app.use()
Spring의 Filter와 비슷한 것 같다고 느꼈습니다.
요청이 왔을 때 모든 요청 혹은 지정한 URL에 대한 요청에 대해 등록한 middleware function을 실행합니다.
app.use() 함수는 Express 앱에서 항상 실행하는 미들웨어의 역할을 합니다. app.get(), app.post() 등과 달리 요청 URL을 지정하지 않아도 app.use()를 사용할 수 있으며, 해당 경우에는 URL에 상관없이 앱이 요청을 수신할 때마다 매번 실행됩니다.
· app.use는 지정된 경로에 지정된 미들웨어 함수를 마운트하는데 사용합니다.
· 모든(또는 특정) 요청에 대한 공통 로직을 처리하기 위해 사용할 수 있습니다.
· 주로 애플리케이션에 대한 미들웨어를 설정하는데 사용됩니다. (모듈식 라우터, 에러 핸들링, 공통 미들웨어, .. 등)
Middleware function
express()를 호출하여 app object를 생성합니다. 이는 Express application을 나타냅니다. app object 의 app.use(), app.get()을 사용하여 요청 핸들러 middleware를 app에 bind 합니다.
형식
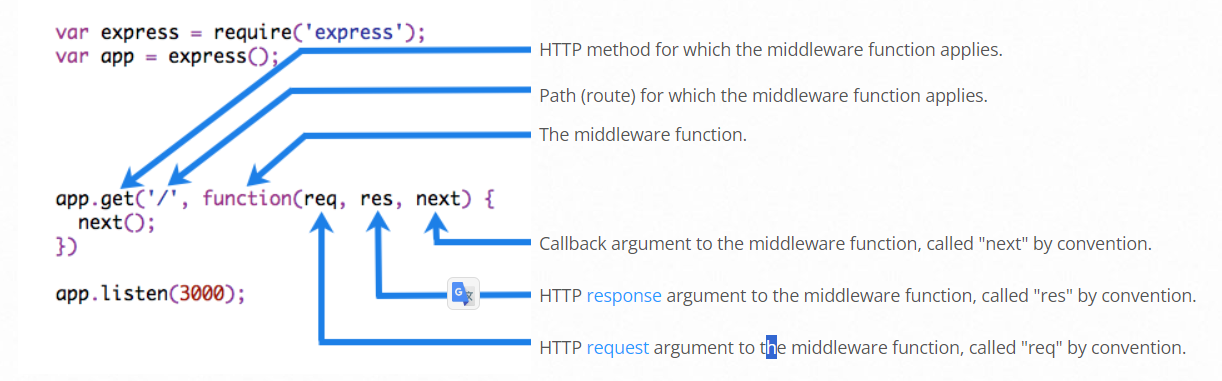
app.use()하면 미들웨어 함수가 로드됩니다. 먼저 로드되는 것이 먼저 실행됩니다.
라우트 핸들러 정의 이후에 미들웨어를 로드하도록 정의하면 실행되지 않습니다.
라우트 핸들러에서 요청-응답 사이클이 종료되기 때문입니다.
const requestTime = function (req, res, next) {
req.requestTime = Date.now()
next()
}
app.use(requestTime)
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
let responseText = 'Hello World!<br>'
responseText += `<small>Requested at: ${req.requestTime}</small>`미들웨어 함수를 처리하고 그 req 객체가 다음 미들웨어(라우트 핸들러)에 전달됩니다.
Configurable middleware
module.exports = function (options) {
return function (req, res, next) {
// Implement the middleware function based on the options object
next()
}
}
The middleware can now be used as shown below.
const mw = require('./my-middleware.js')
app.use(mw({ option1: '1', option2: '2' }))이렇게 설정 가능한 미들웨어를 정의할 수 있습니다. 옵션을 파라미터로 갖는 함수, 옵션에 따라 구현이 바뀌는 미들웨어를 리턴하도록 합니다. 이를 export합니다.
쿠키-세션, 압축 구현할 때 사용할 수 있습니다.
Application level middleware
app.use()로 app object에 바인드 되는 것은 Application level middleware입니다. mount path 가 없는 미들웨어는 경로에 상관없이 매 요청마다 실행됩니다.
app.use('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)
next()
}, (req, res, next) => {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
})하나의 mount path에 대해 연속으로 middleware function를 정의할 수도 있습니다.
app.get('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => {
console.log('ID:', req.params.id)
next()
}, (req, res, next) => {
res.send('User Info')
})
// handler for the /user/:id path, which prints the user ID
app.get('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => {
res.send(req.params.id)
})같은 Method 의 같은 path에 여러 개의 route를 정의할 수 있습니다.
그러나 2번 째 핸들러는 실행되지 않습니다. 1번 째 핸들러가 req-res cycle을 종료시키기 때문입니다.
app.get('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => {
// if the user ID is 0, skip to the next route
if (req.params.id === '0') next('route')
// otherwise pass the control to the next middleware function in this stack
else next()
}, (req, res, next) => {
// send a regular response
res.send('regular')
})
// handler for the /user/:id path, which sends a special response
app.get('/user/:id', (req, res, next) => {
res.send('special')
})next('route')는 app.METHOD()에 의해 로드된 middleware 에서만 동작합니다.
next('route')가 호출되면 next route 로 제어를 넘깁니다.
function logOriginalUrl (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request URL:', req.originalUrl)
next()
}
function logMethod (req, res, next) {
console.log('Request Type:', req.method)
next()
}
const logStuff = [logOriginalUrl, logMethod]
app.get('/user/:id', logStuff, (req, res, next) => {
res.send('User Info')
})middleware는 reusability를 위해 array로 정의될 수 있습니다.
Built-in middleware
express.json parses incoming requests with JSON payloads.
Returns middleware that only parses JSON and only looks at requests where the Content-Type header matches the type option.