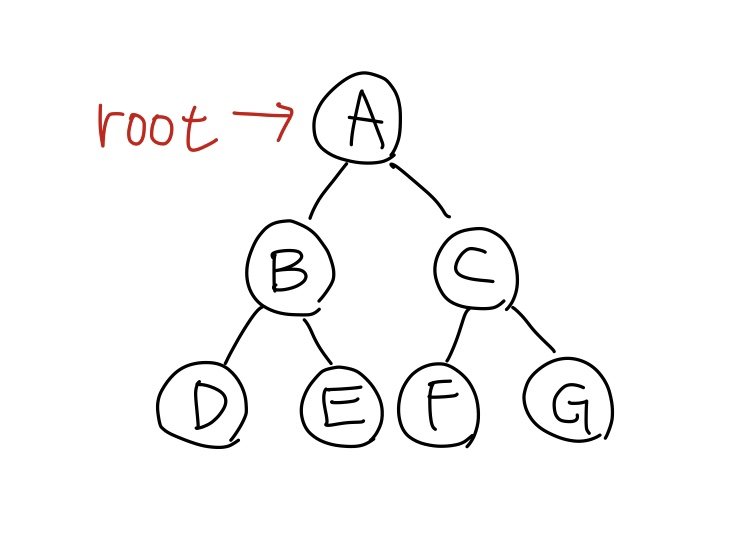
이진트리 (binary tree)
- 각 노드에는 최대 2개까지의 자식 노드가 존재 (즉, 자식 노드가 0개이거나 1개이거나 2개이다)
- 모든 노드의 차수가 2 이하가 된다
- 서브 트리 간의 순서가 존재 (왼쪽->오른쪽)
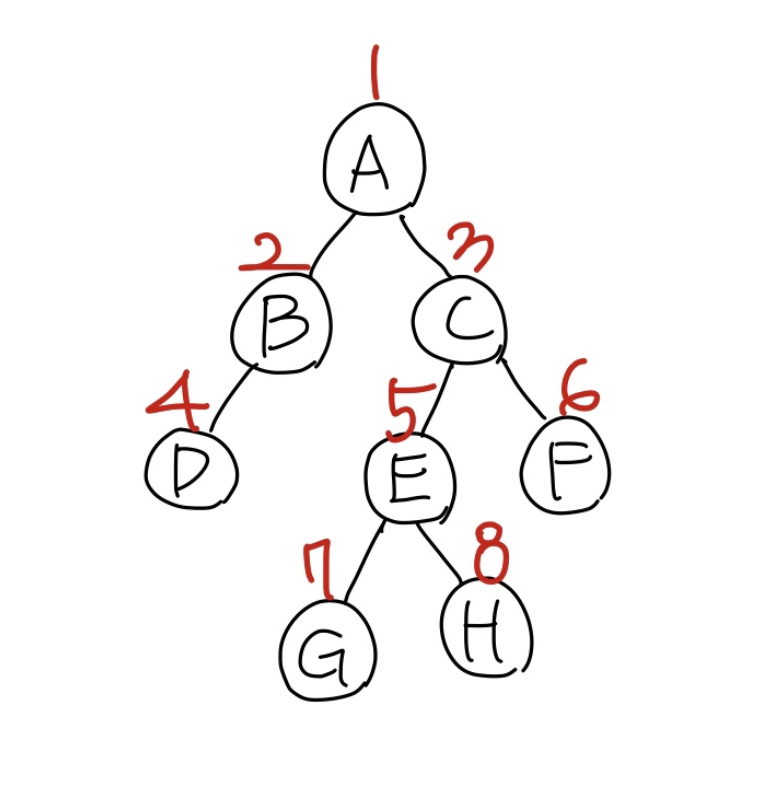
포화 이진 트리 (full binary tree)
트리의 각 레벨에 노드가 꽉 차있는 이진트리
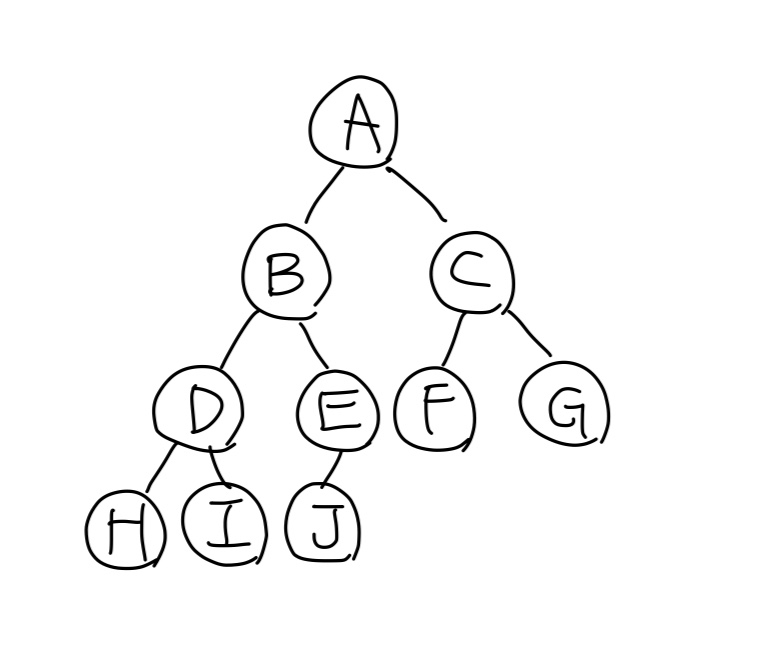
완전 이진 트리 (complete binary tree)
높이가 h일 때 레벨 1부터 h-1까지는 노드가 순서대로 모두 채워져 있고, 마지막 레벨 h에서는 노드가 순서대로 채워진 이진 트리
순서대로 채워지기 때문에 레벨 h에서는 왼쪽에서부터 차있어야 한다
BinaryTree 구현
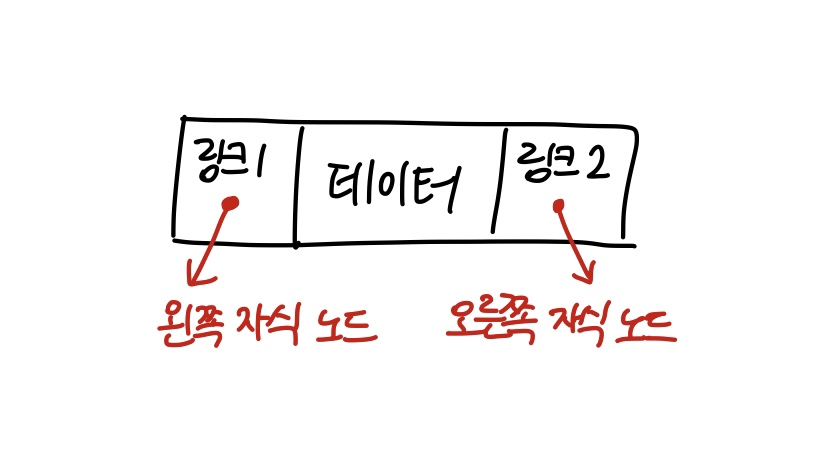
BinaryNode 클래스는 node가 1개이고
BinaryTree 클래스는 BinaryNode 여러 개로 구성되어 있다
BinaryNode 클래스
// BinaryNode 클래스
class BinaryNode {
public:
int data;
BinaryNode* left;
BinaryNode* right;
BinaryNode(int val = 0, BinaryNode* l = NULL, BinaryNode* r = NULL)
:data(val), left(l),right(r){}
~BinaryNode(){}
int setData(int val) {
data = val;
}
void setLeft(BinaryNode* l) {
left = l;
}
void setRight(BinaryNode* r) {
right = r;
}
int getData() {
return data;
}
BinaryNode* getLeft() {
return left;
}
BinaryNode* getRight() {
return right;
}
bool isLeaf() {
return left == NULL && right == NULL;
}
};BinaryTree 클래스
트리는 여러 개의 서브 트리로 구성되어 있기 때문에 재귀적이다
따라서 코드도 재귀 함수를 이용해서 구현해야 한다
// BinaryTree 클래스
class BinaryTree {
BinaryNode* root;
public:
BinaryTree()
:root(NULL){}
~BinaryTree(){}
void setRoot(BinaryNode* node) {
root = node;
}
BinaryNode* getRoot() {
return root;
}
bool isEmpty() {
return root == NULL;
}
int getCount() {
return isEmpty() ? 0 : getCount(root);
}
int getCount(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
else {
return 1 + getCount(node->getLeft()) + getCount(node->getRight());
}
}
int getHeight() {
return isEmpty() ? 0 : getHeight(root);
}
int getHeight(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int hLeft = getHeight(node->getLeft());
int hRight = getHeight(node->getRight());
return (hLeft > hRight) ? 1 + hLeft : 1 + hRight;
}
int getLeafCount() {
return isEmpty() ? 0 : getLeafCount(root);
}
int getLeafCount(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (node->isLeaf()) {
return 1;
}
else {
return getLeafCount(node->getLeft()) + getLeafCount(node->getRight());
}
}
bool isFull() {
return isEmpty() ? 0 : isFull(root);
}
bool isFull(BinaryNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {
return true;
}
if (node->left != NULL && node->right != NULL) {
return isFull(node->left) and isFull(node->right);
}
else return false;
}
int calcLevel(int n) {
return isEmpty() ? 0 : calcLevel(root, n, 1);
}
int calcLevel(BinaryNode* node, int n, int level) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (node->data == n) {
return level;
}
int ll = calcLevel(node->left, n, level + 1);
if (ll != 0) {
return ll;
}
ll = calcLevel(node->right, n, level + 1);
return ll;
}
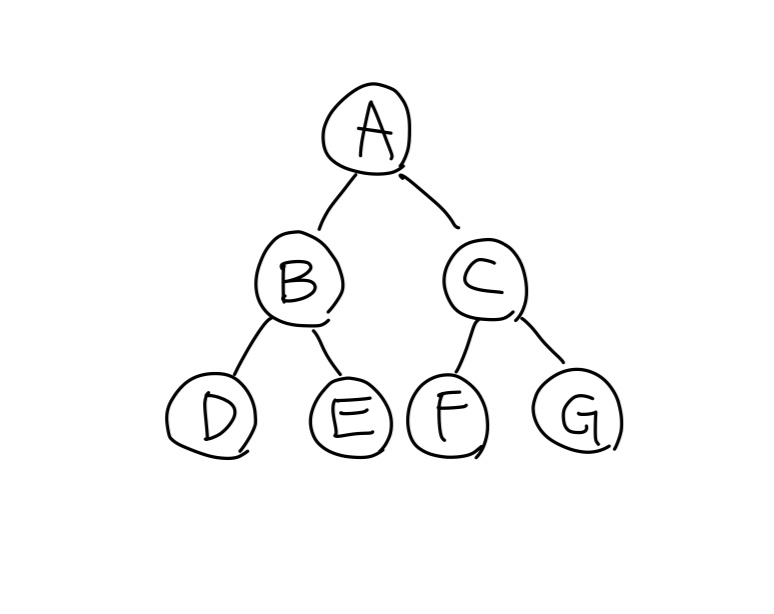
};노드 생성하고 연결해서 트리 만들기
int main() {
BinaryTree tree;
BinaryNode* d = new BinaryNode('D', NULL, NULL);
BinaryNode* e = new BinaryNode('E', NULL, NULL);
BinaryNode* f = new BinaryNode('F', NULL, NULL);
BinaryNode* g = new BinaryNode('G', NULL, NULL);
BinaryNode* b = new BinaryNode('B', d, e);
BinaryNode* c = new BinaryNode('C', f, g);
BinaryNode* a = new BinaryNode('A', b, c);
tree.setRoot(a);
cout << "노드의 총 개수 = " << tree.getCount() << endl;
cout << "단말의 개수 = " << tree.getLeafCount() << endl;
cout << "트리의 높이 = " << tree.getHeight() << endl;
}// 출력
노드의 총 개수 = 7
단말의 개수 = 4
트리의 높이 = 3위의 코드로는 아래의 트리가 생성된다