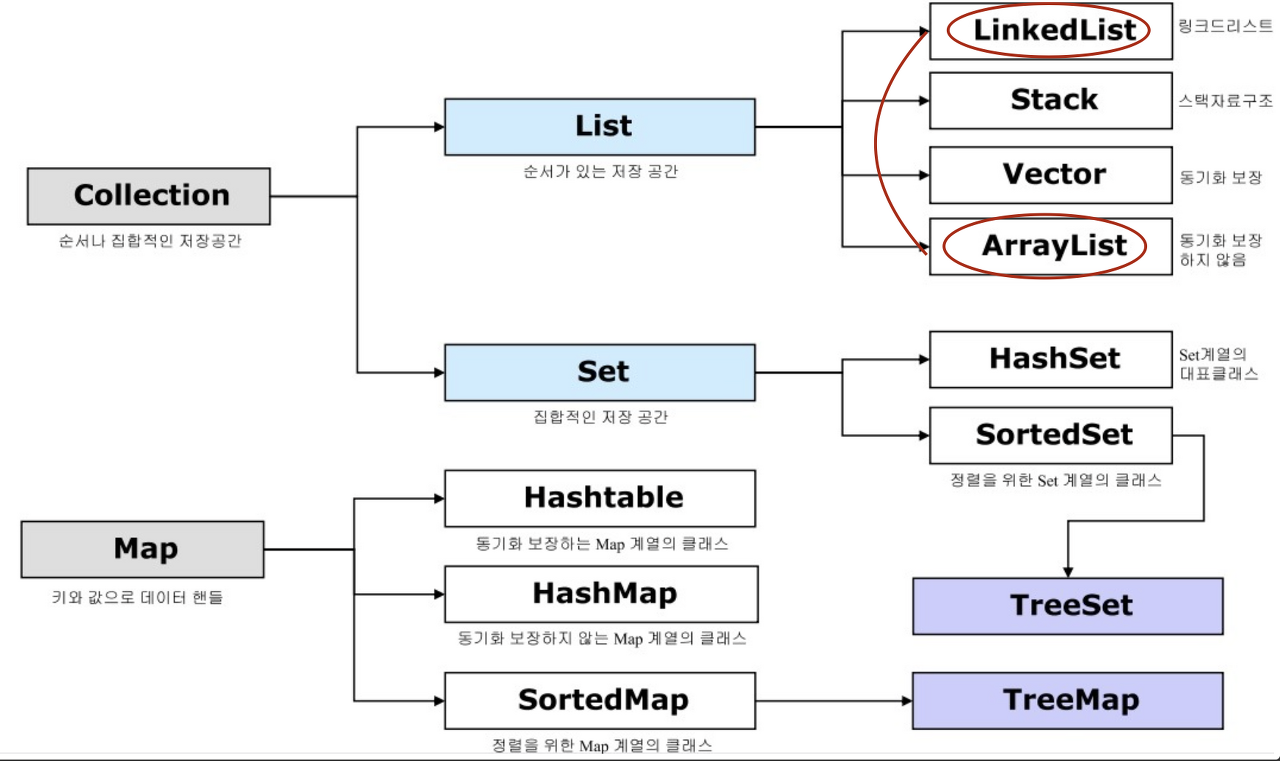
Collection (List, Set)
List (인터페이스)
- 중복 O. 가변 길이. 순서 있음.
- 구현체: ArrayList, LinkedList
구현
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
List<String> texts = new ArrayList<>(); //다형성
// ArrayList의 모든 메소드를 쓸 수는 없음. ArrayList
데이터가 삭제될 경우 빈 공간을 앞으로 당긴다.
메소드
.add(1, "중간");
.set(1, "중간"); //인덱스가 있으므로 Set과 차별화되는 메소드
.get(1); //인덱스가 있으므로 Set과 차별화되는 메소드
.remove(index)
.remove(value)
.size();
최초공간 지정
ArrayList<String> texts = new ArrayList<>(30);공간 늘리기
import java.util.ArrayList;
ArrayList<String> texts = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
// null 값으로 채운다
texts.add(null);
}
int size = texts.size(); //20데이터 삭제
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> texts = new ArrayList<>();
// index 0
texts.add("딸기");
// index 1
texts.add("포도");
// index 2
texts.add("사과");
// 인덱스를 이용한 값 삭제
texts.remove(1);
// 값을 검색하여 값 삭제
texts.remove("포도");
int size = texts.size(); //2
System.out.println(texts.get(1)); //사과
}
}Set
중복 X. 값 자체가 키. null 입력은 가능.
구현체: HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet
HashSet
- 순서 없음.
- 내부적으로 HashMap을 사용.
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>();
//데이터 삽입
set.add("코드라떼");
set.add("codelatte");
boolean isExist = set.contains("codelatte");
//데이터 삭제
set.remove("codelatte");
//데이터 여부 확인
boolean isExist = set.contains("codelatte");LinkedHashSet
- 저장한 순서대로 데이터를 정렬함.
- 내부적으로 LinkedHashMap을 사용.
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
// String value
LinkedHashSet<String> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 데이터 삽입
set.add("1");
set.add("23");
set.add("3");
set.add("14");
set.add("2");
set.add("5");
for (String value : set) {
System.out.println(value);
}
// "1", "23", "3", "14", "2", "5"TreeSet
- 오름차순으로 데이터를 정렬함.
- 내부적으로 TreeMap을 사용.
import java.util.TreeSet;
// String value
TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<>();
// 데이터 삽입
set.add("1");
set.add("3");
set.add("2");
set.add("4");
set.add("2"); //Set은 중복 X므로 무시.
set.add("5");
for (String value : set) {
System.out.println(value);
}
// "1", "2", "3", "4", "5"부분집합
.containsAll()교집합
.retainAll()Map (인터페이스)
- 속성과 값으로 구분됀 데이터 집합의 객체. 중복된 key 불가능.
- 구현체: Hashmap, TreeMap, LinkedHashMap
.entrySet().keySet().values()
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
.put("id", 3);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
.put("title", "hello");
.put("hit", 12);
HashMap<Key, Value> map = new HashMap<>();
//데이터 삽입 "key", "value"
map.put("codelatte", "코드라떼");
Strinv val = map.get("codelatte");
//key 값을 이용하여 삭제
map.remove("codelatte")
//key 값 출력
for(String key : map.keySet()){
System.out.println(key);
}
//value 값 출력
for(String value : map.values()){
System.out.println(value);
}
Hashmap에서 동일한 key 사용해서 저장하면 => 기존 저장 값이 덮어쓰기 됌.