📅 날짜
2025년 2월 27일
📝 학습 내용
1️⃣ 자바 if 문 기초
if문을 사용한 단순 조건문if-else구조- 여러 조건을 평가하는
else if문 - 복잡한 조건 처리를 위한 중첩
if문
✅ 기본 if 문 예제
int age = 10;
if (age >= 8) {
System.out.println("학교에 다닙니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("학교에 다니지 않습니다.");
}2️⃣ 조건문을 활용한 문제 풀이
📌 (1) 정수가 3의 배수인지 판별
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요: ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
if (num % 3 == 0) {
System.out.printf("%d는 3의 배수입니다.\n", num);
}
sc.close();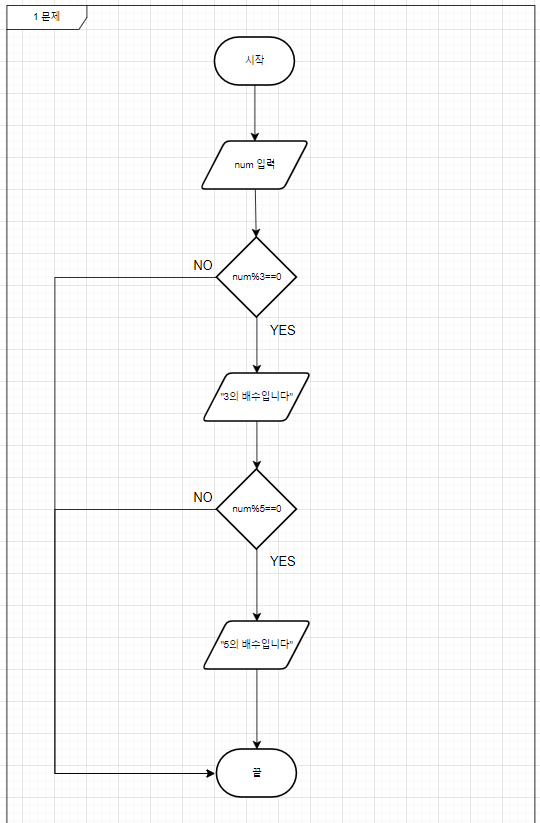
📌 (2) 두 개의 정수 중 큰 값 찾기
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("두 개의 정수를 입력하세요: ");
int n1 = sc.nextInt();
int n2 = sc.nextInt();
if (n1 >= n2) {
System.out.println("큰 수: " + n1);
} else {
System.out.println("큰 수: " + n2);
}
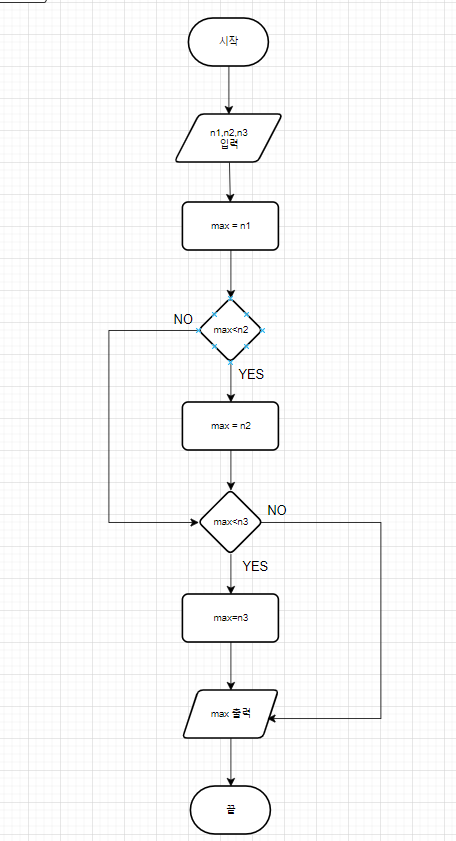
sc.close();📌 (3) 세 개의 정수 중 가장 큰 값 찾기
(방법 1: if 문 비교)
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("세 개의 정수를 입력하세요: ");
int n1 = sc.nextInt();
int n2 = sc.nextInt();
int n3 = sc.nextInt();
int max = n1;
if (max < n2) {
max = n2;
}
if (max < n3) {
max = n3;
}
System.out.println("가장 큰 수: " + max);
sc.close();(방법 2: else if 활용)
if (n1 >= n2 && n1 >= n3) {
System.out.println("가장 큰 수: " + n1);
} else if (n2 >= n1 && n2 >= n3) {
System.out.println("가장 큰 수: " + n2);
} else {
System.out.println("가장 큰 수: " + n3);
}
📌 (4) 세 개의 정수의 합과 평균 구하기
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("세 개의 정수를 입력하세요: ");
int n1 = sc.nextInt();
int n2 = sc.nextInt();
int n3 = sc.nextInt();
int sum = n1 + n2 + n3;
double avg = (double) sum / 3;
System.out.printf("합: %d, 평균: %.2f\n", sum, avg);
sc.close();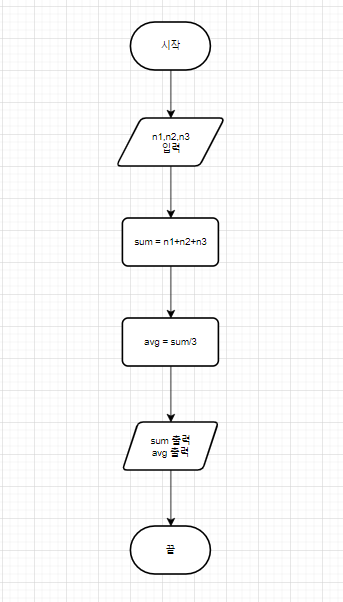
📌 (5) 특정 조건을 만족하는 정수 판별
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요: ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
if (n % 2 == 0 && n % 3 == 0) {
System.out.printf("%d는 짝수이면서 3의 배수입니다.\n", n);
} else if (n % 2 == 1 && n % 5 == 0) {
System.out.printf("%d는 홀수이면서 5의 배수입니다.\n", n);
}
sc.close();📌 (6) 시험 점수에 따른 학점 출력
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("시험 점수를 입력하세요: ");
int score = sc.nextInt();
if (score >= 90) {
System.out.println("A");
} else if (score >= 80) {
System.out.println("B");
} else if (score >= 70) {
System.out.println("C");
} else if (score >= 60) {
System.out.println("D");
} else {
System.out.println("F");
}
sc.close();📌 (7) 나이에 따른 요금 계산
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("나이를 입력하세요: ");
int age = sc.nextInt();
int fare;
if (age < 8) {
fare = 1000;
} else if (age < 14) {
fare = 2000;
} else if (age < 20) {
fare = 2500;
} else {
fare = 3000;
}
System.out.printf("요금은 %d원 입니다.\n", fare);
sc.close();🔗 참고 자료
💡 개선할 점 및 배운 내용
🔍 개선할 점
-
결과를 변수에 저장하여 코드 단순화
if블록 내에서 바로 출력하는 대신, 변수를 사용하여 코드 가독성을 높이기
-
중복 코드 최소화
- 동일한 결과를 가지는 조건들을 그룹화하여 코드 효율성 향상
-
출력 형식 개선
printf("%.2f")를 활용하여 실수값 출력 시 소수점 자리수 조정
-
switch문 고려- 학점 계산과 같은 경우
switch문을 사용하면 코드가 더 간결해짐
- 학점 계산과 같은 경우
📚 배운 점
if,if-else,else if문법 완벽 이해- 다양한 조건을 처리하는 방법 습득
- 문제 해결을 위한 조건문 활용 능력 향상
- 가독성을 높이는 코드 작성법 연습
✨ 요약
if,if-else,else if구조 학습- 다양한 조건문 활용 연습
- 코드 최적화 및 가독성 개선 기법 익힘

