스택과 큐를 활용하는데
큐보다는 deque이 리스트를 사용하기 때문에 속도가 더 빠르다
1260
1260 dfs, bfs
vertex: 노드
edge: 간선
그래프 방식으로 풀기 [[Int]].init(repeating: [], count: numberOfVertex+1)
import Foundation
let line = readLine()!.components(separatedBy: " ").map{ Int(String($0))! }
let numberOfVertex = line[0]
let numberOfEdge = line[1]
let startVertex = line[2]
var graph = [[Int]].init(repeating: [], count: numberOfVertex+1)
// [[], [2, 3, 4], [1, 4], [1, 4], [1, 2, 3]]
var isChecked: [Bool] = [Bool].init(repeating: false, count: numberOfVertex+1)
for _ in 0..<numberOfEdge {
let part = readLine()!.components(separatedBy: " ").map{ Int(String($0))! }
graph[part[0]].append(part[1])
graph[part[1]].append(part[0])
}
for i in 1...numberOfVertex {
graph[i].sort()
}
func dfs(start: Int) {
if isChecked[start] {
return
}
isChecked[start] = true
print(start, terminator: " ")
for vertex in graph[start] {
if !isChecked[vertex] {
dfs(start: vertex)
}
}
}
func bfs(start: Int) {
var queue = [Int]()
isChecked[start] = true
queue.append(start)
while !queue.isEmpty {
let first = queue.removeFirst()
print(first, terminator: " ")
for vertex in graph[first] {
if !isChecked[vertex] {
isChecked[vertex] = true
queue.append(vertex)
}
}
}
}
dfs(start: startVertex)
print()
isChecked = [Bool].init(repeating: false, count: numberOfVertex+1)
bfs(start: startVertex)2606
2606 바이러스
dfs 런타임 에러 발생... 왜why...???
import Foundation
let vertex = Int(readLine()!)!
let edge = Int(readLine()!)!
var graph: [[Int]] = [[Int]].init(repeating: [], count: vertex+1)
var visited: [Bool] = [Bool].init(repeating: false, count: vertex+1)
for _ in 0..<edge {
let pair = readLine()!.components(separatedBy: " ").map{ Int(String($0))! }
//양방향 그래프
graph[pair[0]].append(pair[1])
graph[pair[1]].append(pair[0])
}
for i in 0..<edge {
graph[i].sort()
}
func getCount(start: Int) {
for vertex in graph[start] {
if !visited[vertex] {
visited[vertex] = true
getCount(start: vertex)
}
}
}
getCount(start: 1)
var count: Int = 0
for i in 1..<visited.count {
if visited[i] == true {
count += 1
}
}
print(count-1) //1은 제외한다bfs 오잉 얘도 런타임에러 나는데?
visited를 bool이 아닌 Int(노드 번호)로 변경해봄
queue.append(contentsOf: graph[vertex])이렇게 하면 [2, 5] 이렇게 생긴 형식도 배열에 추가할 수 있음
queue.removeFirst() 잘 활용하기
import Foundation
let vertex = Int(readLine()!)!
let edge = Int(readLine()!)!
var graph: [[Int]] = [[Int]].init(repeating: [], count: vertex+1)
var visited: [Int] = []
for _ in 0..<edge {
let pair = readLine()!.components(separatedBy: " ").map{ Int(String($0))! }
//양방향 그래프
graph[pair[0]].append(pair[1])
graph[pair[1]].append(pair[0])
}
for i in 0..<edge {
graph[i].sort()
}
func bfs(start: Int) {
var queue: [Int] = [start]
while !queue.isEmpty {
let vertex = queue.removeFirst()
if !visited.contains(vertex) {
visited.append(vertex)
queue.append(contentsOf: graph[vertex])
}
}
}
bfs(start: 1)
print(visited.count-1) // 첫번째 1은 카운트 안함통과
continue를 적극적으로 활용하자
import Foundation
let vertex = Int(readLine()!)!
let edge = Int(readLine()!)!
var graph: [[Int]] = [[Int]].init(repeating: [], count: vertex+1)
var visited: [Bool] = [Bool].init(repeating: false, count: vertex+1)
for _ in 0..<edge {
let pair = readLine()!.components(separatedBy: " ").map{ Int(String($0))! }
//양방향 그래프
graph[pair[0]].append(pair[1])
graph[pair[1]].append(pair[0])
}
var count: Int = 0
func dfs(start: Int) {
visited[start] = true
for vertex in graph[start] {
if visited[vertex] {
continue
}
count += 1
dfs(start: vertex)
}
}
dfs(start: 1)
print(count)2667
graph 입력받은 후의 모습
[[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]]
// 지도의 크기
let n = Int(readLine()!)!
// 지도 입력받기
var graph = [[Int]](repeating: [Int](), count: n)
for i in 0..<n {
graph[i] = readLine()!.map{Int(String($0))!}
}
// 상하좌우 이동
let dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
let dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
// 단지 개수 배열
var answer = [Int]()
var cnt = 0 // 단지 개수
func dfs(_ x: Int, _ y: Int) {
graph[x][y] = 0 // 방문 처리
cnt += 1
for k in 0..<4 {
let nx = x + dx[k]
let ny = y + dy[k]
if nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < n {
if graph[nx][ny] == 1 {
dfs(nx, ny)
}
}
}
}
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<n {
if graph[i][j] == 1 {
cnt = 0
dfs(i, j)
answer.append(cnt)
}
}
}
answer.sort()
print(answer.count)
answer.forEach {
print($0)
}2178
2178 미로탐색
import Foundation
let nm = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
let n = nm[0] //행의 수
let m = nm[1] //열의 수
//방법1 그래프 입력받기
//var graph = [[Int]](repeating: [Int](), count: n)
//for i in 0..<n {
// graph[i] = readLine()!.map { Int(String($0))! }
//}
//방법2 그래프 입력받기
var graph = [[Int]]()
for _ in 0..<n {
graph.append(readLine()!.map{Int(String($0))!})
}
//print(graph)
//[[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1],
// [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
// [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1],
// [1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1]]
// 상하좌우
let dx = [0, 0, 1, -1]
let dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
//큐
var queue = [(0, 0)] //처음 시작점
var visited = [[Bool]](repeating: [Bool](repeating: false, count: m), count: n) //방문확인
while !queue.isEmpty {
let (x, y) = queue.removeFirst()
visited[x][y] = true
for k in 0..<4 {
let dx = x + dx[k]
let dy = y + dy[k]
if dx>=0 && dx<n && dy>=0 && dy<m {
if graph[dx][dy]==1 && !visited[dx][dy]{
graph[dx][dy] = graph[x][y] + 1
queue.append((dx, dy))
}
}
}
}
print(graph[n-1][m-1]) //(0, 0)부터 시작하므로bfs 진행 후 graph 모양
[[1, 0, 9, 10, 11, 12],
[2, 0, 8, 0, 12, 0],
[3, 0, 7, 0, 13, 14],
[4, 5, 6, 0, 14, 15]]7576
7576 토마토
시간초과다...😥
import Foundation
let mn = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
let m = mn[0] //열
let n = mn[1] //행
var graph = [[Int]]()
for _ in 0..<n {
graph.append(readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map{ Int(String($0))!} )
}
var queue = [(Int, Int)]()
var visited = [[Bool]](repeating: [Bool](repeating: false, count: m), count: n) //방문확인
//상하좌우
let dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
let dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
//처음 시작 점 queue에 저장하기
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if graph[i][j] == 1 {
queue.append((i, j))
}
}
}
while !queue.isEmpty {
let (x, y) = queue.removeFirst()
visited[x][y] = true
for i in 0...3 {
let dx = x + dx[i]
let dy = y + dy[i]
if dx>=0 && dx<n && dy>=0 && dy<m {
if graph[dx][dy] == 0 && !visited[dx][dy] {
graph[dx][dy] = graph[x][y] + 1
queue.append((dx, dy))
}
}
}
}
var flag = false //모두 익지 않았을 때 체크
var maxValue = 0 //토마토가 모두 익는데 걸리는 최소일수
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if graph[i][j] == 0 {
flag = true
}
if graph[i][j] > maxValue {
maxValue = graph[i][j]
}
}
}
//모두 익지 않으면 -1 리턴
if flag {
print(-1)
} else if maxValue == 1 {
print(0)
} else {
print(maxValue-1) // 왜냐하면 1이 있을 때가 0일이기 때문에
}queue를 list로 구현하는 분들이 많아 저의경우 위 코드에서 그냥 list를 가져와 removeFirst를 deque처럼 사용해줬는데요,
removeFirst는 O(n)의 시간복잡도를 갖는다는것이 문제였습니다.
대신 Queue를 list와 from, to 두개의 index정보(투포인터)를 갖는 구조체로 직접 구현해서 deque(덱)해주도록 했고, 문제없이 통과할 수 있었습니다.
덱 추가하기...(성공)
너무한거 아니냐ㅠㅠ
public struct Deque<T> {
private var array: [T?]
private var head: Int
private var capacity: Int
private let originalCapacity: Int
public init(_ capacity: Int = 10) { //10개짜리 공간
self.capacity = max(capacity, 1)
originalCapacity = self.capacity
array = [T?](repeating: nil, count: capacity)
head = capacity //array 바깥쪽 맨 뒤
}
public var count: Int {
return array.count - head
}
public var isEmpty: Bool {
return count == 0
}
public mutating func enqueue(_ element: T) {
array.append(element)
}
public mutating func dequeueBack() -> T? {
if isEmpty {
return nil
} else {
return array.removeLast()
}
}
public mutating func enqueueFront(_ element: T) {
if head == 0 {
capacity *= 2
let emptySpace = [T?](repeating: nil, count: capacity)
array.insert(contentsOf: emptySpace, at: 0)
head = capacity
}
head -= 1
array[head] = element
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
guard head < array.count, let element = array[head] else {
return nil
}
array[head] = nil
head += 1
if capacity >= originalCapacity && head >= capacity*2 { //처음 설정한 originalCapacity 보다 크고(확장했고), head가 용량의 두배보다 클 때
let amountToRemove = capacity + capacity/2
array.removeFirst(amountToRemove)
head -= amountToRemove
capacity /= 2
}
return element
}
}
let mn = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
let m = mn[0] //열
let n = mn[1] //행
var graph = [[Int]]()
for _ in 0..<n {
graph.append(readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map{ Int(String($0))!} )
}
var deque = Deque<(Int, Int)>()
var visited = [[Bool]](repeating: [Bool](repeating: false, count: m), count: n) //방문확인
//상하좌우
let dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
let dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
//처음 시작 점 queue에 저장하기
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if graph[i][j] == 1 {
deque.enqueue((i, j))
}
}
}
while !deque.isEmpty {
let (x, y) = deque.dequeue()!
visited[x][y] = true
for i in 0...3 {
let dx = x + dx[i]
let dy = y + dy[i]
if dx>=0 && dx<n && dy>=0 && dy<m {
if graph[dx][dy] == 0 && !visited[dx][dy] {
graph[dx][dy] = graph[x][y] + 1
deque.enqueue((dx, dy))
}
}
}
}
var flag = false //모두 익지 않았을 때 체크
var maxValue = 0 //토마토가 모두 익는데 걸리는 최소일수
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if graph[i][j] == 0 {
flag = true
}
if graph[i][j] > maxValue {
maxValue = graph[i][j]
}
}
}
//모두 익지 않으면 -1 리턴
if flag {
print(-1)
} else if maxValue == 1 {
print(0)
} else {
print(maxValue-1) // 왜냐하면 1이 있을 때가 0일이기 때문에
}7569
7569 토마토 3차원
삼차원으로 만드는 것이
import Foundation
public struct Deque<T> {
private var array: [T?]
private var head: Int
private var capacity: Int
private let originalCapacity: Int
public init(_ capacity: Int = 10) { //10개짜리 공간
self.capacity = max(capacity, 1)
originalCapacity = self.capacity
array = [T?](repeating: nil, count: capacity)
head = capacity //array 바깥쪽 맨 뒤
}
public var count: Int {
return array.count - head
}
public var isEmpty: Bool {
return count == 0
}
public mutating func enqueue(_ element: T) {
array.append(element)
}
public mutating func dequeueBack() -> T? {
if isEmpty {
return nil
} else {
return array.removeLast()
}
}
public mutating func enqueueFront(_ element: T) {
if head == 0 {
capacity *= 2
let emptySpace = [T?](repeating: nil, count: capacity)
array.insert(contentsOf: emptySpace, at: 0)
head = capacity
}
head -= 1
array[head] = element
}
public mutating func dequeue() -> T? {
guard head < array.count, let element = array[head] else {
return nil
}
array[head] = nil
head += 1
if capacity >= originalCapacity && head >= capacity*2 { //처음 설정한 originalCapacity 보다 크고(확장했고), head가 용량의 두배보다 클 때
let amountToRemove = capacity + capacity/2
array.removeFirst(amountToRemove)
head -= amountToRemove
capacity /= 2
}
return element
}
}
let mnh = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
let m = mnh[0] //열
let n = mnh[1] //행
let h = mnh[2] //높이
//[Int]()는 [Int]이고
//[Int]는 [Int].type이다
var graph = [[[Int]]](repeating: [[Int]](repeating: [Int](), count: n), count: h)
for z in 0..<h {
for x in 0..<n {
let row = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
graph[z][x] = row
//graph[z][x].append(contentsOf: row) 상동
}
}
var deque = Deque<(Int, Int, Int)>()
//처음 시작 점 queue에 저장하기
for z in 0..<h {
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if graph[z][i][j] == 1 {
deque.enqueue((z, i, j))
}
}
}
}
//상하좌우
let d = [(-1, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), (0, -1, 0), (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, -1), (0, 0, 1)]
while !deque.isEmpty {
let now = deque.dequeue()!
//visited[z][x][y] = true
for i in 0...5 {
let dz = d[i].0+now.0
let dx = d[i].1+now.1
let dy = d[i].2+now.2
if dz>=0 && dz<h && dx>=0 && dx<n && dy>=0 && dy<m {
if graph[dz][dx][dy] == 0 {
graph[dz][dx][dy] = graph[now.0][now.1][now.2] + 1
deque.enqueue((dz, dx, dy))
}
}
}
}
var flag = false //모두 익지 않았을 때 체크
var maxValue = 0 //토마토가 모두 익는데 걸리는 최소일수
for z in 0..<h {
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if graph[z][i][j] == 0 {
flag = true
}
if graph[z][i][j] > maxValue {
maxValue = graph[z][i][j]
}
}
}
}
//모두 익지 않으면 -1 리턴
if flag {
print(-1)
} else if maxValue == 1 {
print(0)
} else {
print(maxValue-1) // 왜냐하면 1이 있을 때가 0일이기 때문에
}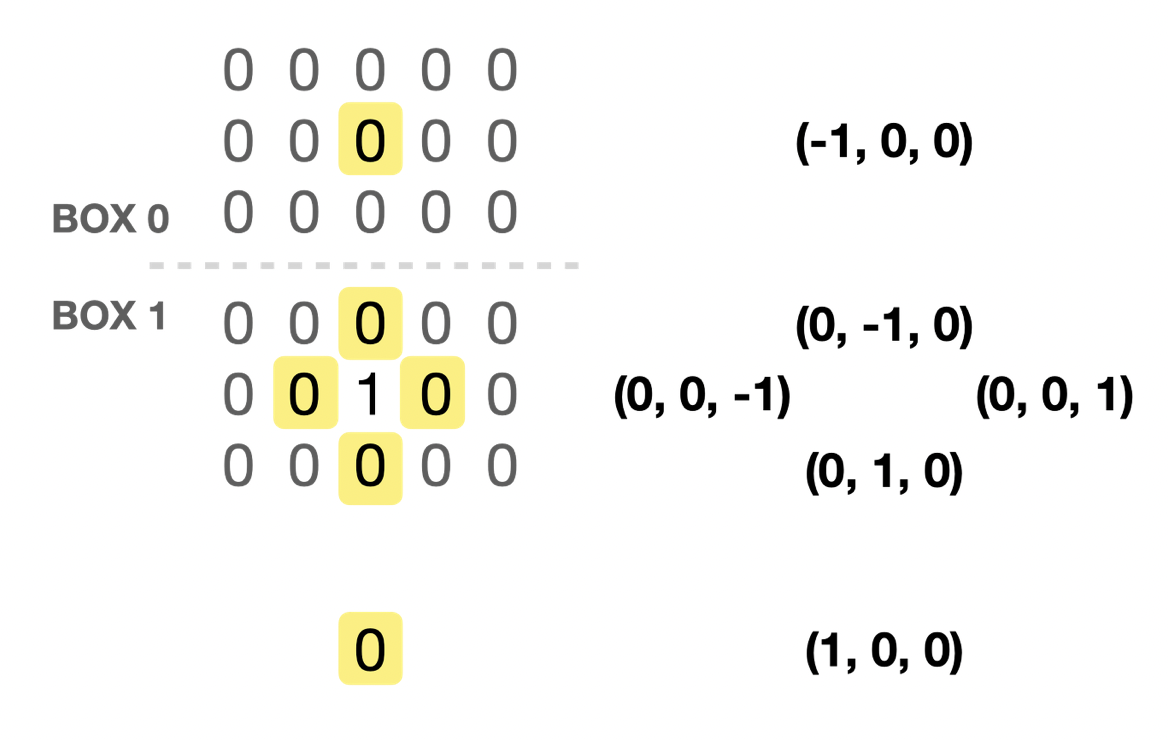
그래프는 아래와 같은 모양으로 생성된다.
음... 그래프 방식 사용안하는데 왜 변수명을 그래프로 했지🥲
[[[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]],
[[1, 1, 1, 1],
[-1, -1, -1, -1],
[1, 1, 1, -1]]]14502
14502 연구소
크기가 6x6사이즈일 때 벽을 3개 세울 수 있는 경우의 수는 36C3이다
36C3 = 36P3 / 3! 과 동일한데
뽑고 순서를 제거한것이라는 말이다.
0: 빈칸
1: 벽
2: 바이러스
let nm = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
let n = nm[0] //세로(행)
let m = nm[1] //가로(열)
var data = [[Int]]()
var temp = [[Int]](repeating: [Int](repeating: 0, count: m), count: n) //임시저장소
for _ in 0..<n {
data.append(readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! })
}
let dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
let dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
//바이러스 퍼트리기
func virus(_ x: Int, _ y: Int) {
for i in 0..<4 {
let nx = x + dx[i]
let ny = y + dy[i]
if nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m {
if temp[nx][ny] == 0 { //빈칸일 때
temp[nx][ny] = 2
virus(nx, ny)
}
}
}
}
//안전영역 구하기
func getScore() -> Int {
var score = 0
for i in 0..<n {
for j in 0..<m {
if temp[i][j] == 0 {
score += 1
}
}
}
return score
}
var result = 0
func dfs(_ count: Int) {
var count = count
//벽3개일 때
if count == 3 {
//벽 세운 후 모양
for x in 0..<n {
for y in 0..<m {
temp[x][y] = data[x][y]
}
}
//바이러스 전파
for x in 0..<n {
for y in 0..<m {
if temp[x][y] == 2 {
virus(x, y)
}
}
}
//전파 후 안전 영역 크기 계산하기
result = max(result, getScore())
return
}
//빈칸에 울타리 설치하기
for x in 0..<n {
for y in 0..<m {
if data[x][y] == 0 {
data[x][y] = 1
count += 1
dfs(count)
data[x][y] = 0
count -= 1
}
}
}
}
dfs(0) //벽 개수 넘기기
print(result)경우의 수를 따지고 싶을 때 이렇게 하면 된다!
dfs하고 다시
뒤로 돌아가서 취소하고 카운트도 빼고
다시 dfs탐색하는방법!
//빈칸에 울타리 설치하기
for x in 0..<n {
for y in 0..<m {
if data[x][y] == 0 {
data[x][y] = 1
count += 1
dfs(count)
data[x][y] = 0
count -= 1
}
}
}
14888
14888 연산자 끼워넣기
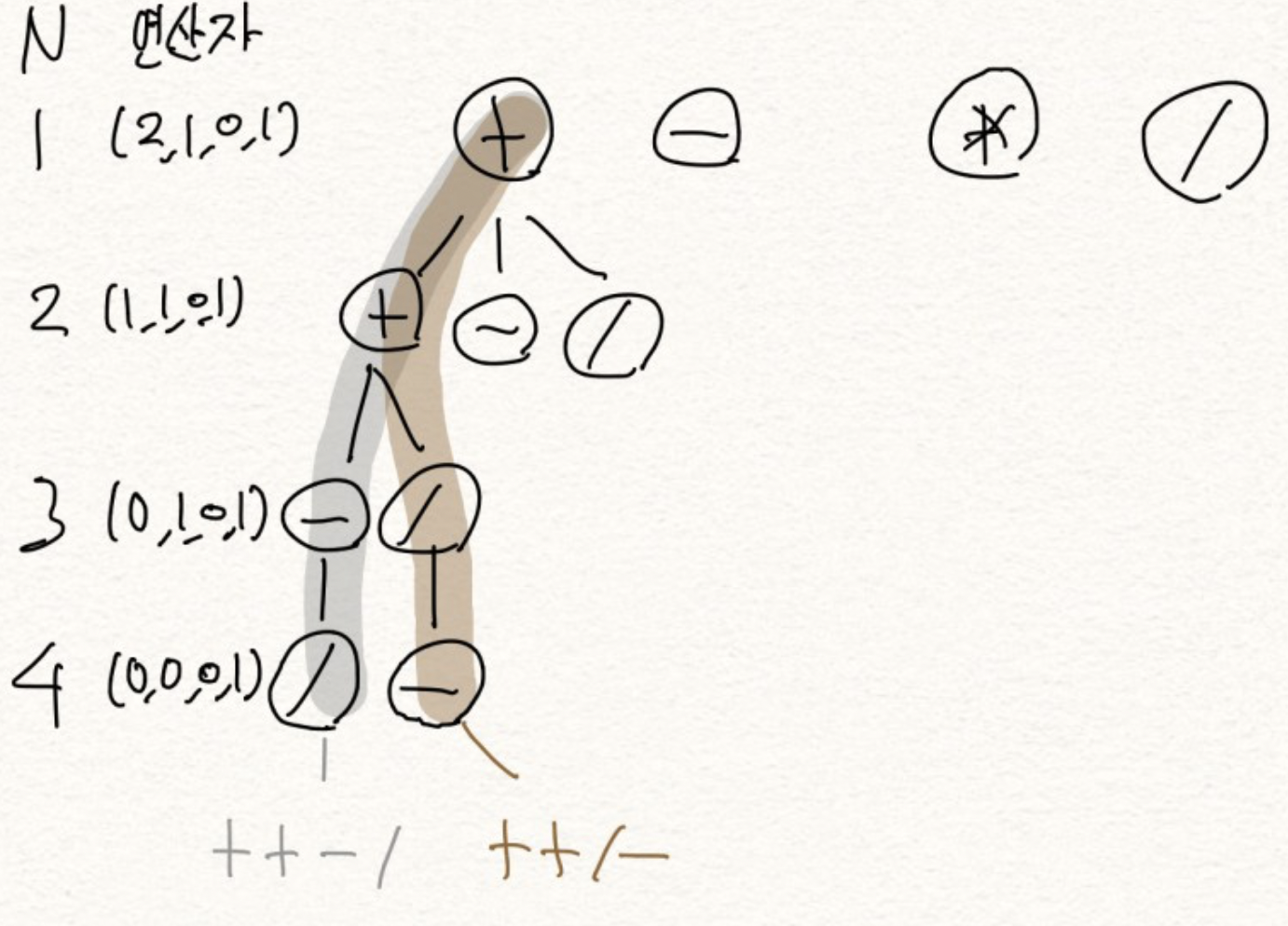
let n = Int(readLine()!)! //수의 개수 n
let numbers = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! }
let op = readLine()!.split(separator: " ").map { Int(String($0))! } // 연산자 + - x / 순서
var maxN = -1000000000
var minN = 1000000000
func dfs(_ idx: Int, _ plus: Int, _ subtraction: Int, _ multiply: Int, _ division: Int, _ tot: Int) {
if idx == n {
maxN = max(tot, maxN)
minN = min(tot, minN)
return
}
if plus<op[0] {
dfs(idx+1, plus+1, subtraction, multiply, division, tot+numbers[idx])
}
if subtraction<op[1] {
dfs(idx+1, plus, subtraction+1, multiply, division, tot-numbers[idx])
}
if multiply<op[2] {
dfs(idx+1, plus, subtraction, multiply+1, division, tot*numbers[idx])
}
if division<op[3] {
dfs(idx+1, plus, subtraction, multiply, division+1, tot/numbers[idx])
}
}
dfs(1, 0, 0, 0, 0, numbers[0])
print(maxN)
print(minN)