서두
지금까지 API 통신 관련 메소드 호출 시, Result 래퍼를 사용하여 통신의 성공/실패 여부를 구분하고, 뷰모델 or 프레젠터에서 이에 따른 처리를 해주었다.
이때, Coroutine의 CancellationException은 다른 Exception과 같이 API 통신 실패에 의해 발생한 '문제'가 아닌 코루틴이 취소될때 발생하는 정상적인 신호이기 때문에, 해당 Exception이 runCatching 함수의 catch 구문에 잡히지 않고, 상위 코루틴에 취소 신호를 전달할 수 있도록, 별도로 처리해주는 작업을 추가 했었다.
@InlineOnly
@SinceKotlin("1.3")
public inline fun <T, R> T.runCatching(block: T.() -> R): Result<R> {
return try {
Result.success(block())
} catch (e: Throwable) {
Result.failure(e)
}
}CancellationException 을 따로 처리하기 위한 cancellableRunCatching 유틸 함수
inline fun <T> cancellableRunCatching(block: () -> T): Result<T> {
return try {
Result.success(block())
} catch (cancellationException: CancellationException) {
throw cancellationException
} catch (exception: Exception) {
Result.failure(exception)
}
}Kotlin의 Exception과 예외처리에 대해선 이 영상을 참고해보면 도움이 될 듯 하다.
본론
그렇다면 언제 이 CancellationException이 발생할까?
사실 이 부분에서 반성을 해야하는게, CancellationException을 따로 처리하는게 맞다고만 생각했지, 어떨때 발생하는지 까지는 생각을 많이 하지 않았었다.
화면 진입시 API 가 호출되는 상황에서 빠르게 뒤로가기를 눌러, 화면에서 벗어나고 그에 의해 viewModelScope or LaunchedEffect 내부의 CoroutineScope가 취소되는 경우(부모에 취소가 자식에게 전파) 정도라고 생각을 했었다.
그 외에 케이스로는 job cancel() 을 통한 명시적 취소(Explicit Cancellation), Timeout 으로 인한 취소, 형제 코루틴의 예외로 인한 취소(예외가 부모에 전달, 부모에 취소가 자식에 전파)등이 있다.
문제 발생
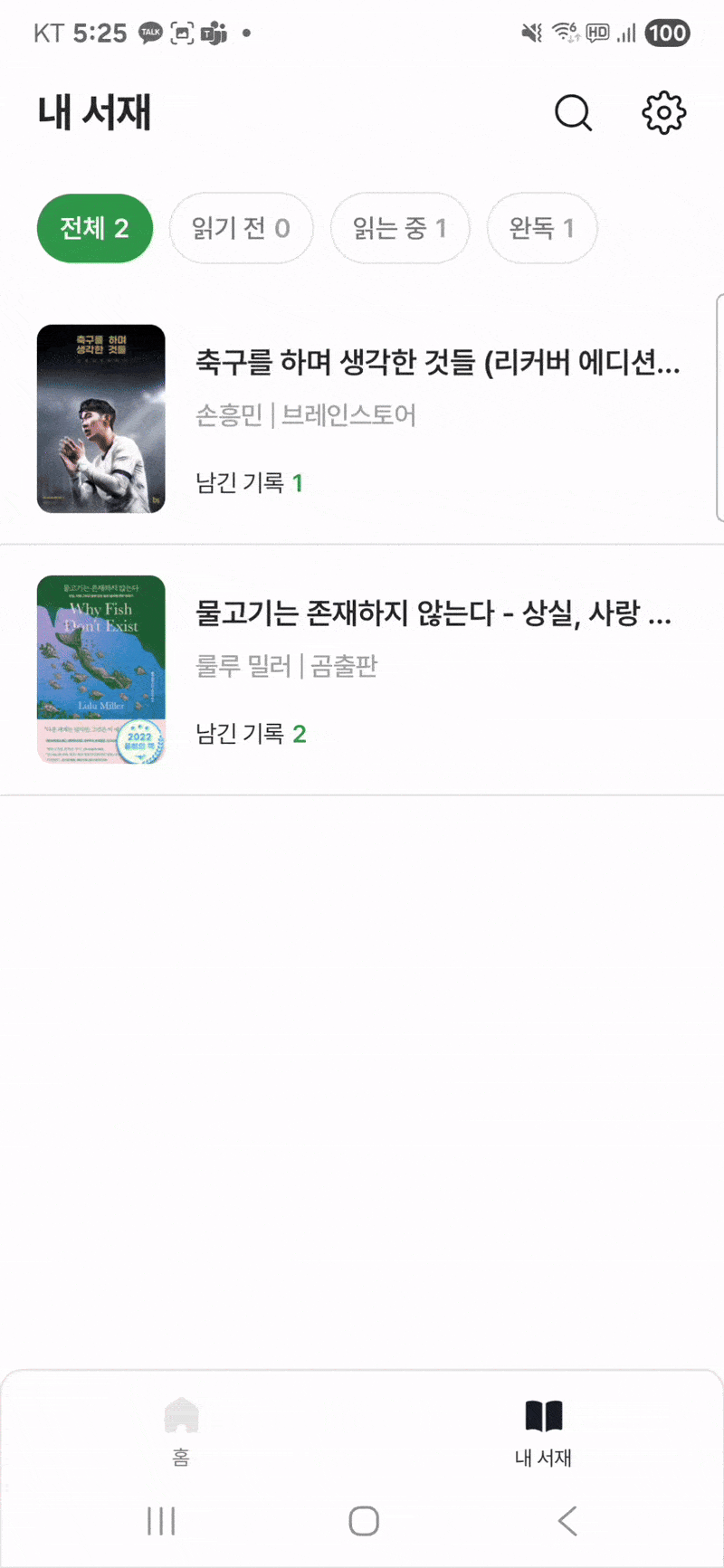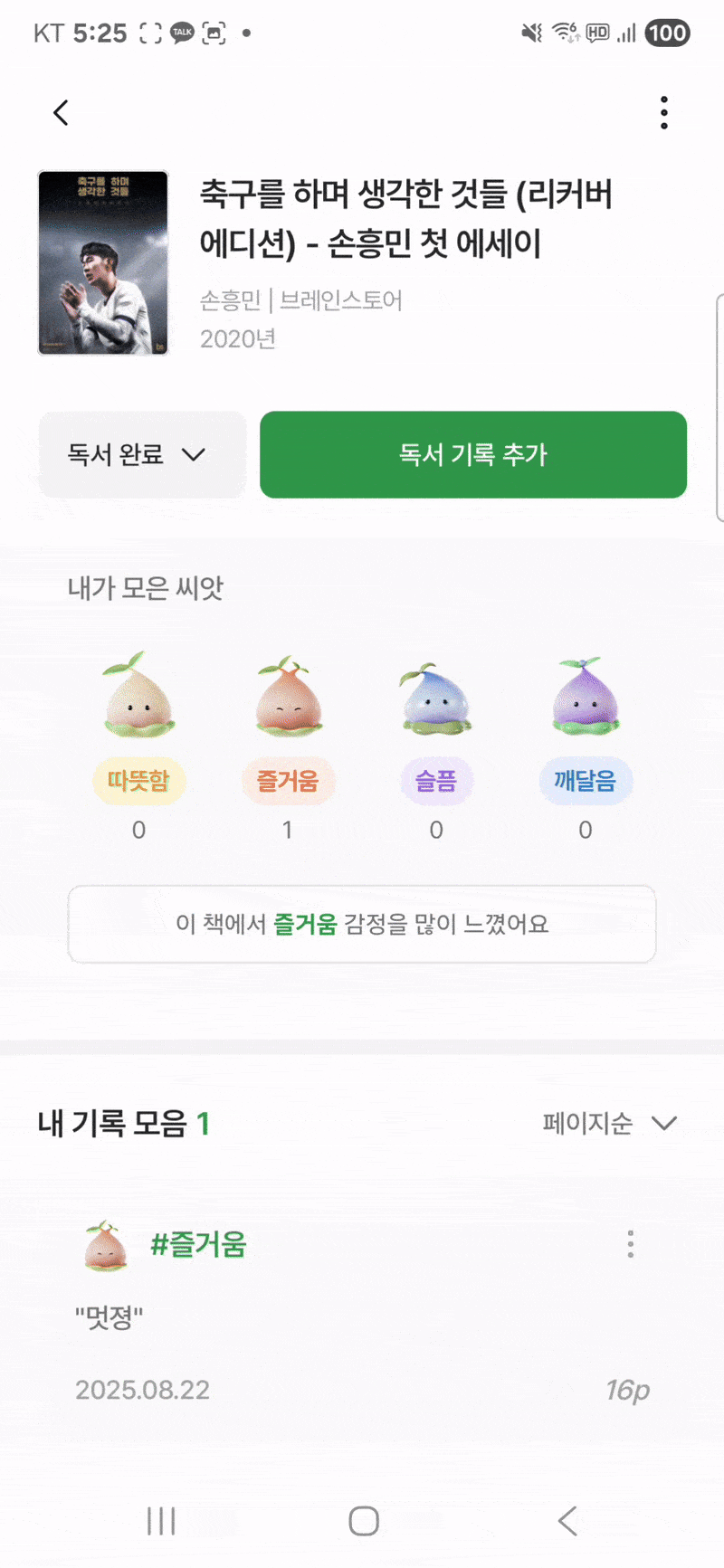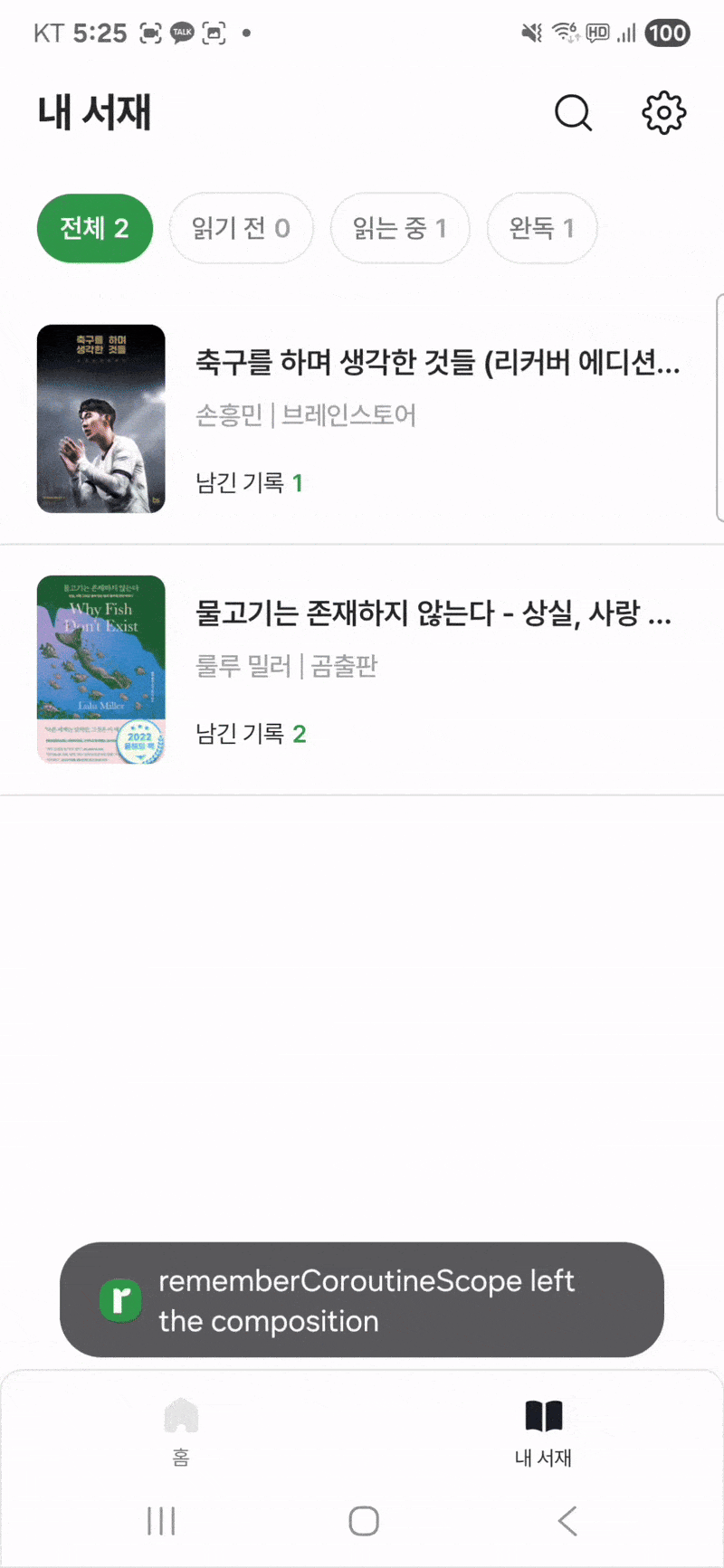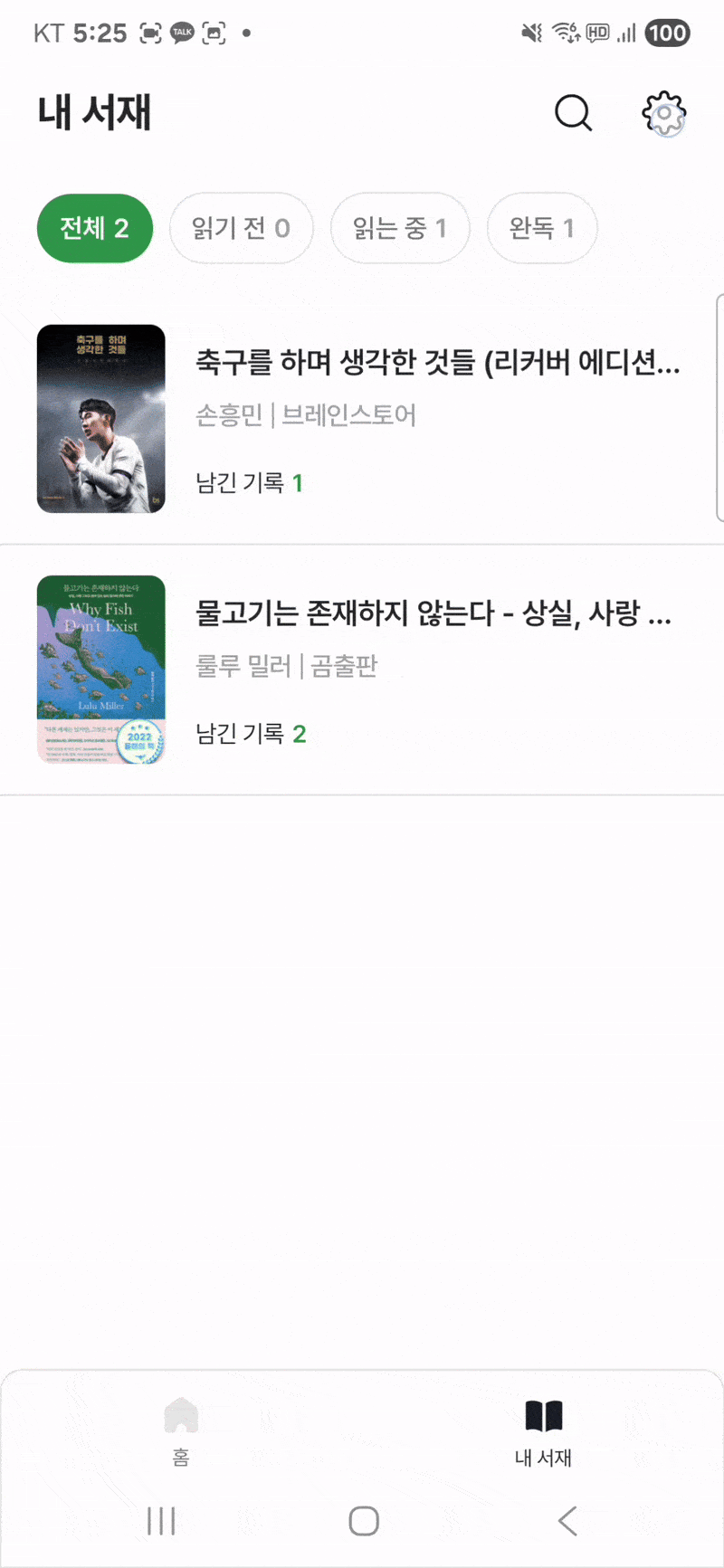
문제를 재현하기 위한 플로우는 다음과 같다.
- 내 서재 화면내의 리스트 화면내에 서로 다른 아이템을 두 손가락으로 동시에 누른다.
- 도서 상세 화면이 navigation 내에 두개가 쌓인다.
- 도서 상세 화면의 TopAppBar 내에 백버튼을 연타한다.
- 내 서재 화면에 돌아왔을때 Toast로 코루틴 관련 에러가 출력되는 것을 확인한다.
반드시 리스트 화면내 아이템일 필요는 없고, 두 손가락으로 다른 화면으로 이동하는 버튼을 동시에 누르면 재현이 가능했다.
rememberCoroutineScope left the composition...?
문제 해결
여태 컴포즈를 쓰면서 처음보는 에러 메세지라 당황했으나, 구글링을 해봤고, 다행히 관련 글을 찾을 수 있었다.
문제가 왜 발생하는가
API 호출 코드는 다음과 같다.
fun initialLoad() {
uiState = UiState.Loading
scope.launch {
try {
coroutineScope {
val bookDetailDeferred = async { bookRepository.getBookDetail(screen.isbn13).getOrThrow() }
val seedsDeferred = async { bookRepository.getSeedsStats(screen.userBookId).getOrThrow() }
val readingRecordsDeferred = async {
recordRepository.getReadingRecords(
userBookId = screen.userBookId,
sort = currentRecordSort.value,
page = START_INDEX,
size = PAGE_SIZE,
).getOrThrow()
}
val detail = bookDetailDeferred.await()
val seeds = seedsDeferred.await()
val records = readingRecordsDeferred.await()
bookDetail = detail
currentBookStatus = BookStatus.fromValue(detail.userBookStatus) ?: BookStatus.BEFORE_READING
selectedBookStatus = currentBookStatus
seedsStates = seeds.categories.toImmutableList()
readingRecords = records.readingRecords.toPersistentList()
readingRecordsTotalCount = records.totalResults
isLastPage = records.lastPage
currentStartIndex = START_INDEX
uiState = UiState.Success
}
} catch (e: Throwable) {
uiState = UiState.Error(e)
val handleErrorMessage = { message: String ->
Logger.e(message)
sideEffect = BookDetailSideEffect.ShowToast(message)
}
handleException(
exception = e,
onError = handleErrorMessage,
onLoginRequired = {
navigator.resetRoot(LoginScreen)
},
)
}
}
}
// 호출
LaunchedEffect(Unit) {
initialLoad()
}`
이 상황에서, 내 서재화면을 A라고 하고, 도서 상세화면을 B라고 하자.
현재 멀티 터치로 인해 B가 두번 쌓여 A -> B -> B 로 화면이 이동되었다.
이때 B의 TopAppBar에 뒤로가기 버튼을 연타하면
- 최상위에 B가 pop 된다.
- 중간에 있던 B의 LaunchedEffect 내부에 Coroutine 블럭이 재호출된다.(API 호출)
- 중간의 B가 연달아 pop 되면서, LaunchedEffect가 취소 된다.(아직 API는 호출 중)
- LaunchedEffect의 CoroutineScope 블록이 취소되면서(부모의 취소), 자식 CoroutineScope에 전파된다.
- 자식 Coroutine에선 CancellationException에 대한 별도의 처리를 하지 않았기 때문에 catch 구문에 잡혀 Toast로 Coroutine 관련 에러메세지가 노출된다.
따라서 해결법은 다음과 같다.
1. CancellationException 따로 처리하기
fun initialLoad() {
uiState = UiState.Loading
scope.launch {
try {
coroutineScope {
val bookDetailDeferred = async { bookRepository.getBookDetail(screen.isbn13).getOrThrow() }
val seedsDeferred = async { bookRepository.getSeedsStats(screen.userBookId).getOrThrow() }
val readingRecordsDeferred = async {
recordRepository.getReadingRecords(
userBookId = screen.userBookId,
sort = currentRecordSort.value,
page = START_INDEX,
size = PAGE_SIZE,
).getOrThrow()
}
val detail = bookDetailDeferred.await()
val seeds = seedsDeferred.await()
val records = readingRecordsDeferred.await()
bookDetail = detail
currentBookStatus = BookStatus.fromValue(detail.userBookStatus) ?: BookStatus.BEFORE_READING
selectedBookStatus = currentBookStatus
seedsStates = seeds.categories.toImmutableList()
readingRecords = records.readingRecords.toPersistentList()
readingRecordsTotalCount = records.totalResults
isLastPage = records.lastPage
currentStartIndex = START_INDEX
uiState = UiState.Success
}
} catch (ce: CancellationException) { // <- 추가
throw ce
} catch (e: Throwable) {
uiState = UiState.Error(e)
val handleErrorMessage = { message: String ->
Logger.e(message)
sideEffect = BookDetailSideEffect.ShowToast(message)
}
handleException(
exception = e,
onError = handleErrorMessage,
onLoginRequired = {
navigator.resetRoot(LoginScreen)
},
)
}
}
}사실 별도로 catch 해서 던지는 것 만으론 따로 처리 했다고 볼 순 없다. CEH(CoroutineExceptionHandler)를 도입해서 던져진 CancellationException에 대한 처리를 해주는 방식으로 보완할 예정이다.
2. Multi Touch 막기
근본적으로 도서 상세 화면이 두 개가 쌓이는게 문제인지라, 리스트내에 서로 다른 아이템을 동시에 누를 수 없도록 막는 장치도 추가하였다.
XML 에서
사실 xml 로 개발할때에도 이러한 부분을 막을 생각을 못해봤었는데, 검색해보니 xml 로 개발할 경우 코드에 한 줄만 추가해주면 쉽게 Multi Touch를 막아줄 수 있었다...!
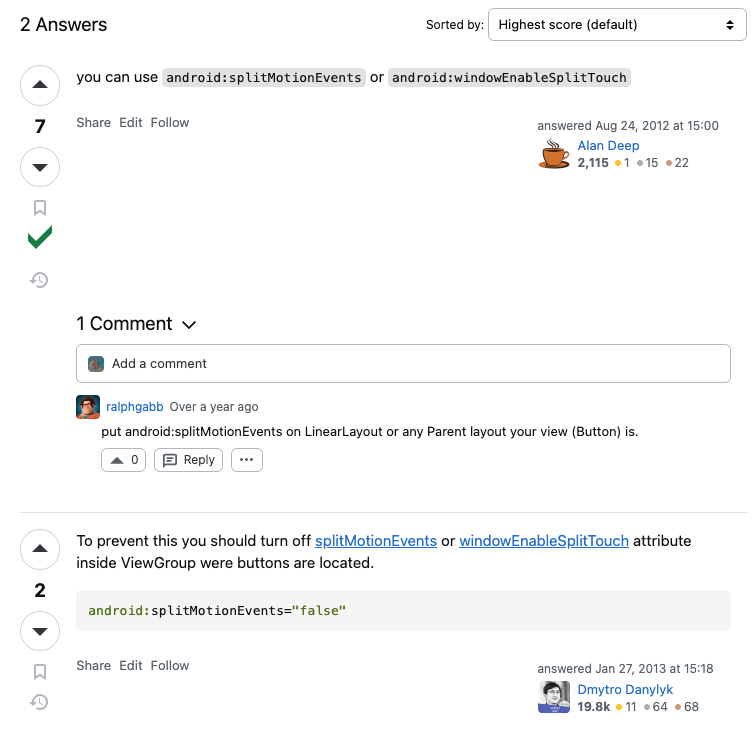
Disabling multitouch in android
Compose 에서
Compose 의 방법으론 아쉽게도 xml과 같은 속성을 지원하지 않아, custom Modifier를 직접 만들어 적용해줘야한다.
/**
* 부모 영역에서 동시 터치(두 손가락 이상)를 차단하는 Modifier
*/
fun Modifier.preventMultiTouch() = pointerInput(Unit) {
// awaitEachGesture: 한 번의 제스쳐 세션을 추상화
awaitEachGesture {
val first = awaitFirstDown(requireUnconsumed = false)
while (true) {
// 이벤트 전파 초기 단계(PointerEventPass.Initial)에서 하위 컴포저블로 이벤트가 내려가기 전에 가로채 소비한다
val event = awaitPointerEvent(pass = PointerEventPass.Initial)
event.changes.forEach { change ->
if (change.id != first.id && change.pressed) {
change.consume()
}
}
// 첫 포인터가 pressed 상태일 동안만 유지한다 (up이거나 cancel되면 pressed=false로 루프 종료)
if (event.changes.none { it.id == first.id && it.pressed }) break
}
}
}해당 Modifier를 화면내 부모 레이아웃에 적용하여 Multi Touch를 막을 수 있었다.
매 화면마다 추가해주는게 번거롭다면, 다음과 같이 앱내에서 사용하는 Custom Scaffold 내에 preventMultiTouch Modifier에 적용하여 전역으로 적용하는 방법도 존재한다.
@Composable
fun ReedScaffold(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
topBar: @Composable () -> Unit = {},
bottomBar: @Composable () -> Unit = {},
snackbarHost: @Composable () -> Unit = {},
floatingActionButton: @Composable () -> Unit = {},
containerColor: Color = White,
contentWindowInsets: WindowInsets = ScaffoldDefaults.contentWindowInsets,
content: @Composable (PaddingValues) -> Unit,
) {
Scaffold(
modifier = modifier
.keyboardHide()
.preventMultiTouch(),
topBar = topBar,
bottomBar = bottomBar,
snackbarHost = snackbarHost,
floatingActionButton = floatingActionButton,
containerColor = containerColor,
contentWindowInsets = contentWindowInsets,
) { innerPadding ->
content(innerPadding)
}
}결과
CancellationException 을 다른 Exception과 구분해서 처리해주고, 화면내 다른 화면으로 이동하는 컴포넌트(버튼)들에 대해 Multi Touch 이벤트를 방지함으로써, QA 에서 발견된 앱 내 버그를 해결할 수 있었다.
글을 작성하면서 CoroutineScope()와 coroutineScope{} 를 헷갈려 '내가 알고 있는 코루틴이 잘못되었나'하고 세상이 무너질 뻔했는데, 다행히 무너지진 않았다.
둘의 차이를 요약하자면 CoroutineScope()(생성자)는 새로운 독립적인 스코프를 생성하여 구조화를 깨고, coroutienScope{}(suspend 함수) 현재 코루틴의 자식 스코프를 생성하기 때문에 구조화를 깨지 않는다는 것인데,
더 자세한 설명은 해당 질문 글을 참고하면 좋을 것 같다.
reference)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/69901608/how-to-disable-simultaneous-clicks-on-multiple-items-in-jetpack-compose-list-c
https://slack-chats.kotlinlang.org/t/27119184/how-to-disable-multi-touch-on-compose-i-have-issue-user-clic
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/78290457/code-inside-launchedeffect-throws-the-following-exception-the-coroutine-scope
https://kotlinlang.org/docs/exception-handling.html
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EZccJBM3t78
