
프로토타입 기반 객체 지향 언어
자바스크립트는
프로토타입 기반 객체 지향 언어이다.다른 언어와
OOP개념은 같지만, 클래스 구조와 구현 방법이 다르다.
자바스크립트는prototype에 메서드와 프로퍼티를 연결하고
연결된 메소드로 인스턴스를 생성한다.const Point = class { setPoint(point){ this.point = point; } }; console.log(Point.prototype.setPoint); // setPoint(point){ this.point = point; }
Class 선언
class키워드에 이어 클래스 이름을 작성한다.
이름의첫 문자는 대문자를 사용한다.
이는 관례이다.블록을 작성하고 블록안에 메서드를 작성한다.
class Point { getPoint(){ return 100; } }; const obj = new Point(); console.log(obj.getPoint()); // 100
Class 표현식
변수 이름이 클래스 이름이 된다.
변수에class오브젝트를 할당하는 형태이다.const Point = class { getPoint() { return 100; } }; const obj = new Point(); console.log(obj.getPoint());
Class 작성기준
클래스는 암묵적으로
strict모드에서 실행된다.
- 메소드를
prototype에 연결하여 작성하지 않는다.- 클래스는 열거가 되지 않는다.
- 클래스 밖에서 메소드를
prototype에 연결할 수 있다.const Point = class {}; Point.prototype.getPoint = function(){ return 100; } console.log(Point.getPoint()); // 10
클래스에 메소드 작성방법
function키워드를 작성하지 않는다.- 메서드와 메서드 사이에
,를 작성하지 않는다.- 세미콜론 작성은 선택이다.
클래스의 typeof는function이다.
class타입이 별도로 존재하지 않는다.
constructor
contstructor는 생성자를 의미한다.
인스턴스를 생성하고 초기화한다.
선언 시,prototype.constructor를 오버라이딩 한다.만약
constructor를 선언하지 않으면prototype내부에 있는
constructor가 호출된다. 이때 초기 프로퍼티를 지정할 수 없다.ES5에서는 작성할 수 없었으나 ES6부터는 작성할 수 있다.
class Point constructor(point) { this.point = point; } }; const obj = new Point(100);
new연산자가 Point 클래스 오브젝트의constructor를 호출한다.- 파라미터 값인
100을constructor로 넘겨누다.- 자바스크립트 엔진은 빈 오브젝트{} 생성한다. (이를 인스턴스라고 한다.)
- 인스턴스에 프로퍼티 이름과 값을 설정하여 구조를 만든다.
__proto__,__proto__.constructor등- constructor 블록의 코드를 실행한다.
- this.point = point; -> this 가 생성한 인스턴스를 참조한다.
인스턴스 {} 를 먼저 생성하기 때문에 this로 참조할 수 있다.- point는 인스턴스 프로퍼티가 된다.
- 생성한 인스턴스를 반환한다.
주의점
constructor에서return을 작성하지 않으면생성한 인스턴스를 반환한다.
만약Number,String을 반환하면 이를 무시하고인스턴스를 반환한다.
Object를 반환하면 인스턴스를 반환하지 않고 이Object를 반환한다.
getter
메소드를 호출하여 값을 구한다.
메소드를 호출할 때 name() 처럼 소괄호를 작성하지만
getter는 소괄호()를 작성하지 않고 name만 작성한다.파라미터를 사용할 수 없다.
class Point { constructor(point){ this.point = point; } get getPoint(){ return this.point; } }; const obj = new Point(100); console.log(obj.getPoint); // 100, 소괄호를 작성하지 않는다.
setter
메서드를 호출하여 값을 설정한다.
메서드를 호출할때 소괄호를 사용하지 않는다.class Point { get setPoint(){ this.point = point; } }; const obj = new Point(100); obj.setPoint = 100; // 소괄호를 작성하지 않는다. console.log(obj.point); // 100
static
메서드 앞에
static을 작성한다.
static메서드는 인스턴스의 메서드로 호출하지 않는다.
즉,prototype에 연결되는게 아니라 클래스 자체에 연결된다.클래스만
static을 사용할 수 있다.class Point { static getPoint(){ return 100; } }; const obj = new Point(); console.log(Point.getPoint()); // 100 console.log(obj.getPoint()); // undefined
new.target
함수 또는 생성자가
new연산자로 호출된 여부를 반환한다.
new연산자로constructor를 호출하면new.target은constructor를 참조한다.class Point { constructor(){ console.log(new.target.name); } }; new Point(); // Point함수로 호출하면 undefined를 반환한다.
function book() { console.log(new.target); } book(); // undefined
상속
클래스에 다른 클래스를 포함시키는 형태이다.
따라서 포함 시킨 클래스의 메소드와 프로퍼티를 본인의 것처럼 사용할 수 있다.
extends 키워드로 상속할 수 있다.
subClass extends superClass {... }class Book { constructor(title){ this.title = title; }; getTitle() { return this.title; } }; class Point extends Book { setPoint(point) { this.point = point; } }; const obj = new Point("책"); console.log(obj.getTitle()); // 책
메소드 오버라이딩
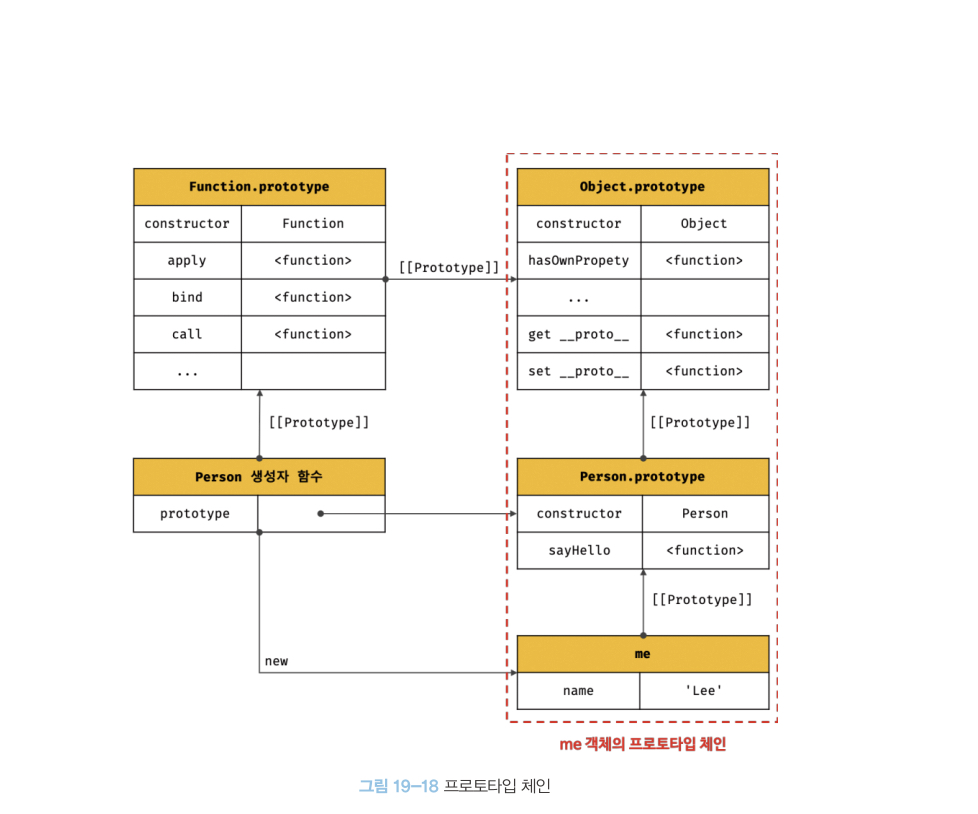
상속으로부터 받은 메소드의 이름과같은 이름으로 자식 클래스에 작성하고
이 자식 클래스로 인스턴스를 만들어서 이 메서드를 실행하면
자식 클래스에 선언한 메서드가 실행된다.
이는프로토타입 체인과 연관이 있다.자식 클래스 인스턴스에서
메서드를 호출하면
자식 클래스 인스턴스에서해당 메서드가 있는지 확인한다.
없으면 프로토타입 체인을 통해 부모 클래스에서 검색한다.
부모 클래스에 해당 식별자를 가진 메서드가 있다면 호출된다.
이 과정을 메서드 식별자를 찾을때 까지반복한다.이러한 메커니즘으로 인해서 상속받은 메서드와 프로퍼티를 사용할 수 있는 것이다.
super
super 키워드를 사용하면
부모 클래스의 프로퍼티 및 메서드에 접근할 수 있다.class Book{ getTitle(){ // 같은 이름의 메서드 console.log("슈퍼") } }; class Point extends Book { getTitle(){ // 같은 이름의 메서드 super.getTitle(); console.log("서브"); } }; new Point().getTitle(); /* 슈퍼 서브 */
상속된 class의 constructor 호출
서브 클래스와 슈퍼 클래스에 모두
constructor를 작성하지않으면
default constructor가 호출된다.Point 클래스(서브 클래스)에
constructor를 작성하지 않으면
Point.prototype.constructor가 호출된다.이어서 Book 클래스(부모 클래스)의
constructor를 호출한다.Book 클래스에
constructor를 작성하지 않으면
Book.prototype.constructor가 호출된다.즉, 각 클래스의
constructor를 작성하지 않으면
클래스의prototype.constructor가 호출된다.class Book{ setTitle(){ this.title = title; } }; class Point extends Book { }; const obj = new Point(); obj.setTitle("책"); console.log(obj.title); // 책
서브 클래스에 작성하지 않고 슈퍼에만 작성하면
파라미터 값을 슈퍼로 넘겨준다.class Book { constructor(title){ this.title = title; }; }; class Point extends Book { };
서브 클래스에는 작성하고 슈퍼 클래스에 작성하지 않으면 에러가 난다.
class Book { setTitle(title){ this.title = title; } }; class Point extends Book { // constructor(title){ // this.title = title; // }; }; const obj = new Point(100);
서브 클래스와 슈퍼 클래스에 모두
constructor를 모두 작성하면
서브에서 super()로 호출해야 한다.class Book { constructor(title) { this.title = title; }; }; class Point extends Book{ constructor(title, point){ super(title); this.point = point; }; };
Built-in 오브젝트 상속
빌트인 오브젝트를 상속 받을 수 있다.
인스턴스가빌트인 오브젝트의 특징을 갖게되며
this로빌트인 오브젝트에 접근할 수 있다.class Point extends Array { constructor() { super(); } getTotal(){ let total = 0; for (const value of this) { total += value; }; return total; } } const obj = new Point(); obj.push(10,20,30); // Array.prototype.push console.log(obj.getTotal()); // 60
Image 상속
Image오브젝트는DOM객체이다.class Home extends Image { constructor() { super(); } setAttr(){ this.src = "../../image/rainbow.png"; this.alt = "집과 나무가 있고 " + "무지개가 있는 모습"; this.title = "무지개"; } }; const obj = new Home(); obj.setAttr(); document.qeurySelector("#show").appendChild(obj); // #show라는 태그 내부에 Img 태그 삽입
static
static이 붙은메서드와프로퍼티는class의 prototype에 포함되지 않는다.
따라서 인스턴스에서 참조할 수 없다.
static 내부의 this는인스턴스가 아닌 클래스를 참조한다.class Point { static setPoint(point){ this.value = point; // 여기서 this는 생성될 인스턴스가 아닌 클래스이다. }; }; Pont.setPoint(100); console.log(Point.value); // 100 console.log(new Point().value); // undefined
클래스 내부의 Generator
클래스의 Generator는 Prototype에 연결된다.
따라서 인스턴스로 호출해야한다.당연히 static을 붙여서 선언할 수도 있다.
class Point{ *getPoint(){ yield 10; yield 20; } }; const gen = new Point(); const obj = gen.getPoint(); console.log(obj.next()); // {value: 10, done: false} console.log(obj.next()); // {value: 20, done: false} console.log(obj.next()); // {value: undefined, done: true}
