상위문서: GoF 디자인 패턴
컴포지트(Composite)
- 상위 Category : 구조(Structural) 패턴
객체를 component와 composite로 구성하여 트리 구조로 구성하여 표현하는 전체-부분 패턴으로, 사용자가 단일 객체와 복합 객체 모두 동일하게 다루도록 한다.
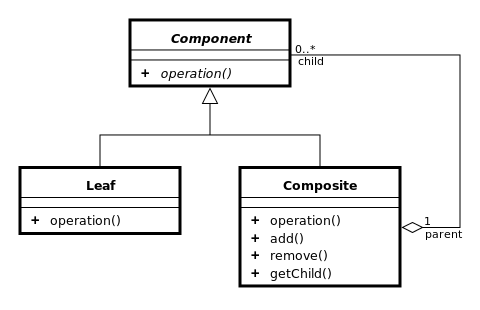
Directory-File이 대표적인 예이다.
예시 : 컴퓨터 장치 추가하기
1. CLASS 정의
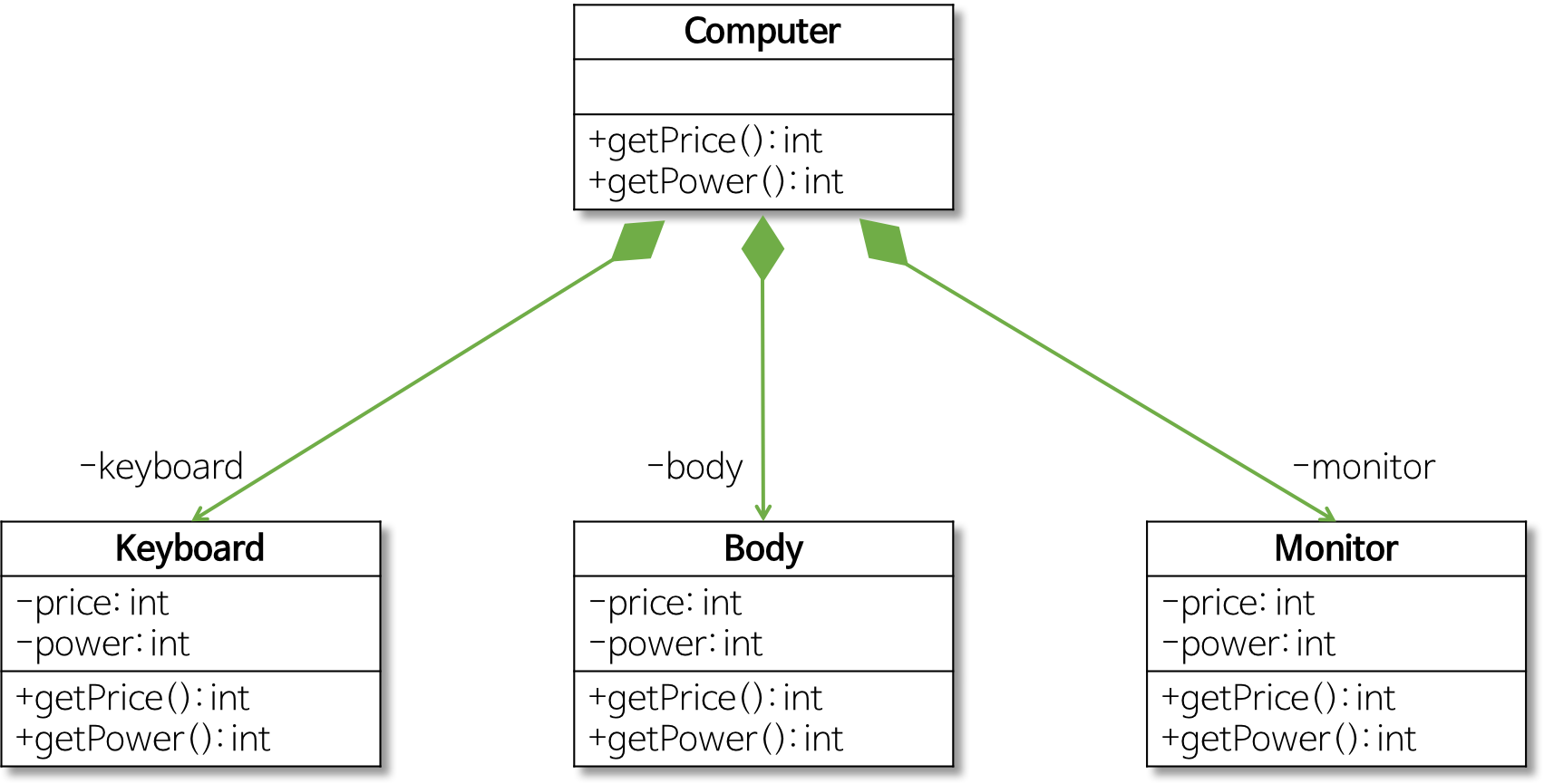
위 마름표 화살표 표시는 합성관계를 나타낸다.
합성 관계 :
생성자에서 필드에 대한 객체를 생성하는 경우
전체 객체의 라이프타임과 부분 객체의 라이프 타임은 의존적이다.
즉, 전체 객체(마름모가 표시된 클래스)가 없어지면 부분 객체도 없어진다.
- 컴퓨터(Computer 클래스) 모델링
- 키보드(Keyboard 클래스): 데이터를 입력받는다.
- 본체(Body 클래스): 데이터를 처리한다.
- 모니터(Monitor 클래스): 처리 결과를 출력한다.
- Computer 클래스 –‘합성(Composite) 관계’– 구성 장치
// 구성장치 class
public class Keyboard {
private int price;
private int power;
public Keyboard(int power, int price) {
this.power = power;
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice() { return price; }
public int getPower() { return power; }
}
public class Body { 동일한 구조 }
public class Monitor { 동일한 구조 }
// Computer class
public class Computer {
private Keyboard Keyboard;
private Body body;
private Monitor monitor;
public addKeyboard(Keyboard keyboard) { this.keyboard = keyboard; }
public addBody(Body body) { this.body = body; }
public addMonitor(Monitor monitor) { this.monitor = monitor; }
public int getPrice() {
int keyboardPrice = keyboard.getPrice();
int bodyPrice = body.getPrice();
int monitorPrice = monitor.getPrice();
return keyboardPrice + bodyPrice + monitorPrice;
}
public int getPower() {
int keyboardPower = keyboard.getPower();
int bodyPower = body.getPower();
int monitorPower = monitor.getPower();
return keyboardPower + bodyPower + monitorPower;
}
}
// main
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 컴퓨터의 부품으로 Keyboard, Body, Monitor 객체를 생성
Keyboard keyboard = new Keyboard(5, 2);
Body body = new Body(100, 70);
Monitor monitor = new Monitor(20, 30);
// Computer 객체를 생성하고 부품 객체들을 설정
Computer computer = new Computer();
computer.addKeyboard(keyboard);
computer.addBody(body);
computer.addMonitor(monitor);
// 컴퓨터의 가격과 전력 소비량을 구함
int computerPrice = computer.getPrice();
int computerPower = computer.getPower();
System.out.println("Computer Price: " + computerPrice + "만원");
System.out.println("Computer Power: " + computerPower + "W");
}
// 결과
// Computer Price: 102만원
// Computer Power: 120W2. 장치 추가하기
만약 다른 부품이 추가되는 경우에는?
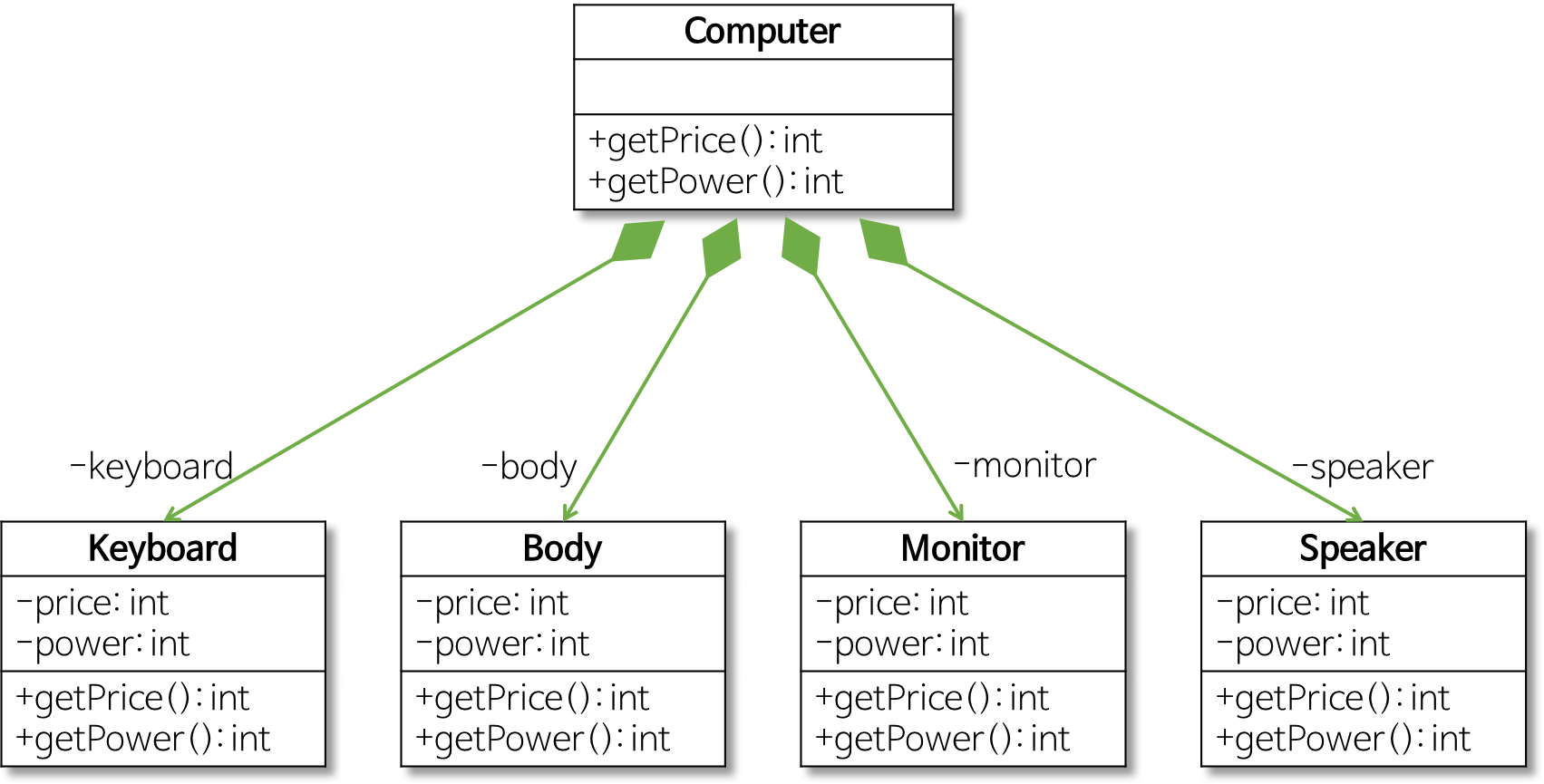
Speaker라는 장치를 추가해보자
// Speaker class
public class Speaker {
private int price;
private int power;
public Speaker(int power, int price) {
this.power = power;
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice() { return price; }
public int getPower() { return power; }
}
// Computer class
public class Computer {
. . .
private Speaker speaker; // 추가
. . .
public addSpeaker(Speaker speaker) { this.speaker = speaker; } // 추가
public int getPrice() {
. . .
int speakerPrice = speaker.getPrice(); // 추가
return keyboardPrice + bodyPrice + monitorPrice + speakerPrice;
}
public int getPower() {
. . .
int speakerPower = speaker.getPower(); // 추가
return keyboardPower + bodyPower + monitorPower + speakerPower;
}
}
- 새로운 부품을 추가할 때마다 Computer 클래스를 이처럼 수정해야 한다.
- 새로운 부품에 대한 참조를 필드로 추가한다.
- 새로운 부품 객체를 설정하는 setter 메서드로 addDevice와 같은 메서드를 추가한다.
- getPrice, getPower 등과 같이 컴퓨터의 부품을 이용하는 모든 메서드에서는 새롭게 추가된 부품 객체를 이용할 수 있도록 수정한다.
위와 같은 방법으로 추가하게 되면 확장성에 좋지 않다. 즉, OCP를 만족하지 않는다.
문제점의 핵심은 Computer 클래스에 속한 부품의 구체적인 객체를 가리키면 OCP를 위반하게 된다는 것이다.
OCP : Open-Closed Principle
'소프트웨어 개체(클래스, 모듈, 함수 등등)는 확장에 대해 열려 있어야 하고, 수정에 대해서는 닫혀 있어야 한다' 는 프로그래밍 원칙. 객체 지향 프로그래밍의 핵심 원칙이라고 할 수 있다. 이 원칙을 무시한다면 OOP의 가장 큰 장점인 유연성, 재사용성, 유지보수성을 결코 얻을 수 없다.
3. 컴포지트 패턴 사용
구체적인 부품들을 일반화한 클래스를 정의하고 이를 Computer 클래스가 가리키도록 설계한다.
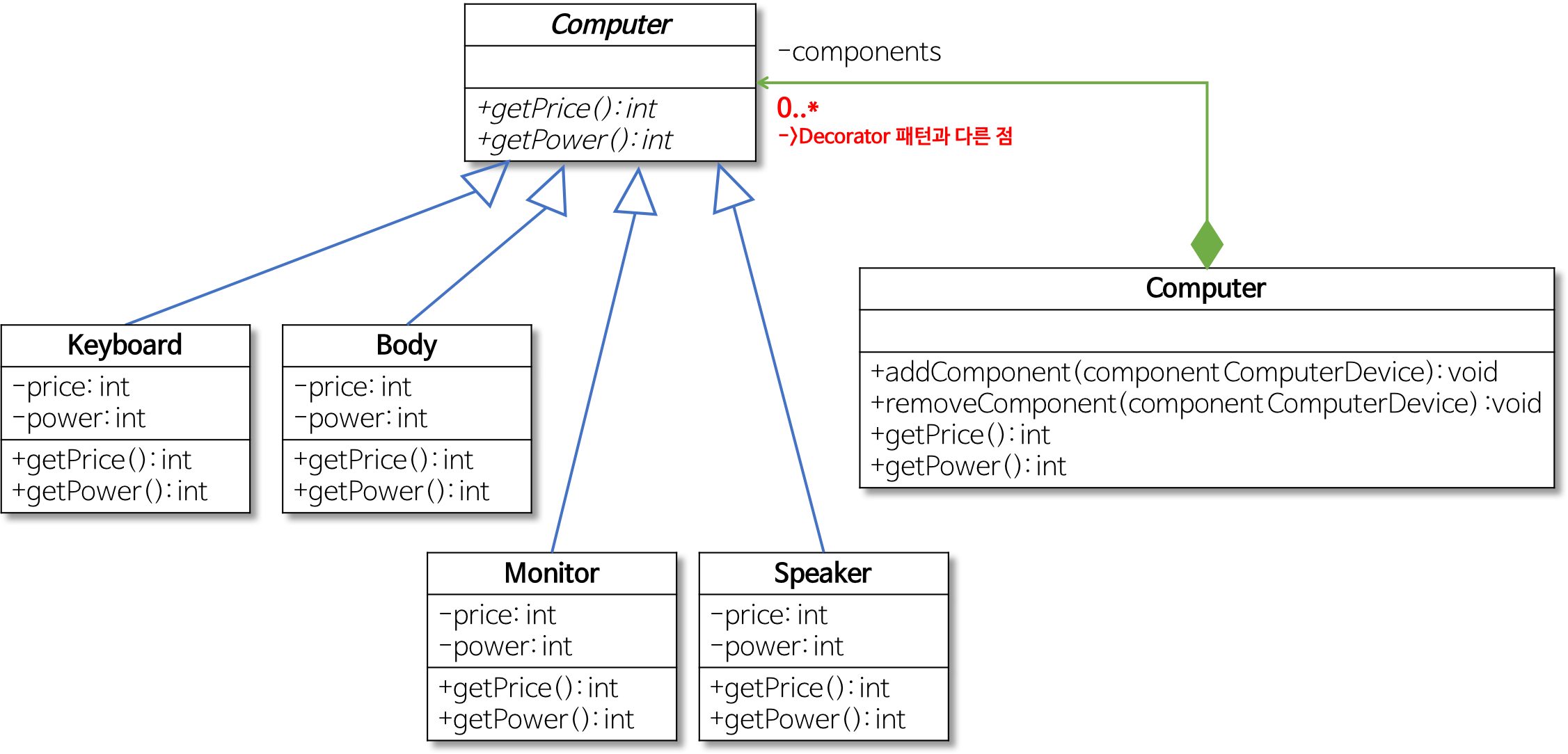
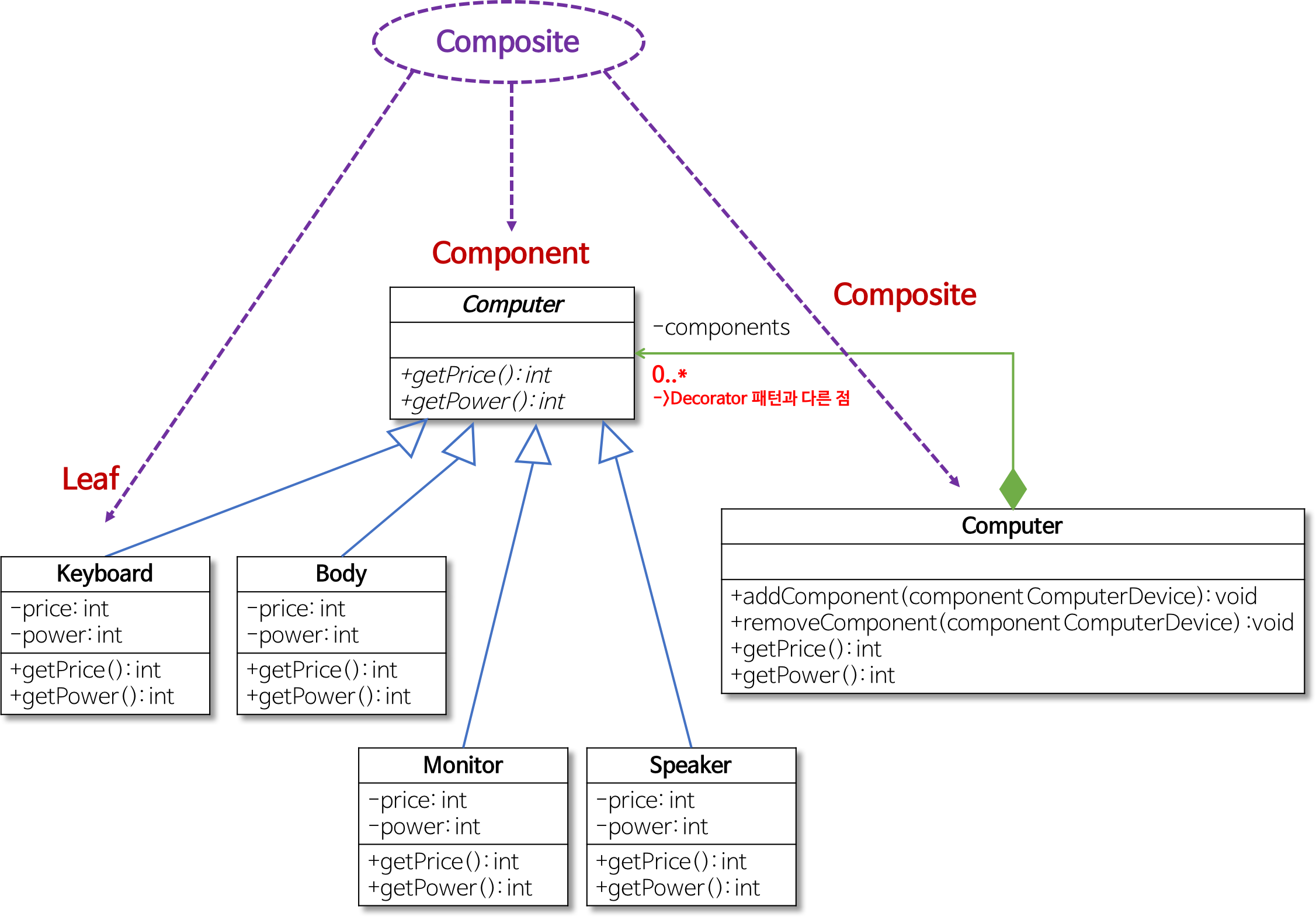
- 구체적인 부품들을 일반화한 ComputerDevice 클래스를 정의
- ComputerDevice 클래스는 구체적인 부품 클래스의 공통 기능만 가지며 실제로 존재하는 구체적인 부품이 될 수는 없다. (즉, ComputerDevice 객체를 실제로 생성할 수 없다.)
- 그러므로 ComputerDevice 클래스는 추상 클래스가 된다.
구체적인 부품 클래스들(Keyboard, Body 등)은 ComputerDevice의 하위 클래스로 정의 - Computer 클래스는 복수 개( 0..* )의 ComputerDevice 객체를 갖음
- Computer 클래스도 ComputerDevice 클래스의 하위 클래스로 정의
- 즉, Computer 클래스도 ComputerDevice 클래스의 일종
- ComputerDevice 클래스를 이용하면 Client 프로그램은 Keyboard, Body 등과 마찬가지로 Computer를 상용할 수 있다.
// ComputerDevice : Component
public abstract class ComputerDevice {
public abstract int getPrice();
public abstract int getPower();
}
// 구성 장치들 : Components
public class Speaker extends ComputerDevice {
private int price;
private int power;
public Speaker(int power, int price) {
this.power = power;
this.price = price;
}
public int getPrice() { return price; }
public int getPower() { return power; }
}
public class Keyboard { 동일한 구조 }
public class Body { 동일한 구조 }
public class Monitor { 동일한 구조 }
// Computer class : Composite
public class Computer extends ComputerDevice {
// 복수 개의 ComputerDevice 객체를 가리킴
private List<ComputerDevice> components = new ArrayList<ComputerDevice>();
// ComputerDevice 객체를 Computer 클래스에 추가
public addComponent(ComputerDevice component) { components.add(component); }
// ComputerDevice 객체를 Computer 클래스에서 제거
public removeComponent(ComputerDevice component) { components.remove(component); }
// 전체 가격을 포함하는 각 부품의 가격을 합산
public int getPrice() {
int price = 0;
for(ComputerDevice component : components) {
price += component.getPrice();
}
return price;
}
// 전체 소비 전력량을 포함하는 각 부품의 소비 전력량을 합산
public int getPower() {
int power = 0;
for(ComputerDevice component : components) {
price += component.getPower();
}
return power;
}
}
// main
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 컴퓨터의 부품으로 Keyboard, Body, Monitor 객체를 생성
Keyboard keyboard = new Keyboard(5, 2);
Body body = new Body(100, 70);
Monitor monitor = new Monitor(20, 30);
Speaker speaker = new Speaker(10, 10);
// Computer 객체를 생성하고 addComponent()를 통해 부품 객체들을 설정
Computer computer = new Computer();
computer.addComponent(keyboard);
computer.addComponent(body);
computer.addComponent(monitor);
computer.addComponent(speaker);
// 컴퓨터의 가격과 전력 소비량을 구함
int computerPrice = computer.getPrice();
int computerPower = computer.getPower();
System.out.println("Computer Price: " + computerPrice + "만원");
System.out.println("Computer Power: " + computerPower + "W");
}
// 결과
// Computer Price: 112만원
// Computer Power: 130W