State를 사용해 input 다루기
해당 시나리오를 따른다고 가정하자.
1. 폼에 무언가를 입력하면 “제출” 버튼이 활성화된다.
2. ”제출” 버튼을 누르면 폼과 버튼이 비활성화되고 스피너가 나타난다.
3. 네트워크 요청이 성공하면 폼은 숨겨지고 “감사합니다.” 메시지가 나타난다.
4. 네트워크 요청이 실패하면 오류 메시지가 보이고 폼은 다시 활성화된다.
1. 컴포넌트의 다양한 시각적 state 확인하기
사용자가 볼 수 있는 UI의 모든 'state'를 시각화한다.
- Empty: 폼은 비활성화된 “제출” 버튼을 가지고 있다.
- Typing: 폼은 활성화된 “제출” 버튼을 가지고 있다.
- Submitting: 폼은 완전히 비활성화되고 스피너가 보인다.
- Success: 폼 대신에 “감사합니다” 메시지가 보인다.
- Error: “Typing” state와 동일하지만 오류 메시지가 보인다.
2. 무엇이 state 변화를 트리거하는지 알아내기
휴먼 인풋과 컴퓨터 인풋으로 인해 state가 변경되는 상황을 확인한다.
- 텍스트 인풋을 변경하면 (휴먼) 텍스트 상자가 비어있는지 여부에 따라 state를 Empty에서 Typing 으로 또는 그 반대로 변경해야 한다.
- 제출 버튼을 클릭하면 (휴먼) Submitting state를 변경해야 한다.
- 네트워크 응답이 성공적으로 오면 (컴퓨터) Success state를 변경해야 한다.
- 네트워크 요청이 실패하면 (컴퓨터) 해당하는 오류 메시지와 함께 Error state를 변경해야 한다.
3. 메모리의 state를 useState로 표현하기
- state는 적을 수록 좋다.
const [answer, setAnswer] = useState('');
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [isEmpty, setIsEmpty] = useState(true);
const [isTyping, setIsTyping] = useState(false);
const [isSubmitting, setIsSubmitting] = useState(false);
const [isSuccess, setIsSuccess] = useState(false);
const [isError, setIsError] = useState(false);4. 불필요한 state 변수를 제거하기
- state가 역설을 일으키지는 않는지 확인한다.
- isTyping과 isSubmitting이 동시에 true일 수는 없다. 따라서, 두 boolean에 대한 유효한 state는 세 개뿐이고 이러한 “불가능한” state를 제거하기 위해 세 가지 값 'typing', 'submitting', 'success'을 하나의 status로 합칠 수 있다. - 다른 state 변수에 이미 같은 정보가 담겨있진 않는지 확인한다.
- isEmpty와 isTyping은 동시에 true가 될 수 없다. 이 경우에는 isEmpty를 지우고answer.length === 0으로 체크할 수 있다. - 다른 변수를 뒤집었을 때 같은 정보를 얻을 수 있진 않는지 확인한다.
- isError는error !== null로도 대신 확인할 수 있기 때문에 필요하지 않다.
결과
const [answer, setAnswer] = useState('');
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [status, setStatus] = useState('typing'); // 'typing', 'submitting', 'success'state 설정을 위해 이벤트 핸들러 연결하기
전체 코드
import { useState } from 'react';
export default function Form() {
const [answer, setAnswer] = useState('');
const [error, setError] = useState(null);
const [status, setStatus] = useState('typing');
if (status === 'success') {
return <h1>That's right!</h1>
}
async function handleSubmit(e) {
e.preventDefault();
setStatus('submitting');
try {
await submitForm(answer);
setStatus('success');
} catch (err) {
setStatus('typing');
setError(err);
}
}
function handleTextareaChange(e) {
setAnswer(e.target.value);
}
return (
<>
<h2>City quiz</h2>
<p>
In which city is there a billboard that turns air into drinkable water?
</p>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<textarea
value={answer}
onChange={handleTextareaChange}
disabled={status === 'submitting'}
/>
<br />
<button disabled={
answer.length === 0 ||
status === 'submitting'
}>
Submit
</button>
{error !== null &&
<p className="Error">
{error.message}
</p>
}
</form>
</>
);
}
function submitForm(answer) {
// 네트워크에 접속한다고 가정해봅시다.
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
let shouldError = answer.toLowerCase() !== 'lima'
if (shouldError) {
reject(new Error('Good guess but a wrong answer. Try again!'));
} else {
resolve();
}
}, 1500);
});
}
State 구조 선택하기
State 구조화 원칙
- 연관된 state 그룹화하기
- 두 개 이상의 state 변수를 항상 동시에 업데이트한다면, 단일 state 변수로 병합하는 것을 고려해야 한다.
- state 모순 피하기
- 불필요한 state 피하기
- 렌더링 중에 컴포넌트의 props나 기존 state 변수에서 일부 정보를 계산할 수 있다면, 컴포넌트의 state에 해당 정보를 넣지 않아야 한다.
- state의 중복 피하기
- 깊게 중첩된 state 피하기
- 깊게 계층화된 state는 업데이트하기 쉽지 않다. 가능하면 state를 평탄한 방식으로 구성하는 것이 좋다.
연관된 state 그룹화하기
- 두 개의 state 변수가 항상 함께 변경된다면, 단일 state 변수로 통합하는 것이 좋다.
// 단일
const [x, setX] = useState(0);
const [y, setY] = useState(0);
// 다중
const [position, setPosition] = useState({ x: 0, y: 0 });state 모순 피하기
// 기존
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const [isSending, setIsSending] = useState(false);
const [isSent, setIsSent] = useState(false);setIsSending과setIsSent은 동시에 true여서는 안된다.- 따라서 이 두 변수를 'typing'(초기값), 'sending', 'sent' 세가지 유효한 상태중 하나를 가질 수 있는 status 변수로 대체하는 것이 좋다.
// 변경
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const [status, setStatus] = useState('typing');불필요한 state 피하기
- 렌더링 중에 컴포넌트의 props나 기존 state 변수에서 일부 정보를 계산할 수 있다면, 컴포넌트의 state에 해당 정보를 넣지 않아야 한다.
// 기존
const [firstName, setFirstName] = useState('');
const [lastName, setLastName] = useState('');
const [fullName, setFullName] = useState('');- 렌더링 중에 항상 firstName과 lastName에서 fullName을 계산할 수 있기 때문에 state에서 제거해야한다.
// 변경
const [firstName, setFirstName] = useState('');
const [lastName, setLastName] = useState('');state의 중복 피하기
// 기존
const [items, setItems] = useState(initialItems);
const [selectedItem, setSelectedItem] = useState(
items[0]
);- selectItem의 내용이 items 목록 내의 항목 중 하나와 동일하다.
// 변경
const [items, setItems] = useState(initialItems);
const [selectedId, setSelectedId] = useState(0);깊게 중첩된 state 피하기
// 기존
// 각 place가 자식 장소의 배열을 가지는 트리 구조
childPlaces: [{
id: 1,
title: 'Earth',
childPlaces: [{
id: 2,
title: 'Africa',
childPlaces: [{
id: 3,
title: 'Botswana',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 4,
title: 'Egypt',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 5,
title: 'Kenya',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 6,
title: 'Madagascar',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 7,
title: 'Morocco',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 8,
title: 'Nigeria',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 9,
title: 'South Africa',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 10,
title: 'Americas',
childPlaces: [{
id: 11,
title: 'Argentina',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 12,
title: 'Brazil',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 13,
title: 'Barbados',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 14,
title: 'Canada',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 15,
title: 'Jamaica',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 16,
title: 'Mexico',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 17,
title: 'Trinidad and Tobago',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 18,
title: 'Venezuela',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 19,
title: 'Asia',
childPlaces: [{
id: 20,
title: 'China',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 21,
title: 'India',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 22,
title: 'Singapore',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 23,
title: 'South Korea',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 24,
title: 'Thailand',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 25,
title: 'Vietnam',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 26,
title: 'Europe',
childPlaces: [{
id: 27,
title: 'Croatia',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 28,
title: 'France',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 29,
title: 'Germany',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 30,
title: 'Italy',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 31,
title: 'Portugal',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 32,
title: 'Spain',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 33,
title: 'Turkey',
childPlaces: [],
}]
}, {
id: 34,
title: 'Oceania',
childPlaces: [{
id: 35,
title: 'Australia',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 36,
title: 'Bora Bora (French Polynesia)',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 37,
title: 'Easter Island (Chile)',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 38,
title: 'Fiji',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 39,
title: 'Hawaii (the USA)',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 40,
title: 'New Zealand',
childPlaces: [],
}, {
id: 41,
title: 'Vanuatu',
childPlaces: [],
}]
}]
}, {
id: 42,
title: 'Moon',
childPlaces: [{
id: 43,
title: 'Rheita',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 44,
title: 'Piccolomini',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 45,
title: 'Tycho',
childPlaces: []
}]
}, {
id: 46,
title: 'Mars',
childPlaces: [{
id: 47,
title: 'Corn Town',
childPlaces: []
}, {
id: 48,
title: 'Green Hill',
childPlaces: []
}]
}]- 너무 많이 중첩된 state는 평탄하게 만들어야 한다.
// 변경
// 각 palce가 자식 장소 ID의 배열을 가진다.
0: {
id: 0,
title: '(Root)',
childIds: [1, 42, 46],
},
1: {
id: 1,
title: 'Earth',
childIds: [2, 10, 19, 26, 34]
},
2: {
id: 2,
title: 'Africa',
childIds: [3, 4, 5, 6 , 7, 8, 9]
},
3: {
id: 3,
title: 'Botswana',
childIds: []
},
4: {
id: 4,
title: 'Egypt',
childIds: []
},
5: {
id: 5,
title: 'Kenya',
childIds: []
},
6: {
id: 6,
title: 'Madagascar',
childIds: []
},
7: {
id: 7,
title: 'Morocco',
childIds: []
},
8: {
id: 8,
title: 'Nigeria',
childIds: []
},
9: {
id: 9,
title: 'South Africa',
childIds: []
},
10: {
id: 10,
title: 'Americas',
childIds: [11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18],
},
11: {
id: 11,
title: 'Argentina',
childIds: []
},
12: {
id: 12,
title: 'Brazil',
childIds: []
},
13: {
id: 13,
title: 'Barbados',
childIds: []
},
14: {
id: 14,
title: 'Canada',
childIds: []
},
15: {
id: 15,
title: 'Jamaica',
childIds: []
},
16: {
id: 16,
title: 'Mexico',
childIds: []
},
17: {
id: 17,
title: 'Trinidad and Tobago',
childIds: []
},
18: {
id: 18,
title: 'Venezuela',
childIds: []
},
19: {
id: 19,
title: 'Asia',
childIds: [20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25],
},
20: {
id: 20,
title: 'China',
childIds: []
},
21: {
id: 21,
title: 'India',
childIds: []
},
22: {
id: 22,
title: 'Singapore',
childIds: []
},
23: {
id: 23,
title: 'South Korea',
childIds: []
},
24: {
id: 24,
title: 'Thailand',
childIds: []
},
25: {
id: 25,
title: 'Vietnam',
childIds: []
},
26: {
id: 26,
title: 'Europe',
childIds: [27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33],
},
27: {
id: 27,
title: 'Croatia',
childIds: []
},
28: {
id: 28,
title: 'France',
childIds: []
},
29: {
id: 29,
title: 'Germany',
childIds: []
},
30: {
id: 30,
title: 'Italy',
childIds: []
},
31: {
id: 31,
title: 'Portugal',
childIds: []
},
32: {
id: 32,
title: 'Spain',
childIds: []
},
33: {
id: 33,
title: 'Turkey',
childIds: []
},
34: {
id: 34,
title: 'Oceania',
childIds: [35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41],
},
35: {
id: 35,
title: 'Australia',
childIds: []
},
36: {
id: 36,
title: 'Bora Bora (French Polynesia)',
childIds: []
},
37: {
id: 37,
title: 'Easter Island (Chile)',
childIds: []
},
38: {
id: 38,
title: 'Fiji',
childIds: []
},
39: {
id: 40,
title: 'Hawaii (the USA)',
childIds: []
},
40: {
id: 40,
title: 'New Zealand',
childIds: []
},
41: {
id: 41,
title: 'Vanuatu',
childIds: []
},
42: {
id: 42,
title: 'Moon',
childIds: [43, 44, 45]
},
43: {
id: 43,
title: 'Rheita',
childIds: []
},
44: {
id: 44,
title: 'Piccolomini',
childIds: []
},
45: {
id: 45,
title: 'Tycho',
childIds: []
},
46: {
id: 46,
title: 'Mars',
childIds: [47, 48]
},
47: {
id: 47,
title: 'Corn Town',
childIds: []
},
48: {
id: 48,
title: 'Green Hill',
childIds: []
}컴포넌트 간 State 공유하기
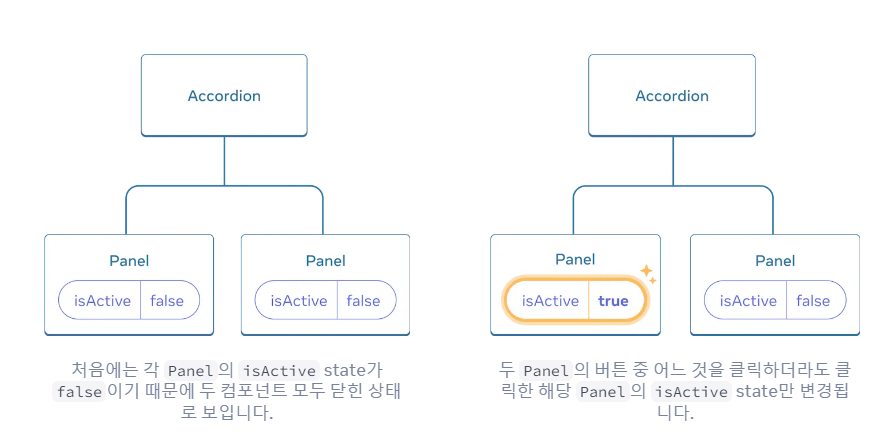
- 두 컴포넌트의 state가 항상 함께 변경되기를 원한다면 각 컴포넌트에서 state를 제거하고 가장 가까운 공통 부모 컴포넌트로 옮긴 후 props로 전달해야한다.(= State 끌어올리기)
- 자식 컴포넌트에서 state 제거하기
- 하드 코딩된 데이터를 부모 컴포넌트로 전달하기
- 공통 부모에 state 추가하기
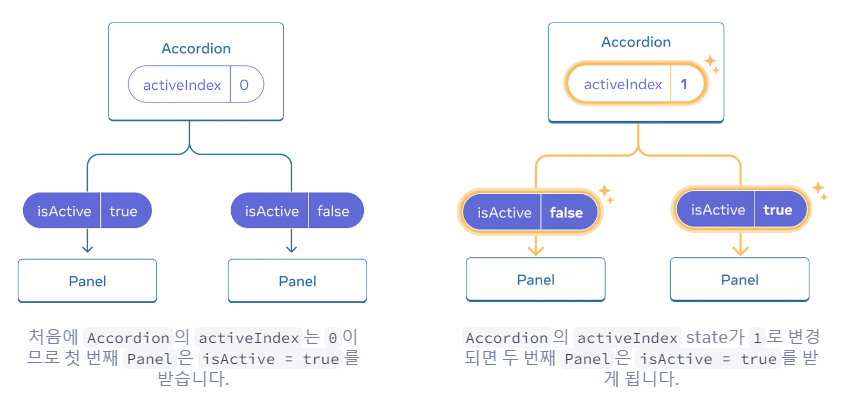
기존 구조
- 한번에 하나의 패널만 열리도록 변경하려면
State 끌어올리기가 필요하다.
자식 컴포넌트에서 state 제거하기
- Panel 컴포넌트에서 state 제거
const [isActive, setIsActive] = useState(false);- Panel Prop 목록에 isActive 추가
function Panel({ title, children, isActive }) {하드 코딩된 데이터를 부모 컴포넌트로 전달하기
- 조정하려는 두 자식의 가장 가까운 공통 부모 컴포넌트(여기선 Accordion)에 하드 코딩 값 전달하기
export default function Accordion() {
return (
<>
<h2>Almaty, Kazakhstan</h2>
<Panel title="About" isActive={true}>
With a population of about 2 million, Almaty is Kazakhstan's largest city. From 1929 to 1997, it was its capital city.
</Panel>
<Panel title="Etymology" isActive={true}>
The name comes from <span lang="kk-KZ">алма</span>, the Kazakh word for "apple" and is often translated as "full of apples". In fact, the region surrounding Almaty is thought to be the ancestral home of the apple, and the wild <i lang="la">Malus sieversii</i> is considered a likely candidate for the ancestor of the modern domestic apple.
</Panel>
</>
);
}공통 부모에 state 추가하기
- 상태 끌어올리기는 종종 state의 특성을 바꾼다.
- 해당 예제는 sate 변수에 bool값을 사용하는 대신, 활성화되어있는 Panel의 인덱스 숫자를 사용한다.
const [activeIndex, setActiveIndex] = useState(0);
<>
<Panel
isActive={activeIndex === 0}
onShow={() => setActiveIndex(0)}
>
...
</Panel>
<Panel
isActive={activeIndex === 1}
onShow={() => setActiveIndex(1)}
>
...
</Panel>
</>