왼쪽, 오른쪽 순으로 놓는다.
3. 짝수 번 철학자인 경우는 젓가락을 오른쪽, 왼쪽 순으로 집어서 밥을 먹고 젓가락을 오른쪽, 왼쪽 순으로 놓는다.
- 교착상태의 4가지 필요조건 중 '환형대기'를 해결하여 이 문제를 해결하고 있다.
코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM_PHILOSOPHER 5
typedef struct _chopstick_t {
int value;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
} chopstick_t;
chopstick_t chopstick[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
void chopstick_init(chopstick_t *c, int value) {
c->value = value;
pthread_mutex_init(&c->lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&c->cond, NULL);
}
void chopstick_wait(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
while(c->value <= 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&c->cond, &c->lock);
}
c->value--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void chopstick_post(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
c->value++;
pthread_cond_signal(&c->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void odd_get_chopstick(int philosopher) {
printf("philosopher %d waits for the left chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[philosopher]);
printf("philosopher %d waits for the right chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
printf("philosopher %d gets the chopsticks. \n", philosopher);
}
void odd_put_chopstick(int philosopher) {
chopstick_post(&chopstick[philosopher]);
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
}
void even_get_chopstick(int philosopher) {
printf("philosopher %d waits for the left chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
printf("philosopher %d waits for the right chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[philosopher]);
printf("philosopher %d gets the chopsticks. \n", philosopher);
}
void even_put_chopstick(int philosopher) {
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
chopstick_post(&chopstick[philosopher]);
}
void *philosopher(int *number) {
int i=(int *) number;
while(1) {
printf("philosopher %d thinks \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
if(i%2==1){
odd_get_chopstick((int *) number);
} else {
even_get_chopstick((int *) number);
}
printf("philosopher %d eats \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
if(i%2==1){
odd_put_chopstick((int *) number);
} else {
even_put_chopstick((int *) number);
}
loop(1000000);
}
}
void loop(int count) {
for(int i=0; i<count; i++);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
chopstick_init(&chopstick[i], 1);
}
pthread_t p[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
printf("[main begin] \n");
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, philosopher, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
pthread_join(p[i], NULL);
}
printf("[main end] \n");
return 0;
}방법 3. 각각의 철학자 상태 구분
철학자가 EATING상태가 되기 위해서 자신이 HUNGRY상태이고, 자신의 왼쪽, 오른쪽 모두 EATING상태가 아니어야 한다.
- HUNGRY: 철학자가 젓가락 집기를 원함. (임계구역 접근을 원함)
- THINKING: 철학자가 젓가락 집기를 원치 않음 (임계구역 접근을 원치 않음)
- EATING: 철학자가 2개의 젓가락을 집어 밥을 먹는다. (임계구역에 접근함)
코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#define NUM_PHILOSOPHER 5
#define HUNGRY 0
#define THINKING 1
#define EATING 2
int state[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
typedef struct _chopstick_t {
int value;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
} chopstick_t;
chopstick_t chopstick[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
void chopstick_init(chopstick_t *c, int value) {
c->value = value;
pthread_mutex_init(&c->lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&c->cond, NULL);
}
void chopstick_wait(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
while(c->value <= 0) {
pthread_cond_wait(&c->cond, &c->lock);
}
c->value--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void chopstick_post(chopstick_t *c) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->lock);
c->value++;
pthread_cond_signal(&c->cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->lock);
}
void get_chopstick(int philosopher) {
printf("philosopher %d waits for the left chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[philosopher]);
printf("philosopher %d waits for the right chopstick. \n", philosopher);
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
printf("philosopher %d gets the chopsticks. \n", philosopher);
}
void put_chopstick(int philosopher) {
chopstick_post(&chopstick[philosopher]);
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(philosopher+1)%5]);
}
void *philosopher(int *number) {
int i=(int *)number;
while(1) {
printf("philosopher %d thinks \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
pickup(i);
printf("philosopher %d eats \n", (int *) number);
loop(1000000);
putdown(i);
loop(1000000);
}
}
void pickup(int i) {
state[i]=HUNGRY;
test(i);
if(state[i]!=EATING) {
chopstick_wait(&chopstick[i]);
}
}
void putdown(int i) {
state[i]=THINKING;
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(i+1)%5]);
chopstick_post(&chopstick[(i+4)%5]);
}
void test(int i) {
if(state[(i+4)%5]!=EATING && state[(i+1)]%5!=EATING && state[i]==HUNGRY) {
state[i]=EATING;
chopstick_post(&chopstick[i]);
}
}
void loop(int count) {
for(int i=0; i<count; i++);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
chopstick_init(&chopstick[i], 1);
}
pthread_t p[NUM_PHILOSOPHER];
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
state[i] = THINKING; // 처음엔 모두 생각
}
printf("[main begin] \n");
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
pthread_create(&p[i], NULL, philosopher, i);
}
for(int i=0; i<NUM_PHILOSOPHER; i++) {
pthread_join(p[i], NULL);
}
printf("[main end] \n");
return 0;
}