1. MVC
MVC는 프로젝트의 구성을 Model, View, Controller로 역할을 구분하는 소프트웨어 디자인 패턴이다.
MVC 패턴을 통해 각각의 역할을 분리하는데 이것을 '관심사 분리'라고 한다.
View는 화면을 그리는 역할, Controller는 모델과 뷰로 명령을 전달하는 역할, Model은 데이터를 관리하는 역할을 수행한다.
HelloController.java
package hello.hellospring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("hello-mvc")
public String helloMvc(@RequestParam("name") String name, Model model) {
// attributeValue로 파라미터로 받은 name을 전달
model.addAttribute("name", name);
return "hello-template";
}
}파라미터로 받은 name을 model attribute의 value로 전달 후 hello-template 화면을 렌더링하는 컨트롤러 메소드를 생성해본다.
hello-template.html
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<body>
<p th:text="'hello ' + ${name}">hello! empty</p>
</body>
</html>hello-template을 리턴하였으니, hello-template.html 또한 생성해준다.
전달받은 name값을 합성하여 화면에 텍스트로 뿌려줄 예정이다.
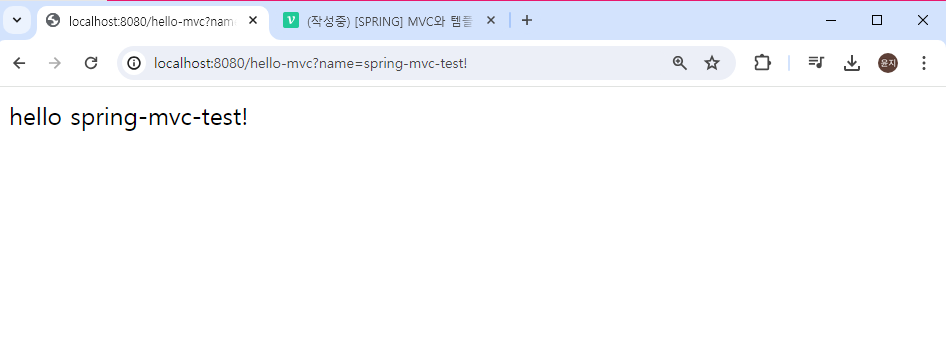
localhost:8080/hello-mvc?name=spring-mvc-test!
name값을 파라미터로 포함하여 url 요청을 보내보면, 전달해준 name값을 반영하여 화면에 표시된다.
2. 동작 원리
요청을 받아 클라이언트에 html을 전달하기까지의 과정을 살펴보자.
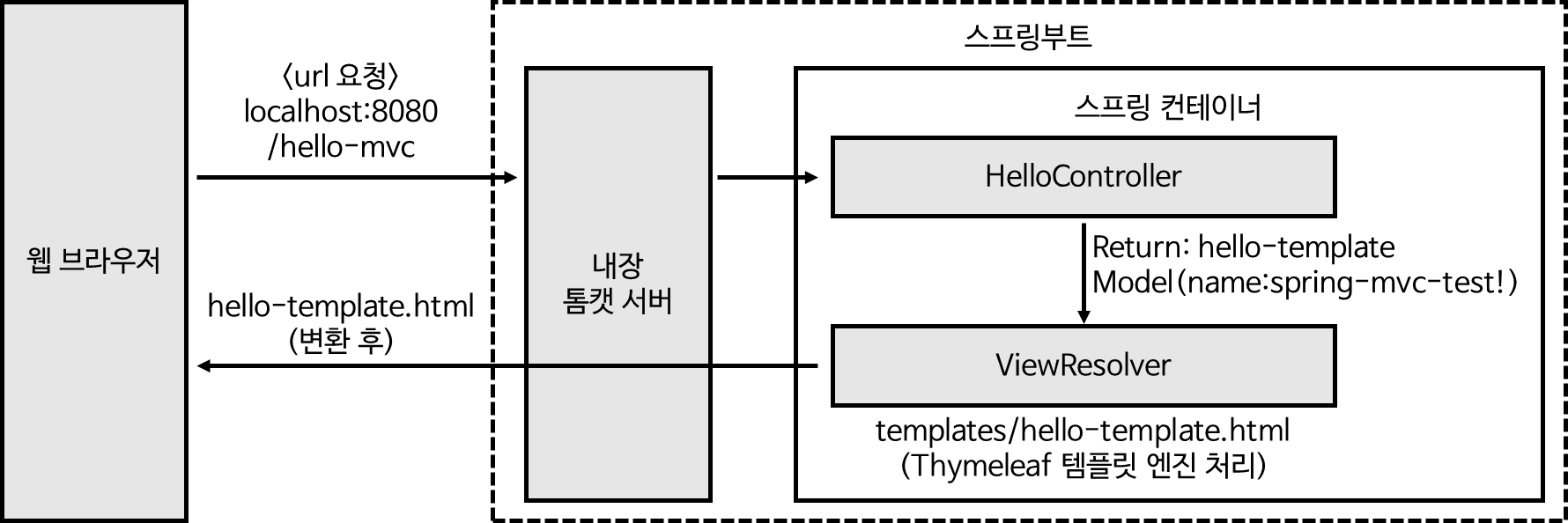
- localhost:8080/hello-mvc?name=spring-mvc-test! 요청을 보낸다.
- 스프링부트의 내장 톰캣 서버에서 요청을 받아 스프링에게 요청을 던진다.
- 스프링이 Model을 만들어주고, url에 해당하는 컨트롤러 메소드가 실행된다.
- 컨트롤러에서 Model에 attribute를 추가 후 viewName을 리턴한다.
- 뷰 리졸버에서
resources/templates + {ViewName} + '.html'페이지를 찾는다. - 타임리프에 의해 data를 처리하여 html을 만든다.
- 만들어진 html을 브라우저에 전달한다.
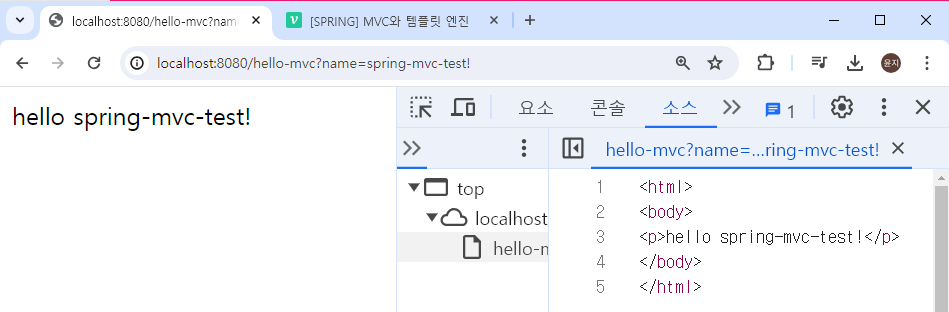
템플릿 엔진은 데이터를 가지고 html을 변환하기 때문에 attribute에 넣어준 값에 따라 소스코드가 반영된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
템플릿 엔진을 거치면 정적 컨텐츠와 달리 html 변환 과정을 거친다.