백준 23629번
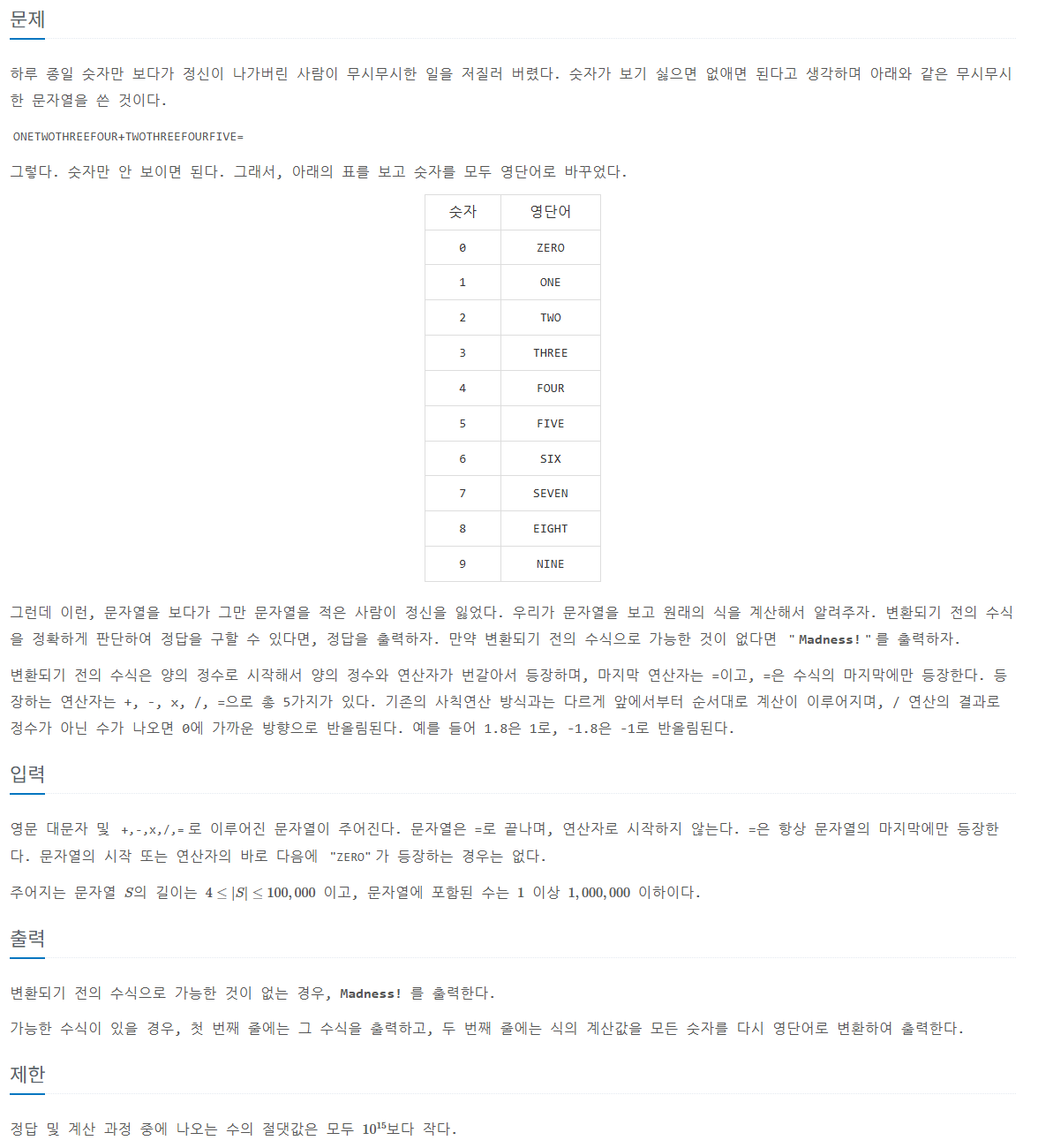
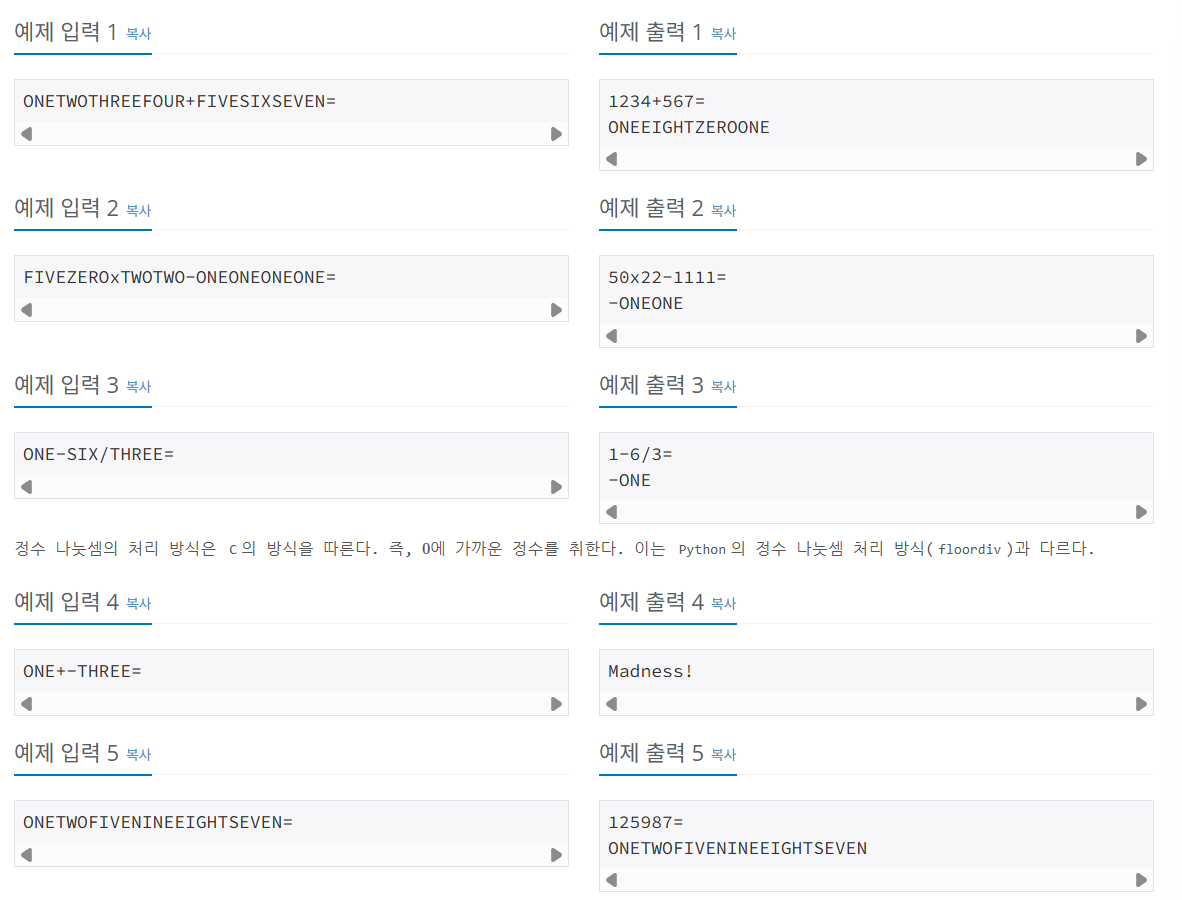
사전 지식: 문자열 파싱, 해시 맵(unordered_map)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
string str_cal;
cin >> str_cal;
unordered_map<string,int> word2digit = {
{"ZERO",0}, {"ONE",1}, {"TWO",2}, {"THREE",3}, {"FOUR",4},
{"FIVE",5}, {"SIX",6}, {"SEVEN",7}, {"EIGHT",8}, {"NINE",9}
};
unordered_map<char,string> digit2word = {
{'0',"ZERO"}, {'1',"ONE"}, {'2',"TWO"}, {'3',"THREE"}, {'4',"FOUR"},
{'5',"FIVE"}, {'6',"SIX"}, {'7',"SEVEN"}, {'8',"EIGHT"}, {'9',"NINE"}
};
string num_cal;
vector<char> ops;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)str_cal.size(); i++) {
if (str_cal[i] == '=') {
num_cal.push_back('=');
ops.push_back('=');
break;
}
if (isupper(str_cal[i])) {
string current;
for (int len = 0; len < 5 && i < (int)str_cal.size() && isupper(str_cal[i]); len++) {
current.push_back(str_cal[i++]);
if (word2digit.count(current)) {
num_cal.push_back(char('0' + word2digit[current]));
current.clear();
break;
}
}
i--;
if (!current.empty()) {
cout << "Madness!";
return 0;
}
}
else if (str_cal[i] == '+' || str_cal[i] == '-' || str_cal[i] == 'x' || str_cal[i] == '/') {
num_cal.push_back(str_cal[i]);
ops.push_back(str_cal[i]);
}
else {
cout << "Madness!";
return 0;
}
}
vector<long long> nums;
string numbuf;
for (char c : num_cal) {
if (isdigit(c)) {
numbuf.push_back(c);
} else {
if (numbuf.empty()) {
cout << "Madness!";
return 0;
}
nums.push_back(stoll(numbuf));
numbuf.clear();
if (c == '=') break;
}
}
int opCount = ops.size();
if ((int)nums.size() != opCount) {
cout << "Madness!";
return 0;
}
long long result = nums[0];
int idx = 0;
for (char op : ops) {
if (op == '=') break;
long long b = nums[++idx];
if (op == '+') result += b;
else if (op == '-') result -= b;
else if (op == 'x') result *= b;
else if (op == '/') {
if (b == 0) {
cout << "Madness!";
return 0;
}
result /= b;
}
}
cout << num_cal << '\n';
bool negative = (result < 0);
if (negative) result = -result;
string str_result = to_string(result);
if (negative) cout << "-";
for (char c : str_result) cout << digit2word[c];
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
코드 설명
- 필요한 라이브러리 가져오기
- 문자열로된 계산식 입력
- 문자열 > 숫자로, 숫자 > 문자열로 변환하는 unordered_map 생성
- 반복문으로 문자열을 하나씩 입력 받음
- 문자열이 = 일경우 : 연산 이 끝났기 때문에 break
- 문자열이 영단어인 경우 : 하나씩 current에 입력 후 word2digit와 비교 > 단어가 완성될 경우 num_cal에 변환하여 입력
- 첫번째 for문이 시작될때 i++이 되기 때문에 문자열 하나를 건너뛰는 현상 발생함 > i - -;로 해결
- current가 비어있지 않다면 대응 되는 단어가 없었다는 것 > Madness 후 코드 종료
- 문자열이 사칙연산인 경우 : 연산자 모음(ops)에 저장
- 위에 세 경우가 아닌 경우 : 대응되지 않은 문자열이기 때문에 Madness 후 코드 종료
- num_cal에서 숫자를 하나씩 꺼내서 numbuf에 임시로 추가
- 연산자일 경우 nums에 그전까지 추가했던 numbuf를 longlong으로 변환후 추가
- 만약 연산자로 시작할 경우 계산이 안되기 때문에 Madness 후 코드 종료
- 숫자 연산자 숫자 =(연산자) 꼴이여야 하기 때문에 연산자와 숫자의 개수가 같아야함 (연산자 숫자 = 꼴일경우 계산이 안되기 때문) > 같이 않다면 Madness 후 코드 종료
- 연산 진행
- 최종 result를 다시 문자열 연산꼴로 변경 (result가 음수일 경우 - 추가)


