🧑🏻💻 문제
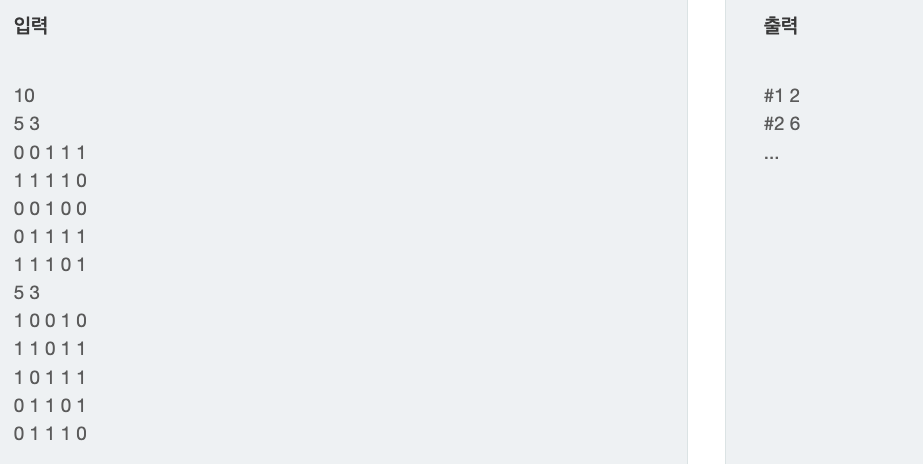
1로 적혀 있는 곳에 글자가 들어갈 수 있으며 첫 라인에 주어지는 두개의 수를 N, K로 저장한다.
N 은 배열의 가로 세로 크기이며, K 는 단어의 길이이다.
처음에 어떻게 접근해야할지 감이 오지 않아 다른 사람의 풀이를 참고하였다.
해결 방법
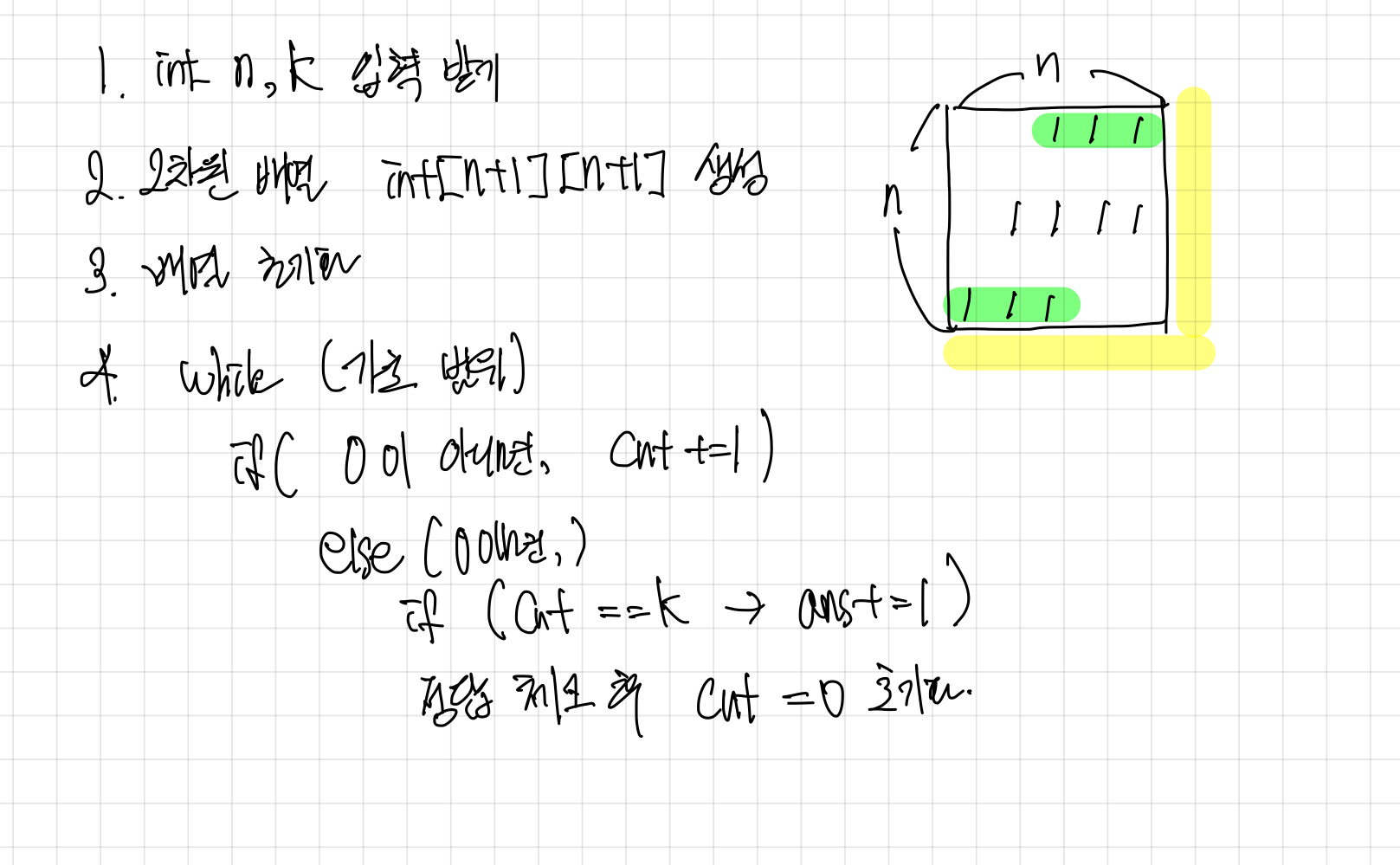
-
배열의 값이 0이 아니면 count 를 진행한다.
1-1. 이를 위해 배열을 int[N+1][N+1] 로 초기화하여 위 그림상 노란 부분은 0으로 만들어 준다. -
만약 0을 만났다면, count 가 K 와 같은지 값을 비교한다.
2-1. 값이 같다면, ans++ 를 진행하고 count 값을 다시 0으로 초기화한다. -
해당 과정을 가로, 세로 총 2번 진행하여 마지막 ans 값을 출력한다.
코드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int T = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
for (int test_case = 1; test_case <= T; test_case++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int K = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] arr = new int[N + 1][N + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int ans = 0;
// 가로
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N + 1; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0) {
cnt += 1;
} else {
if (cnt == K) {
ans += 1;
}
cnt = 0;
}
}
}
// 세로
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < N+1; j++) {
if (arr[j][i] != 0) {
cnt += 1;
} else {
if (cnt == K) {
ans += 1;
}
cnt = 0;
}
}
}
System.out.println("#" + test_case + " " + ans);
}
}
}
