CoroutineContext
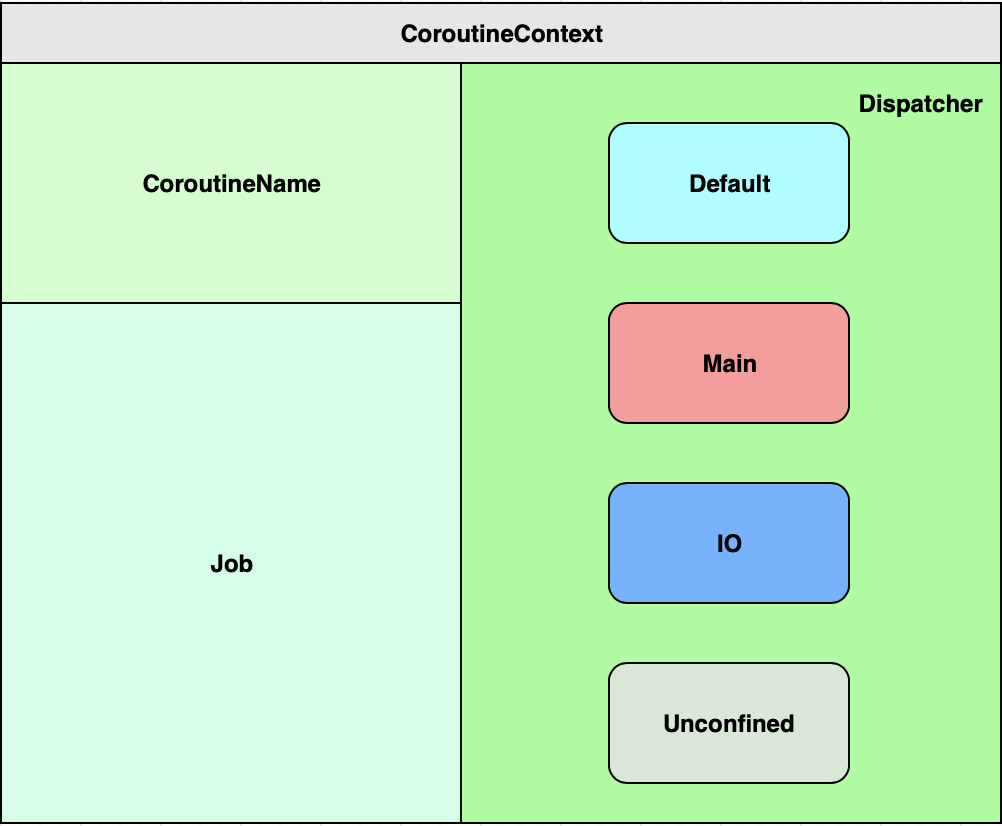
모든 코틀린 코루틴(Coroutine)은 컨텍스트(Context)를 가지고 있는데, 이것은 CoroutineContext 인터페이스를 구현한 객체이다. CoroutineContext 는 다양한 구성요소(Element)를 가지고 있다.
CoroutineContext 는 map 이나 set 과 유사한 형태를 하고 있으며 Job, CoroutineName, CoroutineDispatcher, CoroutineExceptionHandler 와 같은 Element 인스턴스를 순서가 있는 Set(indexed set)으로 관리한다.
각 Element 는 get 이나 fold 메소드를 통해서 추가하거나 꺼내올 수 있으며, 다른 CoroutineContext 를 plus 나 minus 연산을 통해 특정한 Element 를 합치거나 삭제할 수도 있다.
Dispatchers
Dispatcher 는 코루틴을 특정 쓰레드에서 실행할 수 있도록 해준다.
Android Kotlin에서는 코루틴을 실행할 위치를 지정하는데 사용할 수 있는 세 가지 Dispatcher 를 제공한다.
- Dispatchers.Main - 이
Dispatcher는 UI와 상호작용하고 빠른 작업을 실행하기 위해서만 사용해야 한다. 예를 들어 suspend 함수를 호출하고 Android UI 프레임워크 작업을 실행하며 LiveData 객체를 업데이트한다. - Dispatchers.IO - 이
Dispatcher는 기본 스레드 외부에서 디스크 또는 네트워크 I/O를 실행하도록 최적화되어 있다. 예를 들어 Room DB를 사용하고 파일에서 읽거나 파일에 쓰며 네트워크 작업을 실행한다. - Dispatchers.Default - 이
Dispatcher는 CPU를 많이 사용하는 작업을 기본 스레드 외부에서 실행하도록 최적화되어 있다. 예를 들어 목록을 정렬하고 JSON을 파싱한다.
CoroutineScope
CoroutineScope 는 코루틴의 범위를 의미하며, 코루틴의 생명주기를 함께하는 전체적인 Scope이다.
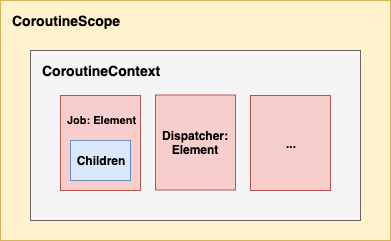
CoroutineScope 인터페이스의 변수는 오직 CoroutineContext 하나만 존재한다. 즉, 코루틴을 관리하는 제일 큰 범위의 인터페이스이다.
CoroutineScope를 사용하면 코루틴을 특정 범위 내에서 실행하고, 해당 범위 내의 코루틴의 실행을 취소할 수 있다.
보통 하나의 CoroutineScope 안에서 여러 코루틴들이 생성되기 때문에 이를 한 곳에서 관리하고, 코루틴이 종료되거나 예외 발생 등 취소를 할 때 같은 CoroutineScope 내의 코루틴을 한번에 취소함으로써 메모리 누수를 방지할 수 있다.
또한 같은 CoroutineScope 내의 코루틴들은 범위 내에서 변수와 같은 데이터를 공유하여 통신할 수 있다.
class MyUIClass {
val scope = MainScope() // the scope of MyUIClass, uses Dispatchers.Main
fun destroy() { // destroys an instance of MyUIClass
scope.cancel() // cancels all coroutines launched in this scope
// ... do the rest of cleanup here ...
}
/*
* Note: if this instance is destroyed or any of the launched coroutines
* in this method throws an exception, then all nested coroutines are cancelled.
*/
fun showSomeData() = scope.launch { // launched in the main thread
// ... here we can use suspending functions or coroutine builders with other dispatchers
draw(data) // draw in the main thread
}
}
Job
launch 또는 async 로 만들어진 각 코루틴은 코루틴을 고유하게 식별하고 수명 주기를 관리하는 Job 인스턴스를 반환한다.
이 Job 을 CoroutineScope 에 전달하여 코루틴의 수명 주기를 추가로 관리할 수도 있다.
class ExampleClass {
...
fun exampleMethod() {
// Handle to the coroutine, you can control its lifecycle
val job = scope.launch {
// New coroutine
}
if (...) {
// Cancel the coroutine started above, this doesn't affect the scope
// this coroutine was launched in
job.cancel()
}
}
}Coroutine Builder
코루틴 빌더(Coroutine Builder) 는 코루틴을 생성하고 실행하기 위해 사용되는 함수들을 말한다.
launch 빌더
코루틴을 생성하고 실행하는 가장 기본적인 방법이다.
새 코루틴을 시작하고 결과를 반환하지 않으며 '실행 후 삭제'로 간주되는 모든 작업은 launch 를 사용하여 시작할 수 있다.
launch {
// 비동기 작업 수행
}async 빌더
launch 와 비슷하지만 반환값을 가질 수 있다. await 이라는 정지 함수를 통해 결과를 반환할 수 있으며 이때 Deferred 라는 형태의 객체로 반환한다.
여러개의 async 를 사용하여 병렬로 작업을 수행하고 결과를 모아서 처리할 수도 있다.
suspend fun fetchTwoDocs() =
coroutineScope {
val deferredOne = async { fetchDoc(1) }
val deferredTwo = async { fetchDoc(2) }
deferredOne.await()
deferredTwo.await()
}suspend fun fetchTwoDocs() = // called on any Dispatcher (any thread, possibly Main)
coroutineScope {
val deferreds = listOf( // fetch two docs at the same time
async { fetchDoc(1) }, // async returns a result for the first doc
async { fetchDoc(2) } // async returns a result for the second doc
)
deferreds.awaitAll() // use awaitAll to wait for both network requests
}runBlocking 빌더
runBlocking 은 코루틴을 실행하는 블록을 만든다. runBlocking 블록 안에서는 새로운 코루틴을 생성하고 실행할 수 있으며, 블록 내의 코드가 모두 완료될 때까지 대기(Blocked)한다.
fun main() = runBlocking {
launch {
// 비동기 작업 수행
}
// 다른 코드
}withContext 빌더
withContext 는 현재 코루틴의 컨텍스트를 변경하여 다른 스레드나 스레드 풀에서 작업을 수행할 때 사용된다.
기존의 코루틴 컨텍스트를 변경하여 작업을 수행하고, 작업이 끝나면 원래의 컨텍스트로 돌아온다.
suspend fun fetchDocs() { // Dispatchers.Main
val result = get("developer.android.com") // Dispatchers.Main
show(result) // Dispatchers.Main
}
suspend fun get(url: String) = // Dispatchers.Main
withContext(Dispatchers.IO) { // Dispatchers.IO (main-safety block)
/* perform network IO here */ // Dispatchers.IO (main-safety block)
} // Dispatchers.Main
}레퍼런스)
1. Kotlin 코루틴으로 앱 성능 향상
2. 처음 시작하는 코루틴, 기본적인 용어와 이해
3. CoroutineScope
4. [Kotlin] Coroutine - 2. CoroutineScope & Context & Dispathcer 을 파헤쳐보자
