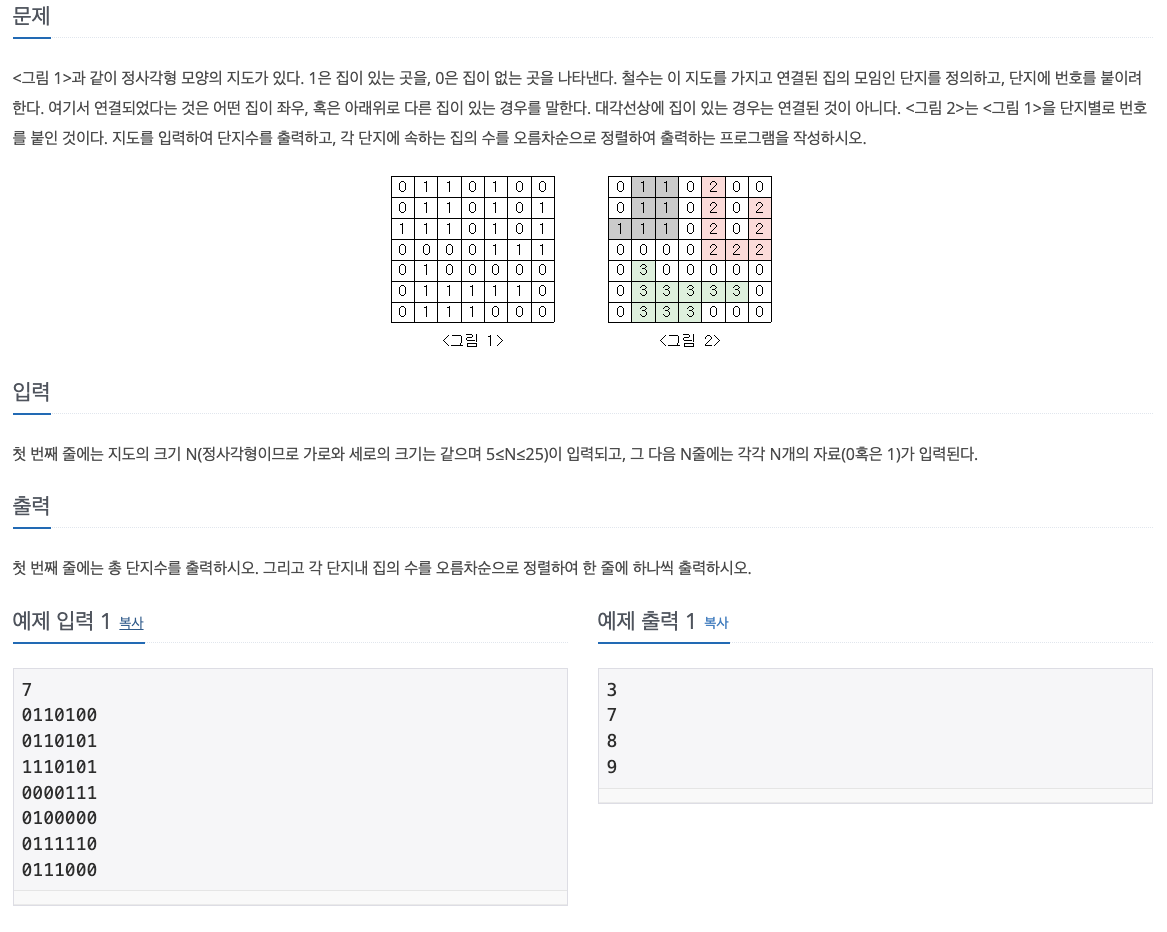
🧑🏻💻 문제
💡문제 분석 요약
DFS를 활용해서 주어진 그래프 내에 각 DFS 안의 노드가 몇개인지 탐색하는 문제이다.
💡알고리즘 설계
- 그래프 배열 생성
- 방문 여부 배열 생성
- 그래프를 처음부터 끝까지 돌면서 1이 있는 인덱스를 만나면 DFS 시작
3-1. DFS가 수행될 때 count를 통해 몇 번 재귀 되는지 탐색 - 각 DFS에서 count 값을 리스트에 저장하여 마지막에 출력
💡코드
public class Main {
static int[][] arr; // 그래프를 저장할 배열
static int N; // 입력 값에서 주어지는 그래프 크기
static boolean[][] visited; // 방문 여부 확인을 위한 배열
static int[] dx = {0, 1, -1, 0}; // 각 노드에서 상하좌우로 이동하기 위한 값
static int[] dy = {1, 0, 0, -1};
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
static ArrayList<Integer> houseCounts = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main (String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new int[N][N];
visited = new boolean[N][N];
// 배열 생성
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
int temp = line.charAt(j) - '0';
arr[i][j] = temp;
}
}
// 그래프 DFS 시작
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0 && !visited[i][j]) {
int houseCount = dfs(i,j); // DFS 결과 값을 저장
houseCounts.add(houseCount); // 값 리스트에 추가
}
}
}
Collections.sort(houseCounts);
System.out.println(houseCounts.size());
for (int h : houseCounts) {
System.out.println(h);
}
}
private static int dfs(int a, int b) {
visited[a][b] = true; // 일단 방문처리하고
int sum = 1; // DFS 반복 카운트를 위한 변수 선언
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 상하좌우기 때문에 4번 반복
int newA = a + dx[i];
int newB = b + dy[i];
// 상하좌우로 이동된 값이 배열 크기 안에 있으며, 방문하지 않았을 때
if (newA >= 0 && newA < N && newB >=0 && newB < N && arr[newA][newB] != 0 && !visited[newA][newB]) {
sum += dfs(newA, newB); // 값 누적
}
}
return sum;
}
}💡시간복잡도
N*N 배열에 대해 깊이 우선 탐색 알고리즘을 사용하였기에 O(N^2)의 시간복잡도를 갖는다.
💡 틀린 이유
DFS 탐색을 진행할 때 상하좌우로 인덱스가 이동하면서 그래프 배열을 벗어나 배열 인덱스 초과 오류가 발생했다. 해당 문제를 해결하기 위해 0보다 작지 않고 N보다 크지 않다는 제약 사항을 추가하였다.
DFS 값을 구할 때
sum += dfs(newA, newB);위와 같은 로직으로 누적되게 해야 하는데 아이디어가 떠오르지 않았다. 다음엔 누적값을 구할 때 static 변수 선언을 한 뒤 함수에서 return 하지 말고 밖에서 접근하는 방식으로 해보자. 아래 코드 처럼
💡 틀린 부분 수정 or 다른 풀이
class Main {
final static int MAX = 25 + 10;
static boolean[][] graph;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int countPerDanji;
static int dirY[] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
static int dirX[] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
static void dfs(int y, int x) {
visited[y][x] = true;
countPerDanji++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newY = y + dirY[i];
int newX = x + dirX[i];
if (!visited[newY][newX] && graph[newY][newX])
dfs(newY, newX);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
graph = new boolean[MAX][MAX];
visited = new boolean[MAX][MAX];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
String s = br.readLine();
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
graph[i][j] = s.charAt(j - 1) == '1';
}
ArrayList<Integer> countList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++)
if (graph[i][j] && !visited[i][j]) {
countPerDanji = 0;
dfs(i, j);
countList.add(countPerDanji);
}
System.out.println(countList.size());
Collections.sort(countList);
for (int i = 0; i < countList.size(); i++)
System.out.println(countList.get(i));
br.close();
}
}
출처: https://coding-grandpa.tistory.com/121 [개발자로 취직하기:티스토리]💡 느낀점 or 기억할정보
- static 변수 활용하기
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException발생이 줄어들도록 연습

