일반적으로 안드로이드에서 생명 주기 관련 동작을 정의할 때 Activity 나 Fragment 의 생명 주기 관련 메소드를 Override해서 구현하는 경우가 많다. 하지만 이는 좋지 못한 코드를 만들게 되고 오류도 자주 발생시킨다.
기존 생명 주기 메소드 재정의 방식의 문제점
class MyActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var myLocationListener: MyLocationListener
override fun onCreate(...) {
myLocationListener = MyLocationListener(this) { location ->
// update UI
}
}
public override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
myLocationListener.start()
// manage other components that need to respond
// to the activity lifecycle
}
public override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
myLocationListener.stop()
// manage other components that need to respond
// to the activity lifecycle
}
}위의 예시처럼 코드를 구성할 경우의 문제점은 아래와 같다.
Activity의 생명 주기 변화에 따라 UI 및 다른 컴포넌트를 관리하기 위한 호출이 지나치게 자주 발생한다.- 화면 구성요소가 많아질수록
onStart()나onStop()과 같은 생명 주기 메소드의 코드량이 증가한다. Activity나Fragment가 종료되기 전에 컴포넌트가 시작된다는 보장이 없다.
이를 해결하기 위해 나온 게 AAC의 Lifecycle 라이브러리이다.
Lifecycle
class MyActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var myLocationListener: MyLocationListener
override fun onCreate(...) {
myLocationListener = MyLocationListener(this) { location ->
// update UI
}
}
public override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
Util.checkUserStatus { result ->
// what if this callback is invoked AFTER activity is stopped?
if (result) {
myLocationListener.start()
}
}
}
public override fun onStop() {
super.onStop()
myLocationListener.stop()
}
}Lifecycle 은 Activity나 Fragment 같은 컴포넌트의 생명 주기 상태 관련 정보를 포함하며 다른 객체가 상태를 관찰할 수 있게 해주는 클래스이다.
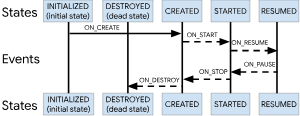
이벤트
프레임워크 및 Lifecycle 클래스에서 전달되는 자체 생명 주기 이벤트가 Activity 나 Fragment 의 콜백 이벤트에 매핑된다.
상태
Lifecycle 객체가 추적한 컴포넌트의 현재 상태를 표시한다.
사용자는 DefaultLifecycleObserver 인터페이스의 onCreate() , onStart() 등의 메소드를 재정의하여 생명 주기 상태를 모니터링할 수 있다.
class MyObserver : DefaultLifecycleObserver {
override fun onResume(owner: LifecycleOwner) {
connect()
}
override fun onPause(owner: LifecycleOwner) {
disconnect()
}
}
myLifecycleOwner.getLifecycle().addObserver(MyObserver())LifecycleOwner
LifecycleOwner 는 클래스에 Lifecycle 이 있음을 나타내는 단일 메소드 인터페이스이다. 이 인터페이스에는 오직 getLifecycle() 메소드 하나만 존재한다.
internal class MyLocationListener(
private val context: Context,
private val lifecycle: Lifecycle,
private val callback: (Location) -> Unit
): DefaultLifecycleObserver {
// DefaultLifecycleObserver 인터페이스 구현
// 생명 주기 상태 변경에 따른 로직이 Activity가 아닌
// MyLocationListener 에서 선언되게 하기 위함.
private var enabled = false
override fun onStart(owner: LifecycleOwner) {
if (enabled) {
// connect
}
}
fun enable() {
enabled = true
if (lifecycle.currentState.isAtLeast(Lifecycle.State.STARTED)) {
// connect if not connected
}
}
override fun onStop(owner: LifecycleOwner) {
// disconnect if connected
}
}
class MyActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var myLocationListener: MyLocationListener
override fun onCreate(...) {
// Activity의 Lifecycle로 초기화
myLocationListener = MyLocationListener(this, lifecycle) { location ->
// update UI
}
Util.checkUserStatus { result ->
if (result) {
myLocationListener.enable()
}
}
}
}위 예시 코드에서 MyLocationListener는 DefaultLifecycleObserver 인터페이스를 구현하고 MyActivity 의 onCreate() 메소드에서 초기화 및 액티비티의 생명 주기를 추적한다.
따라서 MyActivity의 생명 주기 변화에 따른 로직을 MyActivity 가 아닌 MyLocationListener 에서 정의할 수 있게 된다.
레퍼런스)
https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/architecture/viewmodel?hl=ko

