알고리즘 연습할 때 자주 나오는 HashMap 에 대해 이번 기회에 정리해본다.
💡 HashMap ?
맵(map) 인터페이스를 통해 해싱된 맵을 HashMap이라 부른다.
- 맵 : Key와 Value로 구성된 Entry 객체를 저장하는 자료구조.
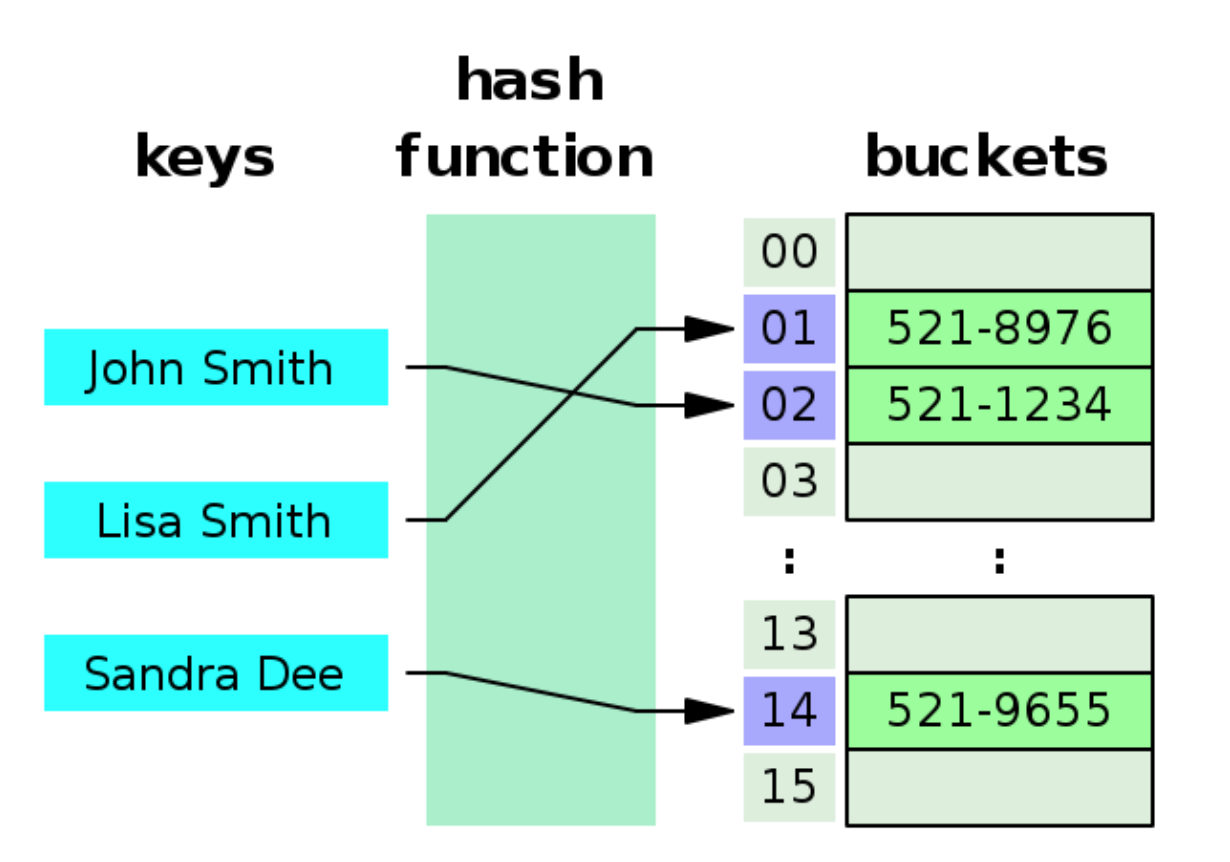
하나의 Key에 대한 Value 값을 저장하기 위해서 Hash Function을 통해 생성된 값(int)으로 배열의 해당 인덱스에 저장한다.
해싱된 값을 통해 인덱스의 값을 찾기 때문에 속도가 빠른 장점이 있다.
💡 HashMap 선언 및 사용법
- 선언
HashMap<Integer,String> hm = new HashMap<Integer, String>(); // 해시 선언- 값 추가
hm.put(1, "one");
hm.put(2, "two");
hm.put(3, "three");
- 출력
- 해시맵 전부 출력
System.out.println(hm);
// 출력 > {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
- 특정 키에 대한 밸류 출력
System.out.println(hm.get(3));
// 출력 > three- EntrySet() 활용 출력
- Key, Value 모든 값을 가져와야할 때 사용
for(Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : hm.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key : " + entry.getKey() + " / value : " + entry.getValue());
}
// 출력 > key : 1 / value : ome
// key : 2 / value : two
// key : 3 / value : three- KeySet() 활용 출력
- Key에 대한 Value 값을 가져와야할 때 사용
for(int i : hm.keySet()){
System.out.println("Key : " + i + " / Value : " + hm.get(i));
}
// 출력 > key : 1 / value : ome
// key : 2 / value : two
// key : 3 / value : three- 값 삭제
hm.remove(key값); // 해당 키에 대한 밸류 값 삭제
hm.clear(); // 해시 전체 삭제크기 계산
hm.sizes();특정 키 포함 확인
hm.contiansKey(3);
